[1] 李帝均,王桂杉,刘海峰,等. 肌腱病动物模型的研究进展[J].中国实验动物学报,2022,30(2):260-266.
[2] LI D, WANG G, LI J, et al. Biomaterials for Tissue-Engineered Treatment of Tendinopathy in Animal Models: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2023;29(4):387-413.
[3] MILLAR NL, SILBERNAGEL KG, THORBORG K, et al. Tendinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):1.
[4] SHARMA P, MAFFULLI N. Biology of tendon injury: healing, modeling and remodeling. J Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2006;6(2):181-190.
[5] LUO J, WANG Z, TANG C, et al. Animal model for tendinopathy. J Orthop Translat. 2023;42:43-56.
[6] KWAN KYC, NG KWK, RAO Y, et al. Effect of Aging on Tendon Biology, Biomechanics and Implications for Treatment Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(20):15183.
[7] WANG Y, LI J. Current progress in growth factors and extracellular vesicles in tendon healing. Int Wound J. 2023;20(9):3871-3883.
[8] ALKHILANI MA, HAMMOODI OT, EMRAN HA, et al. Impact of Using Processed Urinary Bladder Submucosa and Hydrogel Fabricated from Tendon on Skin Healing Process in Rabbits. Vet Med Int. 2024; 2024:6641975.
[9] ALVES AN, FERNANDES KPS, DEANA AM, et al. Effects of Low-Level Laser Therapy on Skeletal Muscle Repair A Systematic Review. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;93(12):1073-1085.
[10] ANJUM S, LI T, SAEED M, et al. Exploring polysaccharide and protein-enriched decellularized matrix scaffolds for tendon and ligament repair: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;254(Pt 2):127891.
[11] KHAKPOUR E, TAVASSOLI A, MAHDAVI-SHAHRI N, et al. Assessing the biocompatibility of bovine tendon scaffold, a step forward in tendon tissue engineering. Cell Tissue Banking. 2023;24(1):11-24.
[12] NING LJ, CUI J, HE SK, et al. Constructing a highly bioactive tendon-regenerative scaffold by surface modification of tissue-specific stem cell-derived extracellular matrix. Regen Biomater. 2022:9:rbac020.
[13] MONTEIRO-LOBATO GM, RUSSO PST, WINCK FV, et al. Proteomic Analysis of Decellularized Extracellular Matrix: Achieving a Competent Biomaterial for Osteogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:6884370.
[14] SMOAK MM, HAN A, WATSON E, et al. Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun Decellularized Muscle-Derived Scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2019;25(5):276-287.
[15] AL-HAKIM KHALAK F, GARCIA-VILLEN F, RUIZ-ALONSO S, et al. Decellularized Extracellular Matrix-Based Bioinks for Tendon Regeneration in Three-Dimensional Bioprinting. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):12930.
[16] OTT HC, MATTHIESEN TS, GOH SK, et al. Perfusion-decellularized matrix: using nature’s platform to engineer a bioartificial heart. Nat Med. 2008;14(2):213-221.
[17] OTT HC, CLIPPINGER B, CONRAD C, et al. Regeneration and orthotopic transplantation of a bioartificial lung. Nat Med. 2010;16(8):927-U131.
[18] SONG JJ, GUYETTE JP, GILPIN SE, et al. Regeneration and experimental orthotopic transplantation of a bioengineered kidney. Nat Med. 2013;19(5):646-651.
[19] ZHANG X, SONG W, HAN K, et al. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of a Structure-, Composition-, and Mechanics-Graded Biomimetic Scaffold Coated with Specific Decellularized Extracellular Matrix to Improve the Tendon-to-Bone Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(24):28964-28980.
[20] XING S, LIU C, XU B, et al. Effects of various decellularization methods on histological and biomechanical properties of rabbit tendons. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(2):628-634.
[21] ZHANG Y, ZHANG C, LI Y, et al. Evolution of biomimetic ECM scaffolds from decellularized tissue matrix for tissue engineering: A comprehensive review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023:246:125672.
[22] CHENG CW, SOLORIO LD, ALSBERG E. Decellularized tissue and cell-derived extracellular matrices as scaffolds for orthopaedic tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(2):462-484.
[23] SANTOS ADL, SILVA CGD, BARRETO LSDS, et al. Automated Assessment of Cell Infiltration and Removal in Decellularized Scaffolds - Experimental Study in Rabbits. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021;57(6):992-1000.
[24] 杨冬逸,李刚.人工肌腱/韧带生物材料研究进展[J].上海纺织科技,2024, 52(4):6-12+63.
[25] WANG S, WANG Y, SONG L, et al. Decellularized tendon as a prospective scaffold for tendon repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77:1290-1301.
[26] ALBERTI KA, XU Q. Biocompatibility and degradation of tendon-derived scaffolds. Regen Biomater. 2016;3(1):1-11.
[27] VEPARI C, KAPLAN DL. Silk as a biomaterial. Prog Polym Sci. 2007;32(8-9):991-1007.
[28] LI J, CHEN X, HU M, et al. The application of composite scaffold materials based on decellularized vascular matrix in tissue engineering: a review. Biomed Eng Online. 2023;22(1):62.
[29] IWASAKI N, ROLDO M, KARALI A, et al. In vitro development of a muscle-tendon junction construct using decellularised extracellular matrix: Effect of cyclic tensile loading. Biomater Adv. 2024:161:213873.
[30] O’BRIEN FJ. Biomaterials & scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater Today. 2011; 14(3):88-95.
[31] ZHAO JP, ZHANG D, LAN QM, et al. Tendon Decellularized Matrix Modified Fibrous Scaffolds with Porous and Crimped Microstructure for Tendon Regeneration. Acs Applied Bio Materials. 2024;7(7):4747-4759.
[32] 黄鑫.循环牵伸应力对脂肪干细胞—肌腱脱细胞支架复合物生物学特性的影响[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2024.
[33] HART DA, AHMED AS, CHEN J, et al. Optimizing tendon repair and regeneration: how does the in vivo environment shape outcomes following rupture of a tendon such as the Achilles tendon? Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1357871.
[34] NA YY, JUE H, XIA T, et al. A composite PET-matrix patch enhances tendon regeneration and tendon-to-bone integration for bridging repair of the chronic massive rotator cuff tears in a rabbit model. Regen Biomater. 2024:11:rbae061.
[35] TANG CQ, CHEN YW, HUANG JY, et al. The roles of inflammatory mediators and immunocytes in tendinopathy. J Orthop Translat. 2018;14:23-33.
[36] PIRES D, XAVIER M, ARAUJO T, et al. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT; 780 nm) acts differently on mRNA expression of anti- and pro-inflammatory mediators in an experimental model of collagenase-induced tendinitis in rat. Lasers Med Sci. 2011;26(1):85-94.
[37] MAO X, YAO L, LI M, et al. Enhancement of Tendon Repair Using Tendon-Derived Stem Cells in Small Intestinal Submucosa via M2 Macrophage Polarization. 2022;11(17):2770.
[38] SOUZA NHC, MESQUITA-FERRARI RA, RODRIGUES MFSD, et al. Photobiomodulation and different macrophages phenotypes during muscle tissue repair. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(10):4922-4934.
[39] SUNWOO JY, ELIASBERG CD, CARBALLO CB, et al. The role of the macrophage in tendinopathy and tendon healing. J Orthop Res. 2020; 38(8):1666-1675.
[40] XU HT, LEE CW, LI MY, et al. The shift in macrophages polarisation after tendon injury: A systematic review. J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:24-34.
[41] ZHAO LL, LUO JJ, CUI J, et al. Tannic Acid-Modified Decellularized Tendon Scaffold with Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities for Tendon Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(13):15879-15892.
[42] AMAROLI A, PASQUALE C, ZEKIY A, et al. Photobiomodulation and Oxidative Stress: 980 nm Diode Laser Light Regulates Mitochondrial Activity and Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:2021:6626286.
[43] MUSAT CL, NICULET E, CRAESCU M, et al. Pathogenesis of Musculotendinous and Fascial Injuries After Physical Exercise-Short Review. Int J Gen Med. 2023;16: 5247-5254.
[44] FOK SW, GRESHAM RCH, RYAN W, et al. Macromolecular crowding and decellularization method increase the growth factor binding potential of cell-secreted extracellular matrices. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023:11:1091157.
[45] NING LJ, ZHANG YJ, ZHANG Y, et al. The utilization of decellularized tendon slices to provide an inductive microenvironment for the proliferation and tenogenic differentiation of stem cells. Biomaterials. 2015;52:539-550.
[46] 刘洁,周永春,惠慧.脱细胞肌腱支架对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(11):1156-1159.
[47] CUI J, ZHANG YJ, LI X, et al. Decellularized tendon scaffolds loaded with collagen targeted extracellular vesicles from tendon-derived stem cells facilitate tendon regeneration. J Control Release. 2023; 360:842-857.
[48] XIE S, ZHOU Y, TANG Y, et al. -Book-shaped decellularized tendon matrix scaffold combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-sheets for repair of achilles tendon defect in rabbit. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(4):887-897.
[49] ROTHRAUFF BB, LAURO BB, YANG G, et al. Braided and Stacked Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Tendon and Ligament Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(9-10):378-389.
[50] ZHAO G, ZHANG J, NIE D, et al. HMGB1 mediates the development of tendinopathy due to mechanical overloading. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0222369.
[51] ANDARAWIS-PURI N, FLATOW EL, SOSLOWSKY LJ. Tendon Basic Science: Development, Repair, Regeneration, and Healing. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(6):780-784.
[52] LANGE P, SHAH H, BIRCHALL M, et al. Characterization of a biologically derived rabbit tracheal scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(7):2126-2135.
[53] WHITLOCK PW, SEYLER TM, PARKS GD, et al. A Novel Process for Optimizing Musculoskeletal Allograft Tissue to Improve Safety, Ultrastructural Properties, and Cell Infiltration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(16):1458-1467.
[54] NING LJ, ZHANG YJ, ZHANG YJ, et al. Enhancement of Migration and Tenogenic Differentiation of Macaca Mulatta Tendon-Derived Stem Cells by Decellularized Tendon Hydrogel. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021:9:651583.
[55] FARNEBO S, WOON CYL, SCHMITT T, et al. Design and Characterization of an Injectable Tendon Hydrogel: A Novel Scaffold for Guided Tissue Regeneration in the Musculoskeletal System. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(9-10):1550-1561.
[56] PARMAKSIZ M. Decellularized tendon-based heparinized nanocomposite scaffolds for prospective regenerative applications: Chemical, physical, thermal, mechanical and in vitro biological evaluations. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2022;134:105387.
[57] 何树坤.肌腱干细胞胞外基质修饰生物仿生支架促进腱骨界面愈合的实验研究[D].成都:四川大学,2021.
[58] OMAE H, ZHAO C, SUN YL, et al. Multilayer Tendon Slices Seeded with Bone Marrow Stromal Cells: A Novel Composite for Tendon Engineering. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(7):937-942.
[59] CUI J, NING LJ, WU FP, et al. Biomechanically and biochemically functional scaffold for recruitment of endogenous stem cells to promote tendon regeneration. NPJ Regen Med. 2022;7(1):26.
[60] 吴辰,江佳慧,苏豆,等.脱细胞皮肤基质/聚氨酯混纺纤维支架促进大鼠皮肤缺损的修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(4):745-751.
[61] ABHARI RE, SNELLING SJB, AUGUSTYNAK E, et al. A Hybrid Electrospun-Extruded Polydioxanone Suture for Tendon Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2024; 30(5-6):214-224.
[62] 韩启斌,白浪,杨兴.生物材料改善肌腱病治疗的应用进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2021,42(3):166-170.
[63] ZHANG YM, XUE YG, REN Y, et al. Biodegradable Polymer Electrospinning for Tendon Repairment. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(6):1566.
[64] HE W, JIANG C, ZHOU P, et al. Role of tendon-derived stem cells in tendon and ligament repair: focus on tissue engineer. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024:12: 1357696.
[65] BAHRAMI S, SOLOUK A, DUPREZ D, et al. Microstructure Manipulation of Polyurethane-Based Macromolecular Scaffold for Tendon/Ligament Tissue Engineering. Macromol Mater Eng. 2022;307(1). doi: 10.1002/mame.202100584
[66] NETTO ADS, ANTEBI U, MORAIS CED, et al. Evaluation of Histological Properties of Human Meniscal Grafts Stored in a Tissue Bank. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2020;55(6):778-782.
[67] AEBERHARD PA, GROGNUZ A, PENEVEYRE C, et al. Efficient decellularization of equine tendon with preserved biomechanical properties and cytocompatibility for human tendon surgery indications. Artif Organs. 2020;44(4):E161-E171.
[68] ZHANG X, HAN K, FANG Z, et al. Enhancement of Tendon-to-Bone Healing: Choose a Monophasic or Hierarchical Scaffold? Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(10):2688-2700.
[69] SZCZESNY SE, CORR DT. Tendon cell and tissue culture: Perspectives and recommendations. J Orthop Res. 2023;41(10):2093-2104.
[70] TAO M, LIANG F, HE J, et al. Decellularized tendon matrix membranes prevent post-surgical tendon adhesion and promote functional repair. Acta Biomater. 2021;134:160-176.
[71] KOÇ-DEMIR A, ELÇIN AE, ELÇIN YM. Magnetic biocomposite scaffold based on decellularized tendon ECM and MNP-deposited halloysite nanotubes: physicochemical, thermal, rheological, mechanical andin vitrobiological evaluations. Biomed Mater. 2024;19(3). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ad38ab.
[72] LIU Z, YU MZ, PENG H, et al. Decellularized tilapia fish skin: A novel candidate for tendon tissue engineering. Mater Today Bio. 2022:17:100488.
[73] YUAN Z, CAO F, GAO C, et al. Decellularized Human Umbilical Cord Wharton Jelly Scaffold Improves Tendon Regeneration in a Rabbit Rotator Cuff Tendon Defect Model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(2):371-383.
[74] HUANG X, LV ZT, CHENG P, et al. A Novel Low Air Pressure-Assisted Approach for the Construction of Cells-Decellularized Tendon Scaffold Complex. Curr Med Sci. 2022;42(3):569-576.
[75] LOVATI AB, BOTTAGISIO M, MORETTI M. Decellularized and Engineered Tendons as Biological Substitutes: A Critical Review. Stem Cells Int. 2016:2016:7276150.
[76] NAHUMI A, PEYMANI M, ASADI A, et al. Decellularized tracheal scaffold as a promising 3D scaffold for tissue engineering applications. Tissue Cell. 2023;85:102258.
[77] 张珂珂,李红梅,刘畅.脱细胞随机肌腱支架促进骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化[J].中国病理生理杂志,2020,36(4):762-768. |

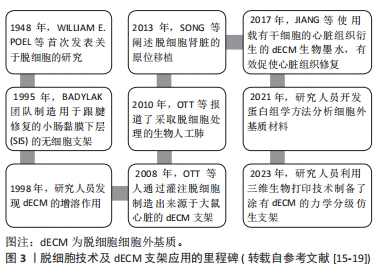

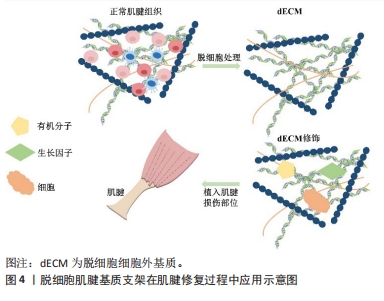

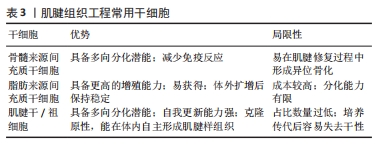


 脱细胞细胞外基质(decellularized extracellular matrix,dECM)支架是由同种或异种组织和细胞在经过脱细胞处理后形成的生物材料,能够与生物活性物质或细胞结合,在肌肉骨骼系统疾病的治疗上具备较大的应用前景和优势[10]。
脱细胞细胞外基质(decellularized extracellular matrix,dECM)支架是由同种或异种组织和细胞在经过脱细胞处理后形成的生物材料,能够与生物活性物质或细胞结合,在肌肉骨骼系统疾病的治疗上具备较大的应用前景和优势[10]。
