中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (34): 7376-7384.doi: 10.12307/2025.477
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
开发纳米水凝胶系统搭载新型抗氧化剂与抗氧化剂联合治疗椎间盘退变
苏永昆1,孙 红2,刘 淼2,杨 华2,李青松1,3
- 1贵州医科大学临床医学院,贵州省贵阳市 550004;2贵州医科大学附属医院骨科,贵州省贵阳市 550004;3贵阳市第四人民医院骨三科,贵州省贵阳市 550002
-
收稿日期:2024-07-06接受日期:2024-08-17出版日期:2025-12-08发布日期:2025-01-17 -
通讯作者:杨华,主任医师,贵州医科大学附属医院骨科,贵州省贵阳市 550004 李青松,硕士生导师,主任医师,贵州医科大学临床医学院,贵州省贵阳市 550004;贵阳市第四人民医院骨三科,贵州省贵阳市 550002 -
作者简介:苏永昆,男,1999年生,贵州省贵阳市人,汉族,贵州医科大学在读硕士,主要从事脊柱疾病的基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:贵州省科技厅基础研究计划项目(黔科合基础-ZK[2022]一般430),项目负责人:刘淼
Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration
Su Yongkun1, Sun Hong2, Liu Miao2, Yang Hua2, Li Qingsong1, 3
- 1Clinical Medical College of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 3Third Department of Orthopedics, Fourth People’s Hospital of Guiyang City, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-06Accepted:2024-08-17Online:2025-12-08Published:2025-01-17 -
Contact:Yang Hua, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China Li Qingsong, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Clinical Medical College of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Third Department of Orthopedics, Fourth People’s Hospital of Guiyang City, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Su Yongkun, Master candidate, Clinical Medical College of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Basic Research Program of Guizhou Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. Qiankehe Foundation-ZK[2022]General 430 (to LM)
摘要:

文题释义:
抗氧化剂:是能够抑制或中和活性氧、减少氧化应激,从而保护细胞和组织免受氧化损伤的一类物质的总称。椎间盘退变:是椎间盘自然退变和衰老的生理和病理过程,是各种临床脊柱疾病的基础,如椎体不稳、椎间盘突出和椎管狭窄,通常伴随有神经根或脊髓受压症状的下腰痛。
背景:抗氧化剂能够减轻氧化应激引起的细胞损伤和基质降解,具有保护椎间盘结构和功能的作用,从而延缓椎间盘退变的发生与发展。
目的:综述抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变治疗中的研究现状。方法:由第一作者检索中国知网、PubMed数据库中收录的文章,文献检索时限为各数据库建库至2024年6月,以“椎间盘退变,抗氧化剂,氧化应激,信号通路”为中文检索词,以“antioxidants,oxidative stresses,oxidative DNA damage,intervertebral disc degenerations,degenerative disc disease*,disc degeneration*,signal pathway”为英文检索词,最终选取符合标准的92篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变的治疗中具有多重作用,包括减轻氧化应激、抑制炎症反应、促进细胞自噬、抑制细胞凋亡及保护细胞外基质。通过多途径的综合作用,抗氧化剂有望成为椎间盘退变治疗中的重要手段。②纳米水凝胶系统能将抗氧化剂快速稳定地靶向输送至椎间盘内部,提高抗氧化剂的生物利用度。因此,开发纳米水凝胶系统搭载的新型抗氧化剂以及抗氧化剂的联合治疗策略将会是未来研究的重点方向。
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-0020-234X (苏永昆)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
苏永昆, 孙 红, 刘 淼, 杨 华, 李青松. 开发纳米水凝胶系统搭载新型抗氧化剂与抗氧化剂联合治疗椎间盘退变[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384.
Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384.
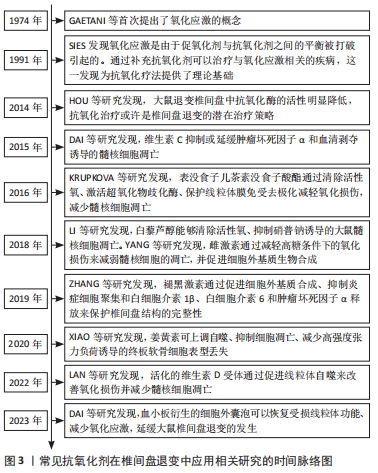
2.2 椎间盘退变与氧化应激 椎间盘是椎骨之间的无血管结缔组织,主要由髓核、纤维环、终板组成[8]。椎间盘退变的发生发展涉及细胞衰老和凋亡、炎症、氧化应激等多种病理过程[9],其中氧化应激被广泛认为是导致椎间盘退变的重要原因。氧化应激是由于机体内活性氧的产生和抗氧化剂保护机制之间的失衡所导致的[10]。活性氧是细胞有氧代谢过程中产生的一种不稳定且高反应性的含氧物质,主要包括超氧阴离子、羟基自由基、过氧化氢和次氯酸根离子等[4],活性氧的过度积累会诱发氧化应激,进而导致分子氧化损伤和细胞破坏,对机体产生不利影响[11]。
细胞衰老是由DNA损伤、端粒脱帽、氧化应激、促炎细胞因子等引起的不可逆细胞周期停滞。由于椎间盘的无血管性质,免疫细胞难以进入椎间盘内部,部分限制了免疫介导的清除机制,导致衰老细胞在椎间盘中异常积累,加速椎间盘退变的发展。作为椎间盘细胞衰老的重要触发因素,活性氧会靶向攻击DNA分子中的核苷酸并通过DNA损伤反应信号通路快速诱导细胞衰老[12]。在糖尿病患者中,高糖环境通过引起线粒体损伤来增强椎间盘细胞中活性氧的产生,并通过p16-Rb通路介导椎间盘细胞衰老[13]。
此外,线粒体是活性氧攻击的主要目标。氧化应激产生的过量活性氧会导致线粒体DNA、脂质和蛋白质的氧化损伤,加重线粒体功能障碍[14],受损的线粒体又会释放大量活性氧,由此形成恶性循环。同时,线粒体内过多的活性氧通过促进释放细胞色素C与其他促凋亡蛋白的表达,在胞浆中以凋亡小体的形式激活Caspase-3,从而激活Caspase凋亡级联反应,诱导椎间盘细胞凋亡[15],这些变化最终导致椎间盘细胞的丧失和炎症微环境的持续(图4)。另一方面,活性氧作为信号分子影响多条信号通路,包括核因子κB、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路[16],上述信号通路参与椎间盘细胞中炎症反应、衰老、凋亡、细胞外基质降解和线粒体功能障碍等病理过程[17]。磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路是重要的抗凋亡通路,是目前研究中少数延缓椎间盘退变的信号通路之一。丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路参与调节细胞活性并介导了椎间盘退变的炎性反应。核因子κB通路在调节炎症递质、细胞凋亡及细胞外基质代谢中发挥着重要作用:在椎间盘退变中,核因子κB信号被显示异常上调,而抑制核因子κB有助于增加髓核细胞的活性,从而增加蛋白聚糖合成,改善椎间盘中的炎症反应并抑制髓核细胞的凋亡[18]。研究发现,活性氧通过激活核因子κB通路和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路导致椎间盘细胞中细胞外基质降解和合成之间的失衡,以及增加促炎因子的分泌[19-20],加速椎间盘退变的发展。
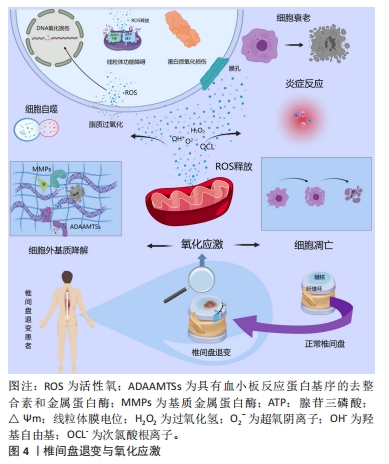
在正常生理条件下,人体拥有由抗氧化酶、非酶抗氧化剂组成的抗氧化系统,包括谷胱甘肽、超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、维生素C、维生素E和类胡萝卜素等[17],通过人体自身的抗氧化系统,活性氧得以被及时清除,从而调节椎间盘中各种病理生理过程,包括细胞凋亡和衰老、细胞外基质的分解代谢、线粒体的功能障碍、炎症反应、自噬等,最终有效避免椎间盘退变的发生。然而在退化的髓核细胞中,人体自身合成的抗氧化剂包括超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶和谷胱甘肽的表达水平降低[21]。因此,通过补充外源性抗氧化剂被认为是椎间盘退变的一种潜在治疗策略。
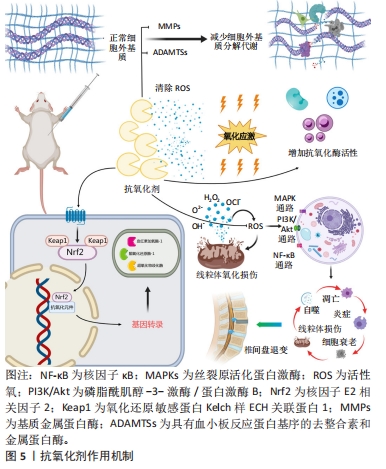
2.3 抗氧化剂作用机制 活性氧作为关键信号分子,在椎间盘退变的发生发展中至关重要,是抗氧化剂治疗椎间盘退变的主要靶点。抗氧化剂可以通过直接清除活性氧或上调抗氧化酶的活性来增强机体自身清除活性氧的能力,同时改善线粒体功能障碍,减少线粒体内活性氧的产生,进而拮抗由活性氧介导的细胞衰老和凋亡、自噬、炎症反应、线粒体氧化损伤,避免了椎间盘细胞丧失和持续的炎症微环境。此外,抗氧化剂还可以激活核因子E2相关因子2信号通路,促进抗氧化元件下游抗氧化基因的转录和上调抗氧化酶的表达活性,增强椎间盘细胞的抗氧化能力。细胞外基质分解代谢酶例如基质金属蛋白酶和具有血小板反应蛋白基序的去整合素和金属蛋白酶(a disintegrin-like and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs,ADAMTS)在退化髓核细胞中显示出高表达水平,最终导致细胞外基质降解[22]。抗氧化剂还可以抑制ADAMTS、基质金属蛋白酶活性,从而降低细胞外基质的降解,这些作用机制使得抗氧化剂在预防和治疗椎间盘退变方面具有潜在的应用前景(图5)。目前常见的抗氧化剂主要有多酚类抗氧化剂、天然小分子物质、激素、维生素D及基于组织工程的新型抗氧化剂等。
2.4 多酚类抗氧化剂与椎间盘退变
2.4.1 白藜芦醇 白藜芦醇是一种天然的非黄酮类多酚化合物,具有良好的抗炎、抗氧化作用[23]。研究发现,白藜芦醇在炎症环境下通过激活磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路来上调细胞自噬,增强髓核细胞的基质合成,抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞凋亡[24-25]。白藜芦醇还可通过改善细胞外基质的代谢稳态、抑制白细胞介素6/Janus激活激酶/信号传导与转录激活因子3通路来减少髓核细胞凋亡,从而有效减轻炎症反应诱导的椎间盘退变[26]。在氧化应激方面,SHAN等[27]研究发现,经白藜芦醇预处理过的纤维环细胞氧化应激模型中活性氧含量显著下降,超氧化物歧化酶总活性增加,这表明白藜芦醇可以减轻肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的纤维环细胞氧化应激损伤。同时,白藜芦醇通过抑制活性氧积累有效减弱机械过载的髓核细胞衰老和硝普钠诱导的大鼠髓核细胞凋亡[28-29]。综合来看,白藜芦醇可能通过其抗炎和抗氧化双重作用来抑制椎间盘退变的进展。
2.4.2 姜黄素 姜黄素是一种酚类化合物,为姜黄的主要成分。姜黄素在多种疾病模型中显示出广泛的药理活性,包括抗炎和抗氧化活性[30-31]。姜黄素通过减少活性氧产生和线粒体功能障碍来保护人髓核细胞免受氧化应激引发的凋亡、衰老和细胞外基质降解,成功逆转了叔丁基过氧化氢诱导的超氧化物歧化酶活性下调,从而有效减轻叔丁基过氧化氢介导的人髓核细胞中氧化应激和线粒体损伤[32]。研究发现,姜黄素除了能增加超氧化物歧化酶等抗氧化酶的活性来发挥抗氧化作用[33],还通过上调自噬来拮抗过度张力诱导的软骨终板细胞凋亡和分泌功能障碍[34],激活内源性抗氧化通路(图5),如核因子E2相关因子2-氧化还原敏感蛋白Kelch样ECH关联蛋白1通路[35]。这些研究表明,姜黄素在预防和治疗椎间盘退变方面有着积极疗效。
2.4.3 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯是一种天然存在于绿茶中的多酚。既往的病例对照研究发现,饮茶习惯是椎间盘退变的保护因素之一[36]。表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯作为清除细胞内活性氧最强大的儿茶素,它通过清除活性氧或螯合金属离子而表现出抗氧化能力[37]。表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯可以通过多种途径来避免椎间盘退变的发生:①延缓线粒体膜去极化的发生,从而保护椎间盘细胞免受过量活性氧诱导的氧化应激伤害,并通过激活磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路减少髓核细胞凋亡[38];②抑制基质金属蛋白酶、ADAMTS的表达,上调合成代谢因子的表达,纠正氧化应激下髓核细胞中合成代谢和分解代谢失衡来发挥其保护作用[39];③此外,TIAN等[40]研究发现,表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯下调环鸟苷酸-腺苷酸合酶/干扰素基因刺激因子/NOD样受体蛋白3信号通路,在氧化应激环境下对细胞活力、细胞凋亡、细胞周期停滞和炎症状态也表现出显著的保护作用。由于缺乏血管,椎间盘内部的受损组织很难得到足够的营养和氧气供应,其自我修复能力受到限制[41]。研究者利用混合负载羟基磷灰石-表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯纳米棒的羧甲基壳聚糖和醛透明质酸溶液,制备了一种可注射的纳米复合水凝胶,该水凝胶作为一种持久有效的生物活性递送系统,能够通过调节巨噬细胞极化、减少促炎细胞因子(包括肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的释放)、促进细胞外基质合成代谢,在椎间盘修复的应用中表现出巨大潜力[42]。同样值得注意的是,LIU等[43]将苯硼酸修饰明胶甲基丙烯酰与天然提取的表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯通过动态硼酸酯偶联制备了另一种水凝胶体系,该水凝胶在高活性氧水平和酸性条件下进一步显示出表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯的响应性释放,在体外过度活跃的活性氧环境和炎性细胞因子过表达环境中对髓核细胞也表现出显著保护作用。这些研究成果为开发椎间盘退变新型治疗方案,特别是针对表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯治疗椎间盘退变的临床应用,提供了有益的启示。
2.5 天然小分子物质与椎间盘退变 许多天然物质具有抗氧化活性,并且在椎间盘退变中得到广泛研究。柚皮苷是一种源自西红柿、葡萄柚和柑橘的生物类黄酮,已被发现具有多种生物学作用,包括抗氧化、抗炎和抗凋亡等[44]。柚皮苷可通过多种途径来维持椎间盘细胞中的氧化还原稳态,包括恢复线粒体跨膜电位水平、增加ATP产生、促进抗氧化表达和抑制活性氧产生等[45]。细胞凋亡和炎症反应是氧化应激诱导的椎间盘退变的重要致病因素,柚皮苷通过下调环氧合酶2表达抑制炎症反应,上调超氧化物歧化酶活性来改善髓核细胞氧化应激和线粒体功能障碍;同时还可调节基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMTS-4的表达,纠正细胞外基质合成和降解的失衡 [46]。多项研究表明,柚皮苷通过激活腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶信号通路来增强自噬通量,从而保护髓核细胞免受氧化应激损伤[46-47]。ZHANG等[48]研究发现,周期性拉伸促进Caspase-3、Caspase-9的过表达,同时激活核因子κB信号通路,诱导大鼠纤维环细胞凋亡;柚皮苷可通过抑制Caspase表达水平和核因子κB信号通路的激活来拮抗上述过程;另外,柚皮苷直接抑制活性氧的产生、增强大鼠纤维环细胞中超氧化物歧化酶表达水平并改善线粒体功能,进而缓解周期性拉伸所致的氧化损伤。槲皮素也是天然类黄酮家族的成员,具有抗炎、抗衰老和抗氧化特性[49]。槲皮素通过调控沉默信息调节因子1和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路来上调自噬,从而拮抗叔丁基过氧化氢诱导的髓核细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解;槲皮素还可以通过丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路减轻氧化应激诱导的髓核细胞衰老及衰老相关分泌表型的表达,进而有效延缓针刺诱导的大鼠椎间盘退变 [50-52]。丹酚酸B在丹参中的含量最高,具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗肿瘤等多种生物活性[53]。丹酚酸B通过激活Janus激活激酶2/信号转导及转录激活因子3信号通路显著降低体外裂解的Caspase-3表达活性,有效抑制过氧化氢诱导的髓核细胞凋亡,提示丹酚酸B有可能通过减少氧化应激条件下的髓核细胞凋亡来治疗椎间盘退变 [54]。芒果苷广泛分布于世界各地的植物中,在各种疾病模型中具有拮抗氧化应激和线粒体功能障碍的作用[55-56]。芒果苷能够下调Bax、Caspase-3水平和上调Bcl-2蛋白表达,从而降低髓核细胞凋亡率;芒果苷通过影响人髓核细胞中线粒体形态和功能相关指标的表达,在线粒体功能中发挥保护作用,这有助于减少线粒体功能障碍和活性氧产生,进而缓解椎间盘退变的过程[20]。综上所述,许多植物来源的小分子物质因强大的抗氧化、抗炎能力在椎间盘退变的治疗中展现出巨大的潜力。
2.6 激素与椎间盘退变
2.6.1 褪黑激素 褪黑激素主要在松果体中产生,以清除自由基的抗氧化特性而闻名[57]。一方面,褪黑素可以在线粒体中高浓度积聚,通过激活解偶联蛋白和防止线粒体通透性转换孔的形成来稳定线粒体膜电位,从而改善线粒体功能;另一方面,褪黑激素通过刺激细胞内抗氧化酶,如过氧化氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶、血红素加氧酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶等,来减轻氧化应激[58]。褪黑激素介导的抗氧化作用涉及核因子E2相关因子2信号通路,当核因子E2相关因子2通路被激活时,核因子E2相关因子2易位到细胞核中并与抗氧化反应元件结合,启动一系列抗氧化和细胞保护基因的转录,如超氧化物歧化酶、醌氧化还原酶1、血红素加氧酶1等(图5),这些基因的表达增加了细胞的抗氧化能力,有助于减轻氧化应激对细胞的损伤[59]。
褪黑激素作为活性氧的主要清除剂,在保护细胞免受活性氧诱导的损伤方面发挥关键作用[60]。多项研究表明,褪黑激素保护髓核细胞免受氧化应激诱导的细胞凋亡[61]、纠正白细胞介素1β诱导的细胞外基质代谢失衡[62],并防止软骨终板钙化[63],有效改善了椎间盘退变。自噬是一种细胞自我降解的过程,可以通过将细胞内部的有害或受损组分送入溶酶体进行降解来维持细胞内环境的稳定,适当自噬的平衡对于维持线粒体稳态至关重要[64]。褪黑激素对自噬的双向调节作用有效改善了椎间盘内氧化应激微环境及髓核细胞凋亡。LEI等[65]研究发现,褪黑激素在生理和病理条件下可通过上调自噬来清除活性氧和受损的线粒体,有助于维持线粒体的健康和功能;同时,褪黑激素还可以下调自噬,减少过度自噬引起的细胞死亡。研究人员目前正在开发一种富含褪黑激素的动态自愈水凝胶,能有效修复受损的纤维环细胞和椎间盘的结构,通过动物实验发现该水凝胶释放的褪黑素通过激活核因子E2相关因子2信号通路及其下游细胞内抗氧化酶来缓解白细胞介素1β诱导的大鼠尾部纤维环细胞氧化应激[66]。水凝胶系统在褪黑激素递送方面具有巨大的潜力,能够显著提高褪黑激素在椎间盘退变治疗中的应用效果,这一创新性方法为褪黑激素治疗椎间盘退变提供了新的可能。
2.6.2 雌激素 绝经后妇女中与椎间盘退变相关的腰痛患病率很高,并且治疗方法也相对有限[67],其中因雌激素流失所致的氧化应激可能是椎间盘退变的危险因素之一。JIN等[68]通过对卵巢切除大鼠模型进行实验发现,椎间盘退变与雌激素水平之间存在负相关关系,雌激素分泌减少降低了髓核细胞的抗氧化能力,补充雌激素可以纠正髓核细胞的氧化应激。研究发现,雌激素通过下调基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶13表达、调控Ⅱ型胶原合成、降低活性氧含量、减少髓核细胞凋亡来有效缓解椎间盘退变[69-70]。然而,关于椎间盘退变雌激素替代疗法的基础研究和临床实践仍然较少,因此,小剂量雌激素替代疗法在椎间盘退变治疗中的具体作用仍待进一步研究。
2.7 维生素D、维生素C、α-硫辛酸与椎间盘退变 维生素D是一种食物来源的脂溶性维生素,经过肝脏及肾脏的代谢作用最终转化为生物活性形式的1,25-二羟维生素D。1,25-二羟维生素D与维生素D受体结合发挥生物学作用,参与调节细胞功能和组织代谢[71]。超氧化物歧化酶1和超氧化物歧化酶2是抗氧化应激的重要指标,研究发现,维生素D处理可显著提高超氧化物歧化酶1和超氧化物歧化酶2水平,并通过抑制核因子κB信号通路降低椎间盘炎症和氧化应激水平,延缓细胞衰老,抑制细胞凋亡[72]。维生素D受体功能障碍可能加速椎间盘退变的发展,活化的维生素D受体通过保护线粒体功能来改善氧化损伤,减少髓核细胞和纤维环细胞凋亡,其中PTEN诱导假定激酶1/E3泛素连接酶信号通路依赖性线粒体自噬参与了这一过程[73-75]。LAN等[73]研究发现,较高剂量的维生素D并不能提供保护作用,在使用维生素D预防椎间盘退变时需要考虑其剂量。另一方面,维生素D可以促进肠道对钙、磷吸收和利用,有助于骨骼生长和维持骨质稳定;维生素D缺乏与中老年人群骨量丢失密切相关,被认为是引发骨质疏松症的重要原因之一[76]。
骨质疏松常常会加重椎间盘退变,骨质疏松症引起的异常骨重塑破坏了终板的结构完整性,导致椎间盘营养供应受损、分解代谢因子表达增加以及Ⅱ型胶原和聚集聚糖水平降低[77]。综上所述,血清维生素D水平可能直接或间接影响椎间盘退变程度,适量补充维生素D可能有助于延缓椎间盘退变的进程[78]。维生素C是一种天然有效的抗氧化剂,维生素C缺乏与一系列骨科疾病有关,例如老年人退行性椎间盘疾病的发展、骨骼发育不良、骨质疏松症及骨关节炎的发展[79]。YI等[80]研究发现,维生素C通过上调增殖生物标志物ALDH1A3来促进髓核细胞增殖。戴丽冰等[81]的进一步研究表明,维生素C对髓核细胞有抗氧化作用,它能够清除活性氧并抑制或延缓肿瘤坏死因子α和血清剥夺诱导的细胞凋亡,作用机制可能与p53-FAS-Caspase 3信号传导通路有关。此外研究人员还发现,低浓度维生素C对髓核细胞有抗氧化作用,高浓度维生素C对髓核细胞有亲氧化作用,因此,将维生素C应用于椎间盘退变治疗时剂量将是影响疗效的关键因素。
α-硫辛酸是一种天然存在的含硫脂肪酸,具有高抗氧化活性,是抗氧化防御系统的重要组成部分。α-硫辛酸在人体中具有多种有益功能,包括清除活性氧、螯合过渡金属和重金属、修复氧化应激损伤和抑制细胞凋亡[82];同时,α-硫辛酸还能促进其他抗自由基分子的再生循环,如谷胱甘肽、维生素C和维生素E [83]。肖琳霄[84]研究发现,α-硫辛酸通过抑制脂多糖诱导的核因子κB信号通路活化在人髓核细胞中表现出较强的抗炎和抗凋亡作用。尽管α-硫辛酸在多种疾病模型中展现了强大的抗氧化能力,但在椎间盘退变方面的基础研究仍然有限,目前尚不足以将其应用于椎间盘退变的临床治疗。
2.8 新型抗氧化剂与椎间盘退变 与传统抗氧化剂相比,由抗氧化物质与组织工程材料组成的新型抗氧化剂,因高效靶向作用于椎间盘细胞的能力成为研究者关注的重点。不同于小分子化合物,纳米颗粒在生理条件下具有更好的稳定性、更高的药物利用率,因此能够发挥更持久的疗效。但用于椎间盘注射治疗的纳米溶液的高流动性通常会带来重大的安全隐患,注射到椎间盘中的溶液可以流向周围关键的区域,如脊髓,从而对生命构成严重威胁[85],这种风险限制了纳米溶液在生物医学领域的应用。单宁酸是一种富含酚羟基的生物有机化合物,具有清除活性氧和抗炎特性[86]。ZHOU等[87]以单宁酸、锰和聚乙烯吡咯烷酮为原料研究开发一种具有高效活性氧清除活性的单宁酸衍生金属酚类纳米溶液,同时研究者将该纳米溶液加载到海藻酸钠-聚乙烯醇-路易斯酸水凝胶上,限制了纳米溶液的高流动性,形成活性氧响应释放平台,进而减少对脊髓等关键部位造成损伤的可能性;体外研究表明,从平台释放的纳米颗粒可以靶向作用于线粒体,有效地改善线粒体功能障碍,清除活性氧和下调细胞外基质降解酶基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMTS-5的表达,阻止细胞外基质降解,并增加椎间盘中的水分含量。相较于传统意义的天然抗氧化剂,该水凝胶平台具有生物相容性,可以按需释放,有效利用纳米颗粒并发挥多边作用。此外,干细胞疗法长期以来被认为是修复椎间盘疾病的有效方法,间充质干细胞具有较强的自我更新能力和多向分化潜力,其分泌的囊泡能促进髓核细胞再生、增加细胞外基质的产生、缓解炎症状态。移植干细胞的存活率和分化效率是保证治疗效果的关键,然而,退变椎间盘中的高活性氧水平会抑制干细胞的增殖并增加细胞凋亡,还会导致移植干细胞的DNA损伤,影响其治疗效果[88]。辅酶Q10是一种有靶向作用于线粒体的疏水抗氧化剂,可以减少活性氧的产生,但辅酶Q10作为一种脂溶性分子的疏水特性限制了其使用和药物释放。SUN等[89]将辅酶Q10封装到卵磷脂胶束中开发出一种可注射载辅酶 Q10的胶束(LM@Co-Q10),以有效地将辅酶 Q10递送至骨髓间充质干细胞中来治疗椎间盘退变,LM@Co-Q10使得不溶性辅酶Q10可分散在水中作为稳定的胶体并将其有效递送至椎间盘内部,通过减少炎症因子、下调基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS-5表达、抑制活性氧的产生和改善线粒体功能障碍等作用来减弱髓核细胞凋亡;同时,辅酶Q10还保护椎间盘中移植干细胞免受氧化应激损伤,提高细胞增殖和存活率。这项研究将干细胞疗法与抗氧化剂治疗相结合展示了一种新的治疗策略,有望为治疗椎间盘退变提供新的方向和可能性。
与合成生物材料相比,细胞外囊泡作为固有的细胞分泌天然产物,具有良好的生物相容性、更低的免疫原性和更高的靶向特异性[90],这些特点使细胞外囊泡在临床应用中具有很高的价值,尤其是作为治疗椎间盘退变的理想药物载体。LIU等[91]开发出氧化还原调节分子谷氧还蛋白3-间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外载体,实验证明该载体通过调节氧化还原稳态来减轻线粒体损伤、拮抗髓核细胞衰老、恢复细胞外基质合成代谢,从而延缓了椎间盘退变的进展。DAI等[92]研究发现,血小板衍生的细胞外囊泡通过沉默信息调节因子1/过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅激活因子/线粒体转录因子A信号通路来恢复受损的线粒体功能、减少氧化应激、恢复细胞代谢,延缓了大鼠模型中椎间盘退变的进展。尽管基于细胞外囊泡的抗氧化剂治疗方案已被证实可以有效延缓椎间盘退变,但有研究发现间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡在治疗骨肉瘤时,既抑制肿瘤进展又促进肿瘤的增殖和转移,因此,将基于细胞外囊泡的抗氧化剂应用于临床治疗椎间盘退变,尤其是合并肿瘤的患者时,其临床效果和安全性还有待商榷。
抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变中的作用机制见表1。

2.9 小结与展望 抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变治疗方面表现出巨大的潜力,随着研究的深入,越来越多抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变中的作用机制将会被明确,特别是天然植物来源的抗氧化活性物质,由于其抗氧化能力突出、来源广泛、可获得性高,将会成为未来的研究热点。同时,由于椎间盘无血管的特性,药物很难通过血液循环进入椎间盘内部,越来越多的研究将集中在如何利用水凝胶等生物材料和纳米技术手段构建一种药物递送系统,以便将抗氧化药物快速稳定地靶向输送至椎间盘内部,提高抗氧化剂的生物利用度。此外,新型抗氧化剂开发以及抗氧化剂的联合治疗策略将会是未来研究的重点方向,通过开发更具靶向性和高效性的抗氧化剂并探索不同抗氧化剂之间的协同作用,有望进一步提升椎间盘退变治疗效果。尽管抗氧化剂在体外实验和动物模型中对椎间盘退变表现出一定的治疗潜力,但抗氧化剂的临床应用仍存在诸多局限性,包括:①现有研究大多基于动物实验和体外研究,这些研究虽然提供了宝贵的抗氧化基础理论支持,但抗氧化剂在高剂量或长期使用下潜在的不良反应仍待进一步阐明,例如高剂量维生素D并不能提供对椎间盘的保护作用、高浓度维生素C对髓核细胞有亲氧化作用等。②虽然目前基于组织工程材料有效提高了抗氧化剂在椎间盘中的生物利用度和靶向性,但其在人体中的应用仍存在未知的风险,需要进一步研究,例如:高流动性的纳米溶液可能流向脊髓,对生命造成严重威胁;以及基于细胞外囊泡为载体的新型抗氧化剂在治疗椎间盘退变合并肿瘤的患者时,是否会促进肿瘤的转移等。③由于不同患者的椎间盘退变病程和病因存在差异,对抗氧化剂的反应也不同,这导致临床试验的设计和开展面临诸多挑战,如患者的选择、治疗方案的制定、疗效评价的标准等。因此,目前仍缺乏大规模、高质量的抗氧化剂治疗椎间盘退变的临床试验数据,这些问题限制了抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变中的临床应用。最后,相信随着抗氧化剂研究的深入以及组织工程材料学的发展,这些挑战有望逐一解决。

| [1] WANG Y, CHENG H, WANG T, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration: molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(9):e13448. [2] CHE H, LI J, LI Y, et al. P16 deficiency attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration by adjusting oxidative stress and nucleus pulposus cell cycle. Elife. 2020;9:e52570. [3] 王啸华,何敢声,谢林.氧化应激在椎间盘退变中的作用进展[J].中医正骨, 2023,35(5):44-48. [4] CAO G, YANG S, CAO J, et al. The role of oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2166817. [5] GAETANI GD, PARKER JC, KIRKMAN HN. Intracellular restraint: a new basis for the limitation in response to oxidative stress in human erythrocytes containing low-activity variants of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974;71(9):3584-3587. [6] SIES H. Oxidative stress: from basic research to clinical application. Am J Med. 1991;91(3C):31S-38S. [7] HOU G, LU H, CHEN M, et al. Oxidative stress participates in age-related changes in rat lumbar intervertebral discs. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2014;59(3):665-669. [8] KRITSCHIL R, SCOTT M, SOWA G, et al. Role of autophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2022;237(2):1266-1284. [9] FAN C, CHU G, YU Z, et al. The role of ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1219840. [10] SEOL D, COLEMAN MC, MARTIN JA, et al. Targeting oxidative stress with amobarbital to prevent intervertebral disc degeneration: Part I. in vitro and ex vivo studies. Spine J. 2021;21(6):1021-1030. [11] ANGELOVA PR. Sources and triggers of oxidative damage in neurodegeneration. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;173:52-63. [12] CHENG F, YANG H, CHENG Y, et al. The role of oxidative stress in intervertebral disc cellular senescence. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1038171. [13] PARK JS, PARK JB, PARK IJ, et al. Accelerated premature stress-induced senescence of young annulus fibrosus cells of rats by high glucose-induced oxidative stress. Int Ortho. 2014;38(6):1311-1320. [14] CHEN C, ZHOU Y, HU C, et al. Mitochondria and oxidative stress in ovarian endometriosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;136:22-34. [15] 李季霖,周红海,余进爵,等.髓核细胞凋亡相关信号通路研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021,31(2):178-182. [16] LI Y, CHEN L, GAO Y, et al. Oxidative stress and intervertebral disc degeneration: pathophysiology, signaling pathway, and therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022; 2022:1984742. [17] FENG C, YANG M, LAN M, et al. ROS: Crucial intermediators in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5601593. [18] 钱嘉铭,祝永刚,肖辉灯,等.髓核细胞退变相关信号通路的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021,31(6):561-566. [19] ZHANG X, ZHANG Z, ZOU X, et al. Unraveling the mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration: an exploration of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1324561. [20] YU H, HOU G, CAO J, et al. Mangiferin alleviates mitochondrial ros in nucleus pulposus cells and protects against intervertebral disc degeneration via suppression of nf-kappab signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:6632786. [21] ZHANG Q, LI J, LI Y, et al. Bmi deficiency causes oxidative stress and intervertebral disc degeneration which can be alleviated by antioxidant treatment. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(16):8950-8961. [22] SUN Y, LYU M, LU Q, et al. Current perspectives on nucleus pulposus fibrosis in disc degeneration and repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(12):6612. [23] 轩莹莹,杨玉田,孙月红,等.白藜芦醇对后肢去负荷雄性大鼠生殖损伤的对抗作用[J].空间科学学报,2024,44(1):133-141. [24] JIANG Y, XIE Z, YU J, et al. Resveratrol inhibits IL-1beta-mediated nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(3):BSR20190043. [25] GAO J, ZHANG Q, SONG L. Resveratrol enhances matrix biosynthesis of nucleus pulposus cells through activating autophagy via the PI3K/Akt pathway under oxidative damage. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(4):BSR20180544. [26] WU C, GE J, YANG M, et al. Resveratrol protects human nucleus pulposus cells from degeneration by blocking IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway. Eur J Med Res. 2021;26(1):81. [27] SHAN Q, LI N, ZHANG F, et al. Resveratrol suppresses annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis through regulating oxidative stress reaction in an inflammatory environment. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:9100444. [28] JIANG Y, DONG G, SONG Y. Nucleus pulposus cell senescence is alleviated by resveratrol through regulating the ROS/NF-kappaB pathway under high-magnitude compression. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(4):BSR20180670. [29] LI K, LI Y, MI J, et al. Resveratrol protects against sodium nitroprusside induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by scavenging ROS. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(5):2485-2492. [30] FAN F, LEI M. Mechanisms underlying curcumin-induced neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:893118. [31] YANG L, CHEN Y, LIU Y, et al. The role of oxidative stress and natural antioxidants in ovarian aging. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:617843. [32] KANG L, XIANG Q, ZHAN S, et al. Restoration of autophagic flux rescues oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction to protect against intervertebral disc degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:7810320. [33] ABRAHAMS S, HAYLETT WL, JOHNSON G, et al. Antioxidant effects of curcumin in models of neurodegeneration, aging, oxidative and nitrosative stress: a review. Neuroscience. 2019;406:1-21. [34] XIAO L, DING B, GAO J, et al. Curcumin prevents tension-induced endplate cartilage degeneration by enhancing autophagy. Life Sci. 2020;258:118213. [35] LIN X, BAI D, WEI Z, et al. Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. PLoS One. 2019;14(5):e0216711. [36] DENG Y, TAN XT, WU Q, et al. Correlations between col2a and aggrecan genetic polymorphisms and the risk and clinicopathological features of intervertebral disc degeneration in a chinese han population: a case-control study. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2017;21(2):108-115. [37] ZWOLAK I. Epigallocatechin gallate for management of heavy metal-induced oxidative stress: mechanisms of action, efficacy, and concerns. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):4027. [38] KRUPKOVA O, HANDA J, HLAVNA M, et al. The natural polyphenol epigallocatechin gallate protects intervertebral disc cells from oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:7031397. [39] MEI L, ZHENG Y, MA T, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration through reprogramming of the circadian clock. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:753548. [40] TIAN Y, BAO Z, JI Y, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects h(2)o(2)-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and inflammation by inhibiting cgas/sting/nlrp3 activation. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:2113-2122. [41] 吴铭杰,康然.微环境影响椎间盘组织工程修复的研究进展[J].江苏医药, 2023,49(3):316-320. [42] ZHAO DW, CHENG Q, GENG H, et al. Decoding macrophage subtypes to engineer modulating hydrogels for the alleviation of intervertebral disk degeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(1):e2304480. [43] LIU L, WANG W, HUANG L, et al. Injectable pathological microenvironment-responsive anti-inflammatory hydrogels for ameliorating intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomaterials. 2024;306:122509. [44] SALEHI B, FOKOU PVT, SHARIFI-RAD M, et al. The therapeutic potential of naringenin: a review of clinical trials. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019;12(1):11. [45] NAN LP, WANG F, RAN D, et al. Naringin alleviates H2O2-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(6):554-567. [46] CHEN R, GAO S, GUAN H, et al. Naringin protects human nucleus pulposus cells against TNF-alpha-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and loss of cellular homeostasis by enhancing autophagic flux via AMPK/SIRT1 activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:7655142. [47] ZHANG Z, WANG C, LIN J, et al. Therapeutic potential of naringin for intervertebral disc degeneration: involvement of autophagy against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Am J Chin Med. 2018:1-20. [48] ZHANG YH, SHANGGUAN WJ, ZHAO ZJ, et al. Naringin inhibits apoptosis induced by cyclic stretch in rat annular cells and partially attenuates disc degeneration by inhibiting the ROS/NF-kappaB pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:6179444. [49] CARRILLO-MARTINEZ EJ, FLORES-HERNANDEZ FY, SALAZAR-MONTES AM, et al. quercetin, a flavonoid with great pharmacological capacity. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):1000. [50] 张树文.基于氧化应激探讨槲皮素防治椎间盘退变的实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2021. [51] ZHANG S, LIANG W, ABULIZI Y, et al. Quercetin alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by modulating p38 mapk-mediated autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6631562. [52] WANG D, HE X, WANG D, et al. Quercetin suppresses apoptosis and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration via the SIRT1-autophagy pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:613006. [53] HE G, CHEN G, LIU W, et al. Salvianolic acid b: a review of pharmacological effects, safety, combination therapy, new dosage forms, and novel drug delivery routes. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(9):2235. [54] DAI S, LIANG T, SHI X, et al. Salvianolic acid b protects intervertebral discs from oxidative stress-induced degeneration via activation of the jak2/stat3 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6672978. [55] ALBERDI E, SANCHEZ-GOMEZ MV, RUIZ A, et al. Mangiferin and morin attenuate oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neurocytotoxicity, induced by amyloid beta oligomers. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:2856063. [56] LUO Y, FU C, WANG Z, et al. Mangiferin attenuates contusive spinal cord injury in rats through the regulation of oxidative stress, inflammation and the Bcl-2 and Bax pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(5):7132-7138. [57] 梁海峰.靶向缓释褪黑素纳米递送系统在骨关节炎中的治疗作用与相关机制研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2023. [58] ZHANG Y, LIU T, YANG H, et al. Melatonin: a novel candidate for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;78:101635. [59] 陈海伟,刘明强,张广智,等.核因子E2相关因子2在椎间盘退变中的作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(4):337-342. [60] SOCACIU AI, IONUT R, SOCACIU MA, et al. Melatonin, an ubiquitous metabolic regulator: functions, mechanisms and effects on circadian disruption and degenerative diseases. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020;21(4):465-478. [61] GE J, ZHOU Q, NIU J, et al. Melatonin protects intervertebral disc from degeneration by improving cell survival and function via activation of the erk1/2 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5120275. [62] ZHANG Y, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin modulates IL-1beta-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(22):10499-10512. [63] ZHANG Z, LIN J, TIAN N, et al. Melatonin protects vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and calcification via the Sirt1-autophagy pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(1):177-193. [64] CHEN T, ZHENG L, LUO P, et al. Crosstalk between m6A modification and autophagy in cancer. Cell Biosci. 2024;14(1):44. [65] LEI X, XU Z, HUANG L, et al. The potential influence of melatonin on mitochondrial quality control: a review. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1332567. [66] HU X, TIAN X, YANG C, et al. Melatonin-loaded self-healing hydrogel targets mitochondrial energy metabolism and promotes annulus fibrosus regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2023;23:100811. [67] LOU C, CHEN H, MEI L, et al. Association between menopause and lumbar disc degeneration: an MRI study of 1,566 women and 1,382 men. Menopause. 2017;24(10):1136-1144. [68] JIN LY, LV ZD, WANG K, et al. Estradiol alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration through modulating the antioxidant enzymes and inhibiting autophagy in the model of menopause rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:7890291. [69] YANG D, ZHU D, ZHU S, et al. 17beta-Estradiol/extrogen receptor beta alleviates apoptosis and enhances matrix biosynthesis of nucleus pulposus cells through regulating oxidative damage under a high glucose condition. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:1004-1009. [70] LIU S, YANG SD, HUO XW, et al. 17beta-Estradiol inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration by down-regulating MMP-3 and MMP-13 and up-regulating type II collagen in a rat model. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup2):182-191. [71] 徐浩伟,王善金,李丽丽,等.维生素D与椎间盘退变的相关性研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(3):239-243. [72] HUANG H, CHENG S, ZHENG T, et al. Vitamin D retards intervertebral disc degeneration through inactivation of the NF-kappaB pathway in mice. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(4):2496-2506. [73] LAN T, YAN B, GUO W, et al. VDR promotes nucleus pulposus cell mitophagy as a protective mechanism against oxidative stress injury. Free Radic Res. 2022;56(3-4):316-327. [74] TONG T, LIU Z, ZHANG H, et al. Age-dependent expression of the vitamin D receptor and the protective effect of vitamin D receptor activation on H2O2-induced apoptosis in rat intervertebral disc cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019;190:126-138. [75] CHRISTAKOS S, DHAWAN P, VERSTUYF A, et al. Vitamin D: metabolism, molecular mechanism of action, and pleiotropic effects. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(1):365-408. [76] 张良明,杨阳,陈振翔,等.中国南方地区中老年患者血清维生素D水平与骨密度的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(28):4448-4453. [77] LI W, NIU Y, QIU Z, et al. New evidence on the controversy over the correlation between vertebral osteoporosis and intervertebral disc degeneration: a systematic review of relevant animal studies. Eur Spine J. 2024;33(6):2354-2379. [78] 王俊武,陈东,南利平,等.中老年腰椎间盘退变程度与椎旁肌退变及维生素D水平的相关性研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(6):539-545. [79] CHEN Z, ZHANG S, DUAN P, et al. Intra-articular injection of ascorbic acid enhances microfracture-mediated cartilage repair. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):3811. [80] YI YY, ZHANG SB, CHEN H, et al. Ascorbic acid promotes nucleus pulposus cell regeneration by regulating proliferation during intervertebral disc degeneration. J Nutr Biochem. 2022;108:109099. [81] 戴丽冰,刘志河,梁伟国,等.维生素C对TNF-α及血清剥夺诱导的人髓核细胞凋亡的作用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(4):490-497. [82] ZIYATDINOVA G, GIMADUTDINOVA L. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for sulfur-containing antioxidants. Micromachines (Basel). 2023;14(7):1440. [83] RODELLA U, HONISCH C, GATTO C, et al. Antioxidant nutraceutical strategies in the prevention of oxidative stress related eye diseases. Nutrients. 2023;15(10):2283. [84] 肖琳霄.α-硫辛酸通过NF-κB信号通路调控人髓核细胞凋亡[D].长沙:中南大学,2023. [85] LV B, LU L, HU L, et al. Recent advances in GelMA hydrogel transplantation for musculoskeletal disorders and related disease treatment. Theranostics. 2023;13(6):2015-2039. [86] LI Z, FENG Y, ZHANG S, et al. A multifunctional nanoparticle mitigating cytokine storm by scavenging multiple inflammatory mediators of sepsis. ACS Nano. 2023;17(9):8551-8563. [87] ZHOU H, HE J, LIU R, et al. Microenvironment-responsive metal-phenolic network release platform with ROS scavenging, anti-pyroptosis, and ECM regeneration for intervertebral disc degeneration. Bioact Mater. 2024;37:51-71. [88] ZHANG W, LI G, LUO R, et al. Cytosolic escape of mitochondrial DNA triggers cGAS-STING-NLRP3 axis-dependent nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(2):129-142. [89] SUN J, YANG F, WANG L, et al. Delivery of coenzyme Q10 loaded micelle targets mitochondrial ROS and enhances efficiency of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in intervertebral disc degeneration. Bioact Mater. 2023;23:247-260. [90] WEI H, CHEN J, WANG S, et al. A nanodrug consisting of doxorubicin and exosome derived from mesenchymal stem cells for osteosarcoma treatment in vitro. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:8603-8610. [91] LIU C, FAN L, GUAN M, et al. A redox homeostasis modulatory hydrogel with GLRX3(+) extracellular vesicles attenuates disc degeneration by suppressing nucleus pulposus cell senescence. ACS Nano. 2023;17(14):13441-13460. [92] DAI Z, XIA C, ZHAO T, et al. Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration by alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction. Mater Today Bio. 2023;18:100512. |
| [1] | 董春阳, 周天恩, 莫孟学, 吕文权, 高 明, 朱瑞凯, 高志伟. 二甲双胍联合血水草敷料治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013. |
| [2] | 杨学涛, 朱梦菡, 张宸熙, 孙一民, 叶 玲. 抗氧化纳米材料在口腔中的应用和不足[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [3] | 陈豪杰, 王 黛, 沈 山. 种植体周围炎中的免疫炎症微环境机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062. |
| [4] | 王 峥, 程 吉, 于金龙, 刘文红, 王召红, 周鲁星. 水凝胶材料在脑卒中治疗中的应用进展与未来展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [5] | 孙尧天, 徐 凯, 王沛云. 运动影响铁代谢对免疫性炎症疾病调控的潜在机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1486-1498. |
| [6] | 油惠娟, 吴姝臻, 荣 融, 陈立沅, 赵玉晴, 王清路, 欧小伟, 杨风英. 巨噬细胞自噬与肺部疾病:作用的两面性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [7] | 潘鸿飞, 庄圳冰, 徐白云, 杨章阳, 林恺瑞, 詹冰晴, 蓝靖涵, 高 恒, 张南波, 林家煜. 不同浓度金诺芬抑制M1型巨噬细胞功能及修复糖尿病小鼠伤口的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [8] | 彭志伟, 陈 雷, 佟 磊. 木犀草素促进糖尿病小鼠创面愈合的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [9] | 贾金文, 艾日法特·艾尼瓦尔, 张 娟. EP300对过敏性鼻炎大鼠相关自噬和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1439-1449. |
| [10] | 侯超文, 李兆进, 孔健达, 张树立. 骨骼肌衰老主要生理变化及运动的多机制调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [11] | 阴勇成, 赵相瑞, 杨志杰, 李 政, 李 芳, 宁 斌. 过氧化物还原酶1在脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞炎症反应中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [12] | 张 迪, 赵 君, 马广悦, 孙 晖, 蒋 蓉. 基于高通量测序技术分析慢性社会挫败应激小鼠抑郁样行为的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [13] | 李郝静, 王 新, 宋成林, 张胜男, 陈云昕. 上斜方肌处体外冲击波与运动控制训练治疗慢性非特异性颈痛[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [14] | 刘 煜, 雷森林, 周锦涛, 刘 辉, 李先辉. 有氧和抗阻运动改善肥胖相关认知障碍的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [15] | 陶云飞, 彭 莉. 血流限制在急性抗阻运动中对内皮功能相关炎性因子的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1184-1195. |
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年6月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库至2024年6月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网和 PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“椎间盘退变,抗氧化剂,氧化应激,信号通路”为中文检索词;以“antioxidants,oxidative stresses,oxidative DNA damage,intervertebral disc degenerations,degenerative disc disease*,disc degeneration*,signal pathway”为英文检索词。
1.1.5 检索类型 包括研究原著、综述、述评、经验交流、荟萃分析。
1.1.6 检索策略 采用主题词和自由词结合的方式进行检索,以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。

1.2 入组标准
纳入标准:抗氧化剂与椎间盘退变相关文献;氧化应激与椎间盘退变相关文献;以氧化应激为靶点治疗椎间盘退变相关文献;抗氧化剂在氧化应激中作用机制的相关文献;抗氧化剂与纳米凝胶相关文献。
排除标准:①与研究目的领域不符的文献;②年代久远的文献;③研究内容落后、研究方法被淘汰、实验器材老化及重复性文献。
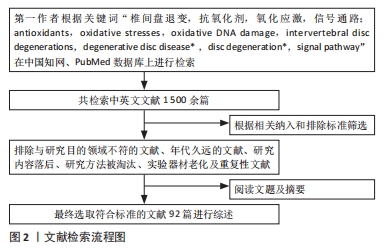
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 通过计算机初步检索得到与研究目的相关的中英文文献1 500余篇,经资料收集人员根据纳入及排除标准进一步筛选,选择与此次综述内容相符的文献,最终确定纳入92篇符合标准的文献进行综述。文献筛选流程见图2。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该文综述了氧化应激在椎间盘退变中所介导的病理生理过程,具体介绍了多酚类抗氧化剂、天然小分子物质、激素、维生素D、维生素C、α-硫辛酸以及新型抗氧化剂联合纳米水凝胶在改善椎间盘氧化应激、细胞代谢、炎症反应、细胞衰老和凋亡等方面的研究进展,同时简要介绍抗氧化剂未来的研究方向,为抗氧化剂应用于椎间盘退变的临床治疗提供新的思路。
3.3 该综述的局限性 该综述的局限性主要体现在以下几个方面:首先,尽管综述了大量文献,但由于抗氧化剂种类繁多,无法涵盖所有类型的抗氧化剂及其作用机制,某些潜在有效的抗氧化剂未被纳入或对作用机制讨论不足;其次,对于未来研究方向的提出可能过于理想化,实际研究中可能面临更多技术和资源的挑战。
3.4 该综述的重要意义 该文旨在对抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变中的研究现状展开综述,对未来椎间盘退变的治疗提供一条新方向,为抗氧化剂未来的研究提供新的见解。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 未来的研究应继续深入探讨抗氧化剂在椎间盘细胞中的具体作用机制,包括其对细胞自噬、凋亡、炎症反应和细胞外基质代谢的影响,同时建立跨学科的研究团队,以整合不同领域的知识和技术,这将有助于理解抗氧化剂的作用机制以及开发新型抗氧化剂。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
抗氧化剂:是能够抑制或中和活性氧、减少氧化应激,从而保护细胞和组织免受氧化损伤的一类物质的总称。椎间盘退变:是椎间盘自然退变和衰老的生理和病理过程,是各种临床脊柱疾病的基础,如椎体不稳、椎间盘突出和椎管狭窄,通常伴随有神经根或脊髓受压症状的下腰痛。
该文首先介绍氧化应激在椎间盘退变发生发展过程中的关键作用,并总结和分析多酚类抗氧化剂、天然小分子物质、褪黑激素、雌激素、维生素D、维生素C、α-硫辛酸等常见抗氧化剂,以及基于组织工程的新型抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变中的研究进展;探讨了抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变治疗中的多重作用机制。最后,文章不仅强调需要更多临床研究验证抗氧化剂在椎间盘治疗中的安全性,还提出开发新的抗氧化剂组合疗法以及构建纳米水凝胶递送系统等建议,以期提高抗氧化剂的治疗效果,为抗氧化剂在椎间盘退变治疗中的应用提供了新的研究思路。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||