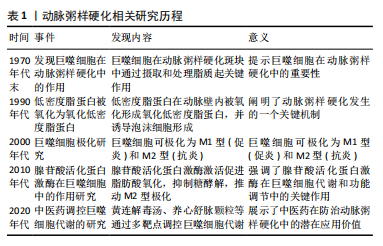
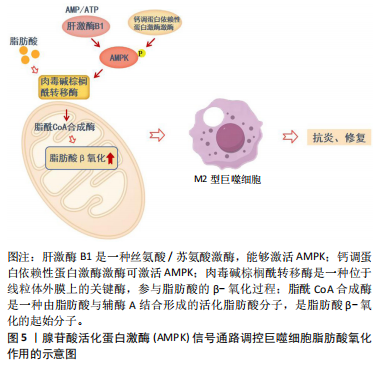
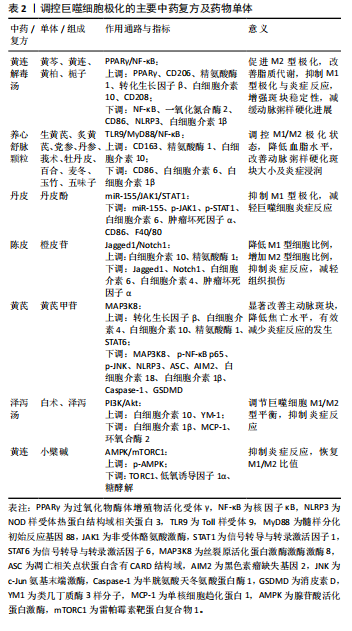
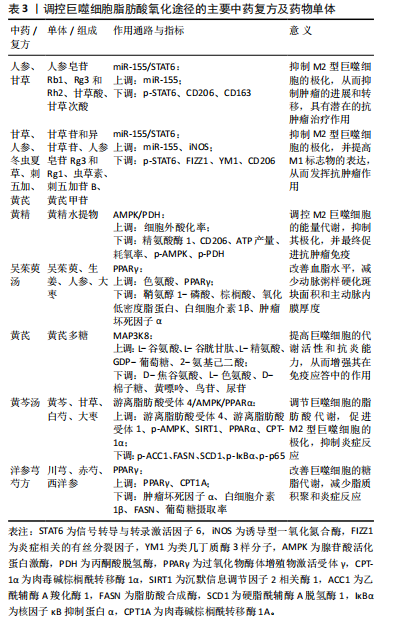
[1] AGARWAL A, HUFFMAN MD. Inclusion of Polypills for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in the 23rd World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines: A Significant Step Towards Reducing Global Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality. Glob Heart. 2024;19(1):24.
[2] LIAO Y, DONG Z, LIAO H, et al. Lipid metabolism patterns and relevant clinical and molecular features of coronary artery disease patients: an integrated bioinformatic analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2022;21(1):87.
[3] LINTON MF, MOSLEHI JJ, BABAEV VR. Akt Signaling in Macrophage Polarization, Survival, and Atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11): 2703.
[4] YANG S, YUAN HQ, HAO YM, et al. Macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;501:142-146.
[5] FARAHI L, SINHA SK, LUSIS AJ. Roles of Macrophages in Atherogenesis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:785220.
[6] MA A, WANG J, YANG L, et al. AMPK activation enhances the anti-atherogenic effects of high density lipoproteins in apoE-/- mice. J Lipid Res. 2017;58(8):1536-1547.
[7] ZHAO Y, ZHAO Y, TIAN Y, et al. Metformin suppresses foam cell formation, inflammation and ferroptosis via the AMPK/ERK signaling pathway in ox‑LDL‑induced THP‑1 monocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2022; 24(4):636.
[8] YANG Y, JIA Y, NING Y, et al. TAK1-AMPK Pathway in Macrophages Regulates Hypothyroid Atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021; 35(3):599-612.
[9] KOTLYAROV S. Involvement of Lipids and Lipid Mediators in Inflammation and Atherogenesis. Curr Med Chem. 2024. doi: 10.2174/0109298673303369240312092913.
[10] DOLFI B, GALLERAND A, HASCHEMI A, et al. Macrophage metabolic regulation in atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis. 2021;334:1-8.
[11] BONACINA F, DA DALT L, CATAPANO AL, et al. Metabolic adaptations of cells at the vascular-immune interface during atherosclerosis. Mol Aspects Med. 2021;77:100918.
[12] 于峰.血清同型半胱氨酸、游离脂肪酸、超敏C反应蛋白以及胱抑素C在冠心病患者中的诊断作用[J].中国现代药物应用,2023, 17(17):71-73.
[13] 赵忠平,刘虎,盛红专.HDL-C/ApoA1、MCP-1水平与中青年冠心病患者病变程度及炎症反应的相关性[J].中国现代医学杂志,2023, 33(16):49-54.
[14] CHO KY, MIYOSHI H, KURODA S, et al. The phenotype of infiltrating macrophages influences arteriosclerotic plaque vulnerability in the carotid artery. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(7):910-918.
[15] ZHANG Y, YANG X, BIAN F, et al. TNF-α promotes early atherosclerosis by increasing transcytosis of LDL across endothelial cells: crosstalk between NF-κB and PPAR-γ. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;72:85-94.
[16] LI L, MOU J, HAN Y, et al. Calenduloside e modulates macrophage polarization via KLF2-regulated glycolysis, contributing to attenuates atherosclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;117:109730.
[17] KING SD, CAI D, FRAUNFELDER MM, et al. Surfactant protein A promotes atherosclerosis through mediating macrophage foam cell formation. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023:2023.03.23.533959.
[18] ZHANG L, LI L, LI Y, et al. Disruption of COMMD1 accelerates diabetic atherosclerosis by promoting glycolysis. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2023;20(1): 14791641231159009.
[19] LIN C. Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease with Image Features of Optical Coherence Tomography under Adaptive Segmentation Algorithm. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;2022:1261259.
[20] KARPOUZAS GA, PAPOTTI B, ORMSETH S, et al. Serum cholesterol loading capacity on macrophages is linked to coronary atherosclerosis and cardiovascular event risk in rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002411.
[21] ROY A, SAQIB U, BAIG MS. NOS1-mediated macrophage and endothelial cell interaction in the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(6):1191-1201.
[22] ZHANG Z, WANG Q, YAO J, et al. Chemokine Receptor 5, a Double-Edged Sword in Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:146.
[23] MEHU M, NARASIMHULU CA, SINGLA DK. Inflammatory Cells in Atherosclerosis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(2):233.
[24] PENG D, ZHUGE F, WANG M, et al. (Sangzhi) alkaloids mitigate atherosclerosis by regulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization. Phytomedicine. 2024;128:155526.
[25] MOON JS, NAKAHIRA K, CHUNG KP, et al. NOX4-dependent fatty acid oxidation promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. Nat Med. 2016;22(9):1002-1012.
[26] YADAV S, GANTA V, SUDHAHAR V, et al. Myeloid Drp1 Deficiency Limits Revascularization in Ischemic Muscles via Inflammatory Macrophage Polarization and Metabolic Reprograming. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023: 2023.11.04.565656.
[27] NOMURA M, LIU J, YU ZX, et al. Macrophage fatty acid oxidation inhibits atherosclerosis progression. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;127:270-276.
[28] REN J, CHANG D, LIU J. Pathophysiological Characteristics of Phlegm-stasis Cementation Syndrome in Coronary Heart Disease:a Review and Update.World Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2015;1(4):38-41.
[29] TARASIUK O, MICELI M, DI DOMIZIO A, et al. AMPK and Diseases: State of the Art Regulation by AMPK-Targeting Molecules. Biology (Basel). 2022;11(7):1041.
[30] DAY EA, TOWNSEND LK, REHAL S, et al. Macrophage AMPK β1 activation by PF-06409577 reduces the inflammatory response, cholesterol synthesis, and atherosclerosis in mice. iScience. 2023;26(11):108269.
[31] GU T, ZHANG Z, LIU J, et al. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Modulating CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17):13516.
[32] CAI Y, WEN J, MA S, et al. Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction Attenuates Atherosclerosis and Increases Plaque Stability in High-Fat Diet-Induced ApoE-/- Mice by Inhibiting M1 Macrophage Polarization and Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization. Front Physiol. 2021;12:666449.
[33] 盛蒙,许滔,于红红,等.黄连解毒汤含药血清激活PPARγ诱导RAW264.7源性泡沫细胞向M2表型极化[J].中国免疫学杂志,2020, 36(3):277-281,288.
[34] 罗舒文,何金涛,王腊,等.基于PPARγ/NF-κB通路探讨黄连解毒汤干预M1/M2极化延缓AS的作用机制[J].时珍国医国药,2022, 33(9):2065-2069.
[35] 黄宏.养心舒脉颗粒调控TLR9/MyD88/NF-κB通路介导巨噬细胞极化改善动脉粥样硬化的机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2022.
[36] 孙颖,刘玲,施晓艳,等.丹皮酚通过下调miR-155/JAK1-STAT1通过抑制巨噬细胞M1极化[J].中国中药杂志,2020,45(9):2158-2164.
[37] 赵兴艳,汤正珍,岳春,等.橙皮苷调控Jagged1/Notch1通路对巨噬细胞极化及细支气管炎小鼠肺损伤的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报,2022,44(5):777-784.
[38] 何信用,张哲,贾连群,等.黄芪甲苷调控MAP3K8介导的细胞焦亡及巨噬细胞极化交互作用防治动脉粥样硬化的机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(5):2311-2316.
[39] 李二稳,崔正浩,高改,等.泽泻汤基于PI3K/AKT通路调节巨噬细胞M1/M2极化平衡机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2024,40(8): 1684-1691.
[40] ZHANG H, WANG SQ, HANG L, et al. GRP78 facilitates M2 macrophage polarization and tumour progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(23): 7709-7732.
[41] SHI W, HUANG Y, YANG Z, et al. Reduction of TMAO level enhances the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaque through promoting macrophage M2 polarization and efferocytosis. Biosci Rep. 2021;41(6): BSR20204250.
[42] WANG D, WANG F, KONG X, et al. The role of metabolic reprogramming in cancer metastasis and potential mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine intervention. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113376.
[43] JIANG YX, CHEN Y, YANG Y, et al. Screening Five Qi-Tonifying Herbs on M2 Phenotype Macrophages. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:9549315.
[44] 侯亚琴,李明,岳利多,等.黄精对白细胞介素-4诱导M2巨噬细胞能量代谢和极化的作用与机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(8): 4400-4404.
[45] LI C, CHI C, LI W, et al. An integrated approach for identifying the efficacy and potential mechanisms of TCM against atherosclerosis-Wu-Zhu-Yu decoction as a case study. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;296:115436.
[46] 李树颖,李科,秦雪梅,等.基于LC-MS代谢组学技术的注射用黄芪多糖活性成分调控巨噬细胞代谢研究[J].中草药,2020,51(6): 1575-1585.
[47] LI MY, WU YZ, QIU JG, et al. Huangqin Decoction ameliorates ulcerative colitis by regulating fatty acid metabolism to mediate macrophage polarization via activating FFAR4-AMPK-PPARα pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;311:116430.
[48] 王红芹,徐凤芹,周庆兵,等.基于RNA-Seq技术探讨洋参芎芍方改善RAW 264.7巨噬细胞代谢及炎症反应的机制[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2023,21(14):2568-2575.
[49] 李雪丽,刘钊.雷公藤甲素通过调控AMPK/mTOR通路抑制脂肪细胞和巨噬细胞炎症机制研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022, 24(12):24-29+237.
[50] 武强,薛才华,王梦杰,等.基于AMPK-mTOR信号通路探讨黑果枸杞花青素对小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7自噬的影响[J].中国兽医学报,2021,41(11):2176-2181.
[51] YI CO, JEON BT, SHIN HJ, et al. Resveratrol activates AMPK and suppresses LPS-induced NF-κB-dependent COX-2 activation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Anat Cell Biol. 2011;44(3):194-203.
[52] LI Y, FENG L, LI G, et al. Resveratrol prevents ISO-induced myocardial remodeling associated with regulating polarization of macrophages through VEGF-B/AMPK/NF-kB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020; 84:106508.
[53] KIM N, LERTNIMITPHUN P, JIANG Y, et al. Andrographolide inhibits inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated macrophages and murine acute colitis through activating AMPK. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;170: 113646.
[54] CHENG JW, YU Y, ZONG SY, et al. Berberine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by restoring macrophage polarization via AMPK/mTORC1 pathway switching glycolytic reprogramming. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;124(Pt B):111024.
[55] ZHANG Y, ZENG M, ZHANG X, et al. Tiaogan daozhuo formula attenuates atherosclerosis via activating AMPK -PPARγ-LXRα pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;324:117814.
[56] ZHANG Z, ZHENG Y, CHEN N, et al. San Huang Xiao Yan recipe modulates the HMGB1-mediated abnormal inflammatory microenvironment and ameliorates diabetic foot by activating the AMPK/Nrf2 signalling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2023;118:154931.
[57] CHEN S, TAO L, ZHU F, et al. BushenHuoxue decoction suppresses M1 macrophage polarization and prevents LPS induced inflammatory bone loss by activating AMPK pathway. Heliyon. 2023;9(5):e15583.
[58] 石莹莹,沙纪越,李志满,等.基于AMPK信号通路探讨人参皂苷对脂质代谢调控的研究进展[J/OL].特产研究,1-7[2024-07-02].https://doi.org/10.16720/j.cnki.tcyj.2023.233.
[59] ZHANG X, QIN Y, RUAN W, et al. Targeting inflammation-associated AMPK//Mfn-2/MAPKs signaling pathways by baicalein exerts anti-atherosclerotic action. Phytother Res. 2021;35(8):4442-4455.
[60] ZHOU J, YU Y, YANG X, et al. Berberine attenuates arthritis in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats associated with regulating polarization of macrophages through AMPK/NF-кB pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019; 852:179-188.
[61] 刘瞩,程明慧,张劝劝,等.芝麻酚通过AMPK信号通路调控巨噬细胞极化减轻脂肪组织炎症[J].中国药理学通报,2023,39(11): 2082-2088.
[62] 曹丽娟,于玲,刘莉.宁心涤痰汤通过AMPK/NF-κB通路抑制巨噬细胞分化改善血管再狭窄的机制研究[J].中国中医急症,2023, 32(4):592-596, 623.
|