中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3915-3924.doi: 10.12307/2025.675
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与阿尔茨海默病的关系
张松江,李龙洋,周春光
- 河南中医药大学医学院,河南省郑州市 450046
-
收稿日期:2024-07-17接受日期:2024-09-05出版日期:2025-06-28发布日期:2024-11-29 -
作者简介:张松江,女,1966年生,河南省郑州市人,汉族,教授,生理学博士,硕士生导师,主要从事老年神经退行性疾病方面的研究。 -
基金资助:河南省重点科技攻关项目(152102310100),项目负责人:张松江
Relationship between alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and Alzheimer’s disease
Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang
- Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-17Accepted:2024-09-05Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-29 -
About author:Zhang Songjiang, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Provincial Key Science and Technology Research Project, No. 152102310100 (to ZSJ)
摘要:
文题释义:
α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体:是由5个α7亚基构成的乙酰胆碱门控离子通道,既是乙酰胆碱受体又是离子通道,广泛分布于神经和肌肉。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在脑内主要存在于海马体和前额叶皮质神经元和胶质细胞膜,对认知和学习记忆功能有重要作用。
α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的正变构调节剂:主要是指人工合成的一些靶向α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体变构位点的化合物,通过对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的变构增加内源性配体乙酰胆碱与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的亲和力或效力。
背景:α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在大脑皮质和海马高度表达,并在阿尔茨海默病的病理发展过程中起重要调控作用,是阿尔茨海默病治疗的潜在靶点。
目的:总结α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体和阿尔茨海默病的密切关系和相互作用机制。
方法:检索中国知网、PubMed数据库中相关文献,中文检索词为“α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,阿尔茨海默病,β-淀粉样蛋白,激动剂,正变构调节剂,拮抗剂”;英文检索词为“alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor,Alzheimer’s disease,beta amyloid protein,agonist,positive allosteric modulator,antagonist”,文献检索时限为各数据库建库至2024年7月,依据入选标准对检索结果进行录用或排除,最终纳入符合标准的83篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体通过与β-淀粉样蛋白的相互作用减轻β-淀粉样蛋白的神经毒性,如促进阿尔茨海默病的突触可塑性和胆碱能突触的快速传递、减轻β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的神经中枢炎症反应、抵抗神经细胞凋亡,从而对阿尔茨海默病患者的脑具有保护作用等。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体作为阿尔茨海默病治疗靶标具有很大的潜能,但是又存在一系列问题有待解决,比如α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的脱敏性、适度活性稳定性及基因多态性等问题。筛选高特异、安全性和以α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体为核心的多靶点结合作用的药物,将成为未来阿尔茨海默病治疗研究的一个方向。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9752-9829(张松江)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
张松江, 李龙洋, 周春光. α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与阿尔茨海默病的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(18): 3915-3924.
Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang. Relationship between alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3915-3924.
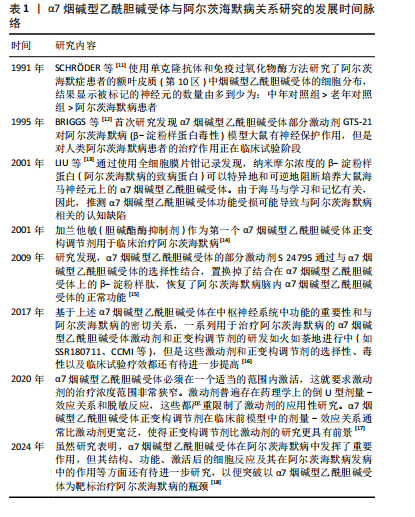
2.2 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体 烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体属于五聚体的配体门控离子通道超家族,分为神经受体和肌肉受体。从哺乳动物大脑中克隆了编码不同神经元烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体亚基的基因,如CHRNA2、CHRNA3、CHRNA4、CHRNA5、CHRNA6、CHRNA7、CHRNA8、CHRNA9、CHRNA10、CHRNB2、CHRNB3、CHRNB4、CHRND、CHRNE和CHRNG。肌肉亚型的基因包括CHRNA1和CHRNB1[19]。烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与乙酰胆碱结合后,通过离子通道的构象改变协助钠、钾、钙等离子在细胞膜内外扩散,改变突触后膜的膜电位,从而影响突触后神经元或效应细胞的兴奋性。目前已知的12个神经元烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体亚单位(α2-α10和β2-β4),其中9个在海马中表达(α2-α7和β2-β4),形成异质或同五聚体烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体[20]。哺乳动物大脑中烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的2种主要亚型是α7和α4β2,它们也是最常见的神经系统疾病亚型,包括阿尔茨海默病[21]。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体作为半胱氨酸环受体超家族的同五聚体阳离子通道,由15号染色体上的CHRNA7基因编码,广泛表达于中枢神经系统,包括神经元、小胶质细胞、星形胶质细胞和内皮细胞[22],尤其是海马体和前额叶皮质中[23]。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体基因长度为75 000 bp,位于15q14染色体,cDNA为1 509 bp,外显子为10个,内含子为9个。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体配体的结合位点存在于第4,6和7个外显子上,每个亚基中有502个氨基酸,其中有M1、M2、M3和M4跨膜结构域。在M3和M4结构域之间有100-200个氨基酸,阳离子转运是通过多肽M2结构域到N端,负责Ca2+的扩散[18](图3)。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体本身是离子型受体,可以存在于突触前膜和突触后膜。存在于突触前膜的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体被激活后可以调节乙酰胆碱的释放,存在于突触后膜上的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体被激活后离子通道开放,允许Na+和Ca2+内流,引起突触后神经元去极化,兴奋性升高。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体可快速活化脱敏,与阿尔茨海默病、癫痫、精神分裂症、帕金森病、炎症等病症密切相关[24]。
2.3 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体和β-淀粉样蛋白的相互作用影响阿尔茨海默病的发生和发展
2.3.1 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体和β-淀粉样蛋白的相互作用 β-淀粉样蛋白是阿尔茨海默病最为重要的特异性致病蛋白,和烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体有很高的亲和力,对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体有激动样作用[25]。CECON等[26]通过特异性定量FRET法,验证了低浓度β-淀粉样蛋白与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的正构结合位点特异性和高亲和力结合,其中以α7β2受体亚型与β-淀粉样蛋白亲和力最高,α7同五聚体次之。β-淀粉样蛋白对烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的激动作用对神经元有保护和损伤双刃作用,这种双刃作用与β-淀粉样蛋白的浓度、溶解性以及不同的β-淀粉样蛋白亚单位片段有关[27],具体的作用机制可能与结合位点、结合强度、结合关键残基位和持续作用后的脱敏有关[28],最终影响离子通道的开放程度。一般生理浓度的β-淀粉样蛋白有神经保护作用,而高浓度的寡聚体β-淀粉样蛋白有神经毒性[25]。
β-淀粉样蛋白对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体有影响的同时,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体对β-淀粉样蛋白也有反作用。研究显示,激活α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体可以在体内外减弱β-淀粉样蛋白的毒性作用,减少β-淀粉样蛋白在海马中的聚积。通过部分逆转突触相关蛋白的表达水平激活Ca2+信号通路,维持突触形态,改善APP/PS1双转基因小鼠的认知能力[29]。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体敲除可导致12月龄小鼠海马突触可塑性和记忆力受损,伴有淀粉样前体蛋白表达和β-淀粉样蛋白表达的增加,同时伴随着众多阿尔茨海默病经典特征,如在Ser 19、Ser 396、Thr 205残基上tau蛋白的过度磷酸化,在Ser 9上GSK-3β的减少,成对螺旋丝和神经纤维缠结的存在,神经元丢失和活化星形胶质细胞的增加等[30]。出现这样结果的原因可能是α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体缺失阻断了β-淀粉样蛋白的正常生理功能,从而导致β-淀粉样蛋白水平的代偿性增加,进而引发阿尔茨海默样病理过程。研究结果表明,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体功能障碍可能早于β-淀粉样蛋白和tau病理,这为解释抗β-淀粉样蛋白治疗阿尔茨海默病失败提供了一个不同的视角,并找到了新的治疗方法,即恢复α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体介导的β-淀粉样蛋白对突触生理功能的维持[30]。
2.3.2 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与阿尔茨海默病的突触可塑性的关系 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与突触可塑性密切相关,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体促进胆碱能突触的快速传递,在突触可塑性和学习记忆中发挥重要作用[8]。生理浓度下的β-淀粉样蛋白有促进胆碱能信号传递的功能。β-淀粉样蛋白结合并激活突触前膜α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,导致钙调神经磷酸酶激活、突触蛋白1去磷酸化,从而导致突触小泡功能池的重组,通过增加突触前释放神经递质来增强突触可塑性和记忆形成[7]。但是,过量的β-淀粉样蛋白是有神经毒性的,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体可抑制β-淀粉样蛋白的这种神经毒性。体外实验表明,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体可以减弱过量β-淀粉样蛋白对突触蛋白表达的抑制作用,上调突触蛋白、突触前膜相关蛋白和突触后致密物质95的表达,抑制神经细胞凋亡[8]。激活α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在减弱β-淀粉样蛋白毒性作用的同时,通过激活CaM-CaMKII-CREB信号通路部分逆转突触相关蛋白的表达水平,维持突触形态、改善APP/PS1转基因阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的认知能力[29]。
2.3.3 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与阿尔茨海默病的中枢炎症的关系 神经炎症是阿尔茨海默病和非阿尔茨海默病痴呆症的重要危险因素[31-33]。神经炎症的发生是通过小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的功能体现的。反应性小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞可以迁移到β-淀粉样蛋白斑块周围,清除有毒的β-淀粉样蛋白沉积物,从而发挥神经保护作用;同时,小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞表面的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体作为胆碱能抗炎通路的一个重要环节,参与阿尔茨海默病炎症调节[34-35]。
小胶质细胞表面的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体被激活后,通过减少肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的释放起到神经元保护作用,在改善认知方面发挥作用[36]。越来越多的证据表明,刺激胆碱能抗炎通路可以调节小胶质细胞活化,减少脑实质中促炎细胞因子的释放[37]。研究表明,乙酰胆碱或α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的其他激动剂可以通过激活α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,调节核因子κB和CREB信号通路,从而抑制脂多糖诱导的促炎细胞因子的产生以及小胶质细胞的吞噬作用[38]。α-GPC(α-choline alphoscerate)作为一种胆碱能神经传递增强剂,可以降低β-淀粉样蛋白介导的神经毒性。同时,α-GPC通过直接激活α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,进而对β-淀粉样蛋白反应的小胶质细胞表型产生影响,拮抗β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的炎症反应,说明以α-GPC为代表的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂可以作为一个潜在的治疗药物,来改善以阿尔茨海默病为代表的炎症性神经退行性疾病[39]。中国传统医学针灸在激动α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体方面也有深入探索,王志刚等[40]研究显示,电针预处理改善了老年大鼠术后长期认知功能障碍和海马炎症,作用机制可能与激活小胶质细胞表面α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体介导的胆碱能抗炎通路有关。
反应性星形胶质细胞的增生、星形胶质细胞在疾病期间的形态、分子和功能转化,与β-淀粉样蛋白病理和阿尔茨海默病的进展有密切关系。星形胶质细胞表面α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体通过影响Ca2+通道和细胞内Ca2+水平,进而影响β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的中枢炎症发生[41]。在β-淀粉样蛋白病理中,Ly6/uPAR蛋白的表达导致小脑胆碱能系统失调,特别是α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体功能失调,导致神经炎症增强和小脑星形胶质细胞功能变性[42]。阿尔茨海默病患者大脑中的β-淀粉样蛋白病理导致炎症反应的发生,从而上调星形胶质细胞表面α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体。由于在疾病初始阶段对脑病理的快速反应,星形胶质细胞表面α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的表达水平可能成为一个很有前途的候选生物标志物[43]。
2.3.4 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与阿尔茨海默病其他病理生理的关系 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与阿尔茨海默病的其他一些病理生理过程也有密切关系,如神经元凋亡、自噬和生长等。首先,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的激活有抗凋亡作用,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体被激活在对阳离子具有渗透性的同时,通过调节caspases和Bcl-2家族蛋白促进细胞抗凋亡信号的反应。在阿尔茨海默病模型中,显示α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激活可通过磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶调节不同的内在凋亡通路,促进Bcl-2家族的抗凋亡分子Bcl-2和Bcl-xl的表达,降低caspases等促凋亡分子的表达,从而减轻β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的神经毒性,使细胞存活[8,44]。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激活还参与神经元的自噬过程。OMI/HTRA2是一种线粒体丝氨酸蛋白酶,参与多种细胞过程,包括自噬、伴侣活性和凋亡。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体基因的表达与OMI/HTRA2基因在大脑中的表达有很强的相关性,与阿尔茨海默病病理中涉及的一些关键蛋白之间的关联模式一致[45]。免疫沉淀数据显示,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体可与自噬体蛋白LC3结合,作为LC3的载体将β-淀粉样蛋白封存于自噬小体,起到神经保护作用[24]。另外,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激活还可以促进神经元的生长。原肌凝蛋白受体激酶A是神经生长因子受体,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激活促进原肌凝蛋白受体激酶A的正常表达,从而促进神经元的生长 [46]。很多研究证实,尼古丁对神经元有促生长作用,这种作用是通过激活α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体实现的[47-48]。所以可以推测,多种原因引起的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体活性下降,可能是导致阿尔茨海默病患者中枢神经功能障碍的一个重要因素。
2.4 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激活可以作为阿尔茨海默病治疗的靶点
2.4.1 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体完全激动剂、部分激动剂和沉默激动剂 从上述α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在阿尔茨海默病病理中的作用可以看出,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体具备作为阿尔茨海默病治疗靶标的潜能。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体可被多种顺位激动剂激活。尼古丁作为烟碱受体的经典完全激动剂,可通过α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体/细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2信号通路抑制H2O2诱导的小鼠海马神经元细胞系HT-22氧化损伤[49]。尼古丁的衍生物可替宁和6-羟基-l-尼古丁可与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体和α4β2烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体结合,在β-淀粉样蛋白25-35诱导的阿尔茨海默病大鼠模型中表现出促认知、抗氧化和抗乙酰胆碱酯酶活性的作用[50]。完全激动剂尼古丁和PNU282987等都是α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体主要的科研工具药[29,51-52]。
目前关于α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体完全激动剂的研究是比较成熟的,但完全激动剂具有成瘾性大、不良反应大等缺点。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的部分激动剂逐渐引起人们的重视[53-54],虽然部分激动剂没有完全激动剂那样强烈的突触效应,但是和完全激动剂相比兼有成瘾性小、毒副作用小、剂量依赖性小和不容易脱敏等优点,因此,对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体部分激动剂进行分子模拟的研究具有重要意义。尽管有这种潜力,由于各种原因目前在临床试验中尚未能找到有效治疗阿尔茨海默病的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体部分激动剂。
还有一种称为α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的沉默激动剂,这种激动剂能与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体敏感结合,不产生或只能产生很少通道离子流,但是可以通过调节细胞内信号通路来影响α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,类似于代谢型受体的作用,还可以稳定与脱敏相关的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体非导电构象[55-56]。沉默激动剂的作用机制可能是:其分子质量较大掩盖了乙酰胆碱的结合位点,阻断了乙酰胆碱与受体的结合,从而阻断了离子通道的开放,类似于受体拮抗剂,但是不同于拮抗剂的是,沉默激动剂激活了细胞内的信号转导通路 [55]。很多研究表明,沉默激动剂是胆碱能抗炎系统的有效激活剂,通过Janus激酶2/信号转导和转录激活因子3途径发出信号,通过抑制核因子κB活化降低促炎细胞因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6)的水平、增加抗炎细胞因子(例如白细胞介素10)的水平[57]。
2.4.2 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的正变构调节剂是阿尔茨海默病治疗研究的很有潜能的一个方向 由于α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在许多神经元和非神经元细胞群中广泛表达,因此,在临床中应用α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂很难在增强α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体功能的同时避免非靶向效应。另外,这些激动剂在临床前试验中还出现了α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体脱敏和倒U型剂量效应关系。所谓脱敏,即α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体对内源性配体或激动剂呈现耐受性,而且这种耐受是瞬间发生的。倒U型剂量效应关系是指突触后效应随着激动剂剂量的增大而增大;然后随着剂量的增大,突触后效应不再增大,维持在一定的水平不变;剂量继续增大到一定程度,突触后效应随着剂量的增大反而下降。所有这些反应限制了激动剂的临床应用[58]。
为了避免α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂上述的一些弊端,目前人工合成的一些靶向α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体变构位点的化合物,通过对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的变构增加内源性激动剂乙酰胆碱与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的亲和力或效力,具有这种特性的化合物被称为正变构调节剂。正变构调节剂与变构位点结合,分为Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型,Ⅰ型正变构调节剂增加了离子通透性,而Ⅱ型正变构调节剂增强了离子通透性的同时延长了离子通道打开时间[59]。与受体的顺位激动剂相比,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体正变构调节剂最明显的优点是降低了α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的脱敏效应[16,58],比如:只有乙酰胆碱存在时,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体5个亚基呈逆时针方向扭转,通道打开且快速转变为脱敏态;而在一种正变构调节剂——伊维菌素存在时,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体5个亚基呈顺时针方向扭转,通道呈关闭状态[60],说明伊维菌素符合正变构调节剂的特点,即对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体无直接作用。但是在伊维菌素存在的情况下给予乙酰胆碱,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体5个亚基呈顺时针方向扭转的同时通道开放增多,即表现为受体活性短暂性增强。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体亚基的这些扭转倾斜运动,可能代表了受体从静息态到通道打开的转变以及从敏感态到脱敏态的转变[60]。
2001年,加兰他敏是第一个用于临床治疗阿尔茨海默病的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体正变构调节剂[61]。为寻找效果更好、毒副作用更小的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体正变构调节剂,目前多种α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的正变构调节剂正在实验室研发中,并取得了预期成果[62-63]。LI等[63]研究显示,作为Ⅰ型α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体正变构剂,JWX-A0108主要增加激动剂诱发的峰值电流,通过改变IκBα和核因子κB p65的表达和磷酸化水平,减少大脑中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6等炎症递质,减轻神经炎症,从而改善APP/PS1小鼠的学习记忆功能。最近的一项研究表明,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂(A582941)和正变构调节剂[Ⅰ型(CCMI)和Ⅱ型(PNU120596)]在单次和重复给药后都表现出促认知作用,这种效应可能是由于细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2和Arc基因水平升高的部分参与[9]。
中国孙崎教授团队在国家自然科学基金面上项目和科技部重大新药创制项目的资助下,先后研发出一系列α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体正变构调节剂,在《Journal of Medicinal Chemistry》等国际杂志上先后发表相关论文[62,64]。
由于激动剂与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体结合的多个正构位点在半胱氨酸环配体门控离子通道中高度保守,设计对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体具有高选择性的激动剂具有挑战性,因此,筛选能与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体上保守程度较低位点结合的变构调节剂,是α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体正变构调节剂研发的一个方向。对各种构象状态下α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体高分辨率结构和门控机制的解析[65],有助于发现新的疗效更加温和、更加特异性的正变构调节剂。
2.4.3 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体拮抗剂 在模拟体内情况的电生理实验中,皮摩尔浓度的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体拮抗剂甲基牛扁亭碱显著增强了受体反应和与记忆过程有关海马谷氨酸的分泌,改善了大鼠的学习能力[66]。汪志刚等[67]体外研究显示,随着作用时间的延长(84 h),激动剂尼古丁对β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的PC12细胞保护作用逐渐消失,而甲基牛扁亭碱逐渐显现出细胞保护作用。汪志刚等[68]和ZHENG等[69]研究也显示,甲基牛扁亭碱可以减轻β-淀粉样蛋白所致的细胞毒性。作者研究团队发现,以α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体为代表的胆碱能抗炎系统对运动疲劳小鼠中枢有抗炎作用。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体表达水平和炎症反应高度关联。α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体完全激动剂PNU282987的应用可以加强炎症的消除,但是随着PNU282987应用次数的增多,其中枢抗炎作用逐渐减小,这种现象的出现可能与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的脱敏有关。令人费解的是,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体拮抗剂甲基牛扁亭碱对运动疲劳小鼠也有中枢抗炎作用,而且随着甲基牛扁亭碱应用次数的增多其中枢抗炎作用越来越强。结合他人的研究成果[66-69],分析认为α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体拮抗剂甲基牛扁亭碱对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的拮抗作用受应用剂量和应用次数的影响,甚至在一定应用时间和剂量情况下对受体有激动作用,这也显示出α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体功能的复杂性,具体的分子变构机制有待进一步研究。所以,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂也许并不适合长时间治疗阿尔茨海默病,而拮抗剂在一定的剂量和时间应用情况下可能会为治疗提供一个新的方向[68]。甲基牛扁亭碱具有良好的安全性,可能是阿尔茨海默病的一种有前景的治疗工具[69]。
2.4.4 以α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体为核心的多靶点药物的研发 以α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体为核心多靶点药物的研发,也是未来阿尔茨海默病治疗研究的一个方向。加兰他敏同时具有胆碱酯酶抑制剂和α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体阳性变构调节剂的功能特点[70],可以和小胶质细胞的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体结合,通过变构增强α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的活性,增加小胶质细胞吞噬β-淀粉样蛋白作用,但体外耗竭胆碱可消除加兰他敏的这种作用[24]。加兰他敏还可以通过激活JNK信号通路来抑制β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的细胞凋亡、增强α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的表达、抑制脱敏和蛋白激酶B信号通路,进一步增加自噬[24]。正是因为加兰他敏对α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的多靶点作用,才使得加兰他敏脱颖而出,作为临床治疗阿尔茨海默病的一线药物。3-[(2,4-二甲氧基)亚苄基]-氨基水杨酸盐作为α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体选择性激动剂的同时,抑制了人类神经母细胞瘤细胞和阿尔茨海默病转基因小鼠大脑中的γ-分泌酶活性[71],减轻阿尔茨海默病转基因模型小鼠脑中β-淀粉样蛋白负荷,从而缓解记忆功能障碍。变构调节剂PNU120596除起到激动和调节α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体发挥神经保护作用外,还可阻止和逆转α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与β-淀粉样蛋白的结合,拮抗β-淀粉样蛋白的神经毒性作用,也具有双靶点的药理作用[26]。另外需要注意的是,正变构调节剂只能消除少数α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的脱敏状态,所以至少还存在其他对正变构调节剂不敏感的脱敏形式有待进一步的研究[55],从而实现以α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体为核心的多靶点药物研发。

| [1] Atanasova M, Dimitrov I, Ivanov S, et al. Virtual screening and hit selection of natural compounds as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Molecules. 2022;27(10):3139. [2] Duan Y, Lv J, Zhang Z, et al. Exogenous Aβ1-42 monomers improve synaptic and cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Neuropharmacology. 2022;209:109002. [3] Wu M, Liu CZ, Barrall EA, et al. Unbalanced regulation of alpha7 nAChRs by Ly6h and NACHO contributes to neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci. 2021;41(41):8461-8474. [4] Cao K, Xiang J, Dong YT, et al. Activation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by its selective agonist improved learning and memory of amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 (APP/PS1)mice via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e933978. [5] Lin MW, Chen YH, Yang HB, et al. Galantamine inhibits Abeta(1-42)-induced neurotoxicity by enhancing alpha7nAChR expression as a cargo carrier for LC3 binding and Abeta(1-42) engulfment during autophagic degradation. Neurotherapeutics. 2020;17(2):676-689. [6] Han C. Corrigendum to “New mechanism of neuroinflflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: The activation of NLRP3 inflflammasome mediated by gut microbiota” [Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 100 (2020) 109884]. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2022;114:110482. [7] Pastor V, Katche C. Dual role of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the retrosplenial cortex for aversive memory acquisition and retrieval. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024;18:1359729. [8] Anni D, Weiss EM, Guhathakurta D, et al. Aβ1-16 controls synaptic vesicle pools at excitatory synapses via cholinergic modulation of synapsin phosphorylation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(11):4973-4992. [9] Ren JM, Zhang SL, Wang XL, et al. Expression levels of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and their effect on synaptic proteins in SH-SY5Y cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(3):2063-2075. [10] Potasiewicz A, Faron-Gorecka A, Popik P, et al. Repeated treatment with alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands enhances cognitive processes and stimulates Erk1/2 and Arc genes in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2021;409:113338. [11] SCHRÖDER H, GIACOBINI E, STRUBLE RG, et al. Nicotinic cholinoceptive neurons of the frontal cortex are reduced in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1991;12(3):259-262. [12] Briggs CA, McKenna DG, Piattoni-Kaplan M. Human alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor responses to novel ligands. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34(6):583-590. [13] Liu Q, Kawai H, Berg DK. beta -Amyloid peptide blocks the response of alpha 7-containing nicotinic receptors on hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(8):4734-4739. [14] Olin J, Schneider L. Galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD001747. [15] Wang HY, Stucky A, Liu J, et al. Dissociating beta-amyloid from alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by a novel therapeutic agent, S 24795, normalizes alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine and NMDA receptor function in Alzheimer’s disease brain. J Neurosci. 2009;29(35):10961-10973. [16] Yang T, Xiao T, Sun Q, et al. The current agonists and positive allosteric modulators of α7 nAChR for CNS indications in clinical trials. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2017;7(6):611-622. [17] Wang X, Bell IM, Uslaner JM. Activators of α7 nAChR as potential therapeutics for cognitive impairment. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2020;45:209-245. [18] Singh S, Agrawal N, Goyal A. Role of alpha-7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(3):384-394. [19] Papke RL, Horenstein NA. Therapeutic targeting of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(3):1118-1149. [20] Zoli M, Pistillo F, Gotti C. Diversity of native nicotinic receptor subtypes in mammalian brain. Neuropharmacology. 2015;96(Pt B): 302-311. [21] TERRY AV JR, JONES K, BERTRAND D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in neurological and psychiatric diseases. Pharmacol Res. 2023;191: 106764. [22] Xu ZQ, Zhang WJ, Su DF, et al. Cellular responses and functions of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation in the brain: A narrative review. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(6):509. [23] Gass N, Weber-Fahr W, Sartorius A, et al. An acetylcholine alpha7 positive allosteric modulator rescues a schizophrenia-associated brain endophenotype in the 15q13.3 microdeletion, encompassing CHRNA7. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol.2016;26(7):1150-1160. [24] Shan H, Wang N, Gao X, et al. Fluorescent alpha-conotoxin [Q1G, deltaR14]LvIB identifies the distribution of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in the rat brain. Mar Drugs. 2024;22(5):200. [25] Roberts CF, Cao Y, Im W, et al. Neuroprotective amyloid beta N-terminal peptides differentially alter human alpha7- and alpha7beta2-nicotinic acetylcholine (nACh) receptor single-channel properties. Br J Pharmacol. 2024;181(17):3172-3191. [26] Cecon E, Dam J, Luka M, et al. Quantitative assessment of oligomeric amyloid β peptide binding to α7 nicotinic receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176(18):3475-3488. [27] Gao X, Guan Y, Wang C, et al. Specific interaction from different Aβ42 peptide fragments to α7nAChR-A study of molecular dynamics simulation. J Mol Model. 2024;30(7):233. [28] Burns LH, Pei Z, Wang HY. Targeting alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and their protein interactions in Alzheimer’s disease drug development. Drug Dev Res. 2023;84(6):1085-1095. [29] Wang XL, Deng YX, Gao YM, et al. Activation of alpha7 nAChR by PNU-282987 improves synaptic and cognitive functions through restoring the expression of synaptic-associated proteins and the CaM-CaMKII-CREB signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(1):543-570. [30] Tropea MR, Li Puma DD, Melone M, et al. Genetic deletion of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors induces an age-dependent Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology. Prog Neurobiol. 2021;206:102154. [31] Mekli K, Lophatananon A, Maharani A, et al. Association between an inflammatory biomarker scoreand future dementia diagnosis in the population-based UK Biobank cohort of 500,000 people. PLoS One. 2023;18(7):e0288045. [32] Wu YG, Song LJ, Yin LJ, et al. The effects and potential of microglial polarization and crosstalk with other cells of the central nervous system in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):947-954. [33] Zhang H, Cao S, Xu Y, et al. Landscape of immune infiltration in entorhinal cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:941656. [34] MizrACHi T, Vaknin-Dembinsky A, Brenner T, et al. Neuroinflammation modulation via α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and its chaperone, RIC-3. Molecules. 2021;26(20):6139. [35] Reale M, Costantini E. Cholinergic modulation of the immune system in neuroinflammatory diseases. Diseases. 2021;9(2):29. [36] Benfante R, Di Lascio S, Cardani S, et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors targeting the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a new therapeutic perspective in aging-related disorders. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33(4):823-834. [37] Piovesana R, Salazar Intriago MS, Dini L, et al. Cholinergic modulation of neuroinflammation: Focus on α7 NicotinicReceptor. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4912. [38] Xia Y, Wu Q, Mak S, et al. Regulation of acetylcholinesterase during the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in microglial cells. FASEB J. 2022;36(3):e22189. [39] Cantone AF, Burgaletto C, Di Benedetto G, et al. Taming microglia in Alzheimer’s disease: Exploring potential implications of choline alphoscerate via alpha7 nAChR modulation. Cells. 2024; 13(4):309. [40] 王志刚,苑进革,徐朋,等.电针预处理对老龄大鼠长期术后认知功能障碍影响及相关机制[J].科学技术与工程,2023,23(28):12004-12011. [41] SANJAY, SOOD R, JAISWAL V, et al. Nobiletin regulates intracellular Ca2+ levels via IP3R and ameliorates neuroinflammation in Aβ42-induced astrocytes. Redox Biol. 2024;73:103197. [42] BYCHKOV ML, ISAEV AB, ANDREEV-ANDRIEVSKIY AA, et al. Aβ1-42 Accumulation Accompanies Changed Expression of Ly6/uPAR Proteins, Dysregulation of the Cholinergic System, and Degeneration of Astrocytes in the Cerebellum of Mouse Model of Early Alzheimer Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19):14852. [43] Fontana IC, Kumar A, Nordberg A. The role of astrocytic alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023;19(5):278-288. [44] Mugayar AA, da Silva Guimarães G, de Oliveira PHT, et al. Apoptosis in the neuroprotective effect of alpha7 nicotinic receptor in neurodegenerative models. J Neurosci Res. 2023;101(12):1795-1802. [45] Darreh-Shori T, Rezaeianyazdi S, Lana E, et al.Increased active OMI/HTRA2 serine protease displays a positive correlation with cholinergic alterations in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(7):4601-4619. [46] Kumro J, Tripathi A, Terry AV Jr, et al. alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are necessary for basal forebrain activation to increase expression of the nerve growth factor receptor TrkA. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024:2024.03.01.582932. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.01.582932. [47] Pucci S, Fasoli F, Moretti M, et al. Choline and nicotine increase glioblastoma cell proliferation by binding and activating alpha7- and alpha9- containing nicotinic receptors. Pharmacol Res. 2021;163:105336. [48] Kawasaki H, Hino H, Takayama F, et al. Regulatory effects of nicotine on neurite outgrowth in rat superior cervical ganglia cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022;148(1):103-107. [49] Dong Y, Bi W, Zheng K, et al. Nicotine prevents oxidative stress-induced hippocampal neuronal injury through α7-nAChR /Erk1/2 signaling pathway. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020;13:557647. [50] Boiangiu RS, Mihasan M, Gorgan DL, et al. Cotinine and 6-Hydroxy-L-Nicotine reverses memory deficits and reduces oxidative stress in Aβ25-35-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(8):768. [51] Ren Z, Dong Z, Xie P, et al. PNU282987 inhibits amyloidβ aggregation by upregulating astrocytic endogenous αBcrystallin and HSP70 via regulation of theα7 AChR, PI3K/Akt/HSF1 signaling axis. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(1):201-208. [52] Chang KW, Zong HF, Wang M, et al. PNU282987 alleviates Aβ-induced anxiety and depressive-like behaviors through upregulation of α7 nAChR by ERK-serotonin receptors pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2020;731:135118. [53] Magnussen JH, Ettrup A, Lehel S, et al. Characterizing the binding of TC-5619 and encenicline on the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor using PET imaging in the pig. Front Neuroimaging. 2024;3: 1358221. [54] Wallace TL, Callahan PM, Tehim A, et al. RG3487, a novel nicotinic α7 receptor partial agonist, improves cognition and sensorimotor gating in rodents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;336(1): 242-253. [55] Papke RL, QuADri M, Gulsevin A. Silent agonists for alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Res. 2023;190:106736.
[56] Li Q, Nemecz Á, Aymé G, et,al. Generation of nanobodies acting as silent and positive allosteric modulators of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023;80(6):164. [57] Zhang Q, Lu Y, Bian H, et al. Activation of the alpha7 nicotinic receptor promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced conversion of M1 microglia to M2. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(3):971-985. [58] Wang X, Daley C, Gakhar V, et al. Pharmacological characterization of the novel and selective alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-positive allosteric modulator BNC375. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020; 373(2):311-324. [59] TAKATA K, KIMURA H, YANAGISAWA D, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and microglia as therapeutic and imaging targets in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules. 2022;27(9):2780. [60] Yang Y, Arai T, Sasaki D, et al. Real-time tilting and twisting motions of ligand-bound states of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Eur Biophys J. 2024;53(1-2):15-25. [61] Maelicke A, Albuquerque EX. Allosteric modulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as a treatment strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;393(1-3):165-170. [62] WANG X, XIAO H, WANG J, et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Triazine Derivatives as Positive Allosteric Modulators of alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J Med Chem. 2021;64(16):12379-12396. [63] Li H, Gao J, Chang Y, et al. JWX-A0108, a positive allosteric modulator of alpha7 nAChR, attenuates cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice by suppressing NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;96:107726. [64] Yang C, Meng Y, Wang X, et al. Allosteric activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by novel 2-arylamino-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid amide derivatives for the improvement of cognitive deficits in mice. J Med Chem. 2024;67(8):6344-6364. [65] NOVIELLO CM, GHARPURE A, MUKHTASIMOVA N, et al. Structure and gating mechanism of the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Cell. 2021;184(8):2121-2134.e13. [66] van Goethem NP, Paes D, Puzzo D, et al. Antagonizing α7 nicotinic receptors with methyllycaconitine (MLA) potentiates receptor activity and memory acquisition. Cell Signal. 2019;62:109338. [67] 汪志刚,戚仁斌,李卫,等.α7 烟碱受体拮抗剂对 Aβ蛋白诱导损伤的PC12 细胞保护作用的研究[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2011, 37(9):540-544. [68] 汪志刚,戚仁斌,李卫,等.α7 烟碱样乙酰胆碱受体拮抗剂减轻淀粉样β蛋白诱导的 PC12 细胞损伤的机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(5):916-922. [69] Zheng X, Xie Z, Zhu Z, et al. Methyllycaconitine alleviates amyloid-β peptides-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111536. [70] Oddsson S, Kowal NM, Ahring PK, et al. Structure-based discovery of dual-target hits for acetylcholinesterase and the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: In silico studies and in vitro confirmation. Molecules. 2020;25(12):2872. [71] Takata K, Amamiya T, Mizoguchi H, et al. α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-specific agonist DMXBA(GTS-21) attenuates amyloid-βaccumulation through suppression of neuronalγ-secretase activity and promotion of microglial amyloid-β phagocytosis and ameliorates cognitive impairment in a mouse mode. Neurobiol Aging. 2018;62: 197-209. [72] Miller DR, Khoshbouei H, Garai S, et al. Allosterically potentiated α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Reduced calcium permeability and current-independent control of intracellular calcium. Mol Pharmacol. 2020;98(6):695-709. [73] LEE CH, HUNG SY. Physiologic functions and therapeuticapplications of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in brain disorders. Pharmaceutics. 2022;15(1):31. [74] 王紫涵,于津鹏,长孙东亭,等.α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体分子伴侣Tmem35a的克隆及其功能研究[J].药学学报,2024,59(7):1993-2001. [75] Puddifoot CA, Wu M, Sung RJ, et al. Ly6h regulates trafcking of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors andnicotine-induced potentiation of glutamatergic signaling. J Neurosci. 2015;35(8):3420-3430. [76] Moriwaki Y, Kubo N, Watanabe M, et al. Endogenous neurotoxin-like protein Ly6H inhibits alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor currents at the plasma membrane. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):11996. [77] Ranglani S, Hasan S, Komorowska J, et al. A novel peptide driving neurodegeneration appears exclusively linked to the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04079-7. [78] Graur A, Sinclair P, Schneeweis AK, et al. The human acetylcholinesterase C-terminal T30 peptide activatesneuronal growth through alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptorsand the mTOR pathway. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):11434 [79] Greenfield SA, Cole GM, Coen CW, et al. A novel process driving Alzheimer’s disease validated in a mouse model: therapeutic potential. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2022;8(1):e12274. [80] Leonard S, Benfante R. Unanswered questions in the regulation and function of the duplicated alpha7 nicotinic receptor gene CHRFAM7A. Pharmacol Res. 2023;192:106783. [81] Pattanaik B, Hammarlund M, Mjörnstedt F, et al. Polymorphisms in alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene, CHRNA7, and its partially duplicated gene, CHRFAM7A, associate with increased inflammatory response in human peripheral mononuclear cells. FASEB J. 2022;36(5):e22271. [82] Jiang Y, Yuan H, Huang L, et al. Global proteomic profiling of the uniquely human CHRFAM7A gene in transgenic mouse brain. Gene. 2019;714:143996. [83] Sumirtanurdin R, Thalib AY, Cantona K, et al. Effect of genetic polymorphisms on Alzheimer’s disease treatment outcomes: an update. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:631-642. |
| [1] | 谢刘刚, 崔书克, 郭楠楠, 李遨宇, 张菁瑞. 干细胞治疗阿尔茨海默病的研究热点与前沿[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [2] | 李 甜, 任俞桦, 高艳萍, 苏 强. 阿戈美拉汀缓解APP/PS1转基因小鼠焦虑及抑郁样行为的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1176-1182. |
| [3] | 韩孟君, 许 芳. 造血干细胞动员:不同方案的优缺点及预测模型与技术提升[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7863-7871. |
| [4] | 李 晨, 刘 晔, 倪新迪, 张宇昂. 多关节运动中小腿三头肌肌纤维和肌腱实时连续刚度仿真分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7529-7536. |
| [5] | 杨 博, 潘新芳, 常留辉, 倪 勇. 超声心动图参数与急性缺血性脑卒中发病3个月时残疾的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7544-7551. |
| [6] | 刘 璇, 丁雨晴, 夏若寒, 汪献旺, 胡淑娟. 运动防治胰岛素抵抗:Keap1/核因子E2相关因子2信号通路的作用与分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [7] | 巩月红, 王梦君, 任 航, 郑 辉, 孙佳佳, 刘军鹏, 张 飞, 杨建华, 胡君萍. 机器学习联合生物信息学筛选与自噬相关的肺纤维化关键基因及实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| [8] | 韩 杰, 潘成镇, 尚昱志, 张 驰. 激素性股骨头坏死免疫诊断标志物的鉴定与药物筛选[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7690-7700. |
| [9] | 方 源, 钱智勇, 何源哈达, 王海燕, 沙丽蓉, 李筱贺, 刘 婧, 贺雅超, 张 凯, 特木日巴根. 蒙药蓝刺头对血管内皮细胞增殖和血管生成能力的潜在作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528. |
| [10] | 鄢来军, 葛海雅, 汪正明, 杨宗睿, 牛立峰, 詹红生. 通督活血汤抑制巨噬细胞炎症延缓大鼠椎间盘退变的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(32): 6851-6857. |
| [11] | 尼格阿依·艾合麦提, 伊丽丹娜·地里夏提, 安 玮, 买买提吐逊·吐尔地. 大鼠颞下颌关节骨关节炎模型中线粒体肌酸激酶2表达及在炎症进展中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(32): 6877-6884. |
| [12] | 王子恒, 吴 霜. 脊髓损伤后氧化应激相关基因及分子机制:基于GEO数据库的数据分析及验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(32): 6893-6904. |
| [13] | 周汝霖, 胡远征, 王宗清, 周国平, 张保朝, 徐 茜, 白方会. 烟雾病生物标志物及中药靶点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(32): 6927-6938. |
| [14] | 赵雪梅, 王 睿, 奥·乌力吉, 包书茵, 江小华. 蒙药沙蓬粗寡糖对小鼠滑膜细胞炎症和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(32): 6939-6946. |
| [15] | 卫虎强, 吴合斌, 侯亚丽, 张翔泳, 王子轩, 王文璇, 白彩琴. 运动与蛋白质交互作用机制的进路整合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(32): 6947-6954. |
因此,该文从α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体对阿尔茨海默病病理生理的影响角度进行阐述,由此提出α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体作为阿尔茨海默病治疗靶标的研究现状、存在的问题以及该受体的基因调控问题和未来研究方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一、二作者在 2024年3月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2024年7月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网和 PubMed 数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,阿尔茨海默病,β-淀粉样蛋白,激动剂,正变构调节剂;拮抗剂”;英文检索词为“alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor,Alzheimer’s disease,beta amyloid protein,agonist,positive allosteric modulator,antagonist”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 中英文数据库检索策略,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 重点检索2019年以来,尤其是2021年以来被SCI和北大中文核心及CSCD收录的文章,共得到文献1 429篇,包括中国知网162篇、PubMed数据库1 267篇。依据纳入标准与排除标准,最终纳入83篇文献,其中英文文献79篇、中文文献4篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①正式发表的、年份较新且高质量的中英文研究原著或综述;②与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体相关的文献;③与阿尔茨海默病相关的文献;④与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂、正变构调节剂、拮抗剂和阿尔茨海默病相关的文献;⑤论文中论据、论点充分且可靠的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复或与研究主题无关的文献;②文献发表年份过于久远的文献;③Meta分析类文献;④无法获得全文的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 文献筛选与质量评估由所有作者共同讨论确认。英文文献借助 EndNote检索软件和依据中国科学院分区标准进行双重质量评估,中文文献手动逐一排查评估。中国科学院分区尽量选取1-3区的文献,尤其是1区和2区的文献。 EndNote检索软件的排序优先选择排名靠前、质量较高的文献。通过查阅相关数据库最初检索到1 429篇文献,阅读题目及摘要后保留187篇,通过阅读全文继续筛选符合文章主题的文献,根据纳入标准纳入主题明确、论证可靠、内容相关的文献,排除证据模糊、内容不清晰的文献,最终纳入83篇文献,包括中文文献4 篇及英文文献79篇。文献筛选流程见图2。
T14通过α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的钙信号在早期发育中起营养作用,然而,鉴于老年人神经元对钙离子通量的耐受性显著降低[78],这一过程在成人脑中被激活时可能会转变为兴奋毒性,成为神经退行性过程的基础,特别是阿尔茨海默病[79]。
α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激活通过钙离子内流引起神经营养作用和神经毒性作用的这种双刃效应,说明了适度α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体活性的重要性,这种α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的平衡理论在一定程度上解释了为什么临床和临床前分析的大多数α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂在低浓度下表现出“激动”,而在高浓度下会产生毒性作用和脱敏的问题[16]。总结上述实验结果,作者做出合理推断:不论是激动剂、变构调节剂、拮抗剂还是其他以α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体为核心多靶点药物的研发,作用的最终目标是维持α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体活性在一个合适的范围,使神经元和脑发挥正常的功能。
3.2 α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体基因多态性问题 人类除了α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体基因CHRNA7以外,还有一种人类特有的CHRFAM7A基因编码α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,其由2个部分重复的FAM7基因,插入到CHRNA7 5’端的同一染色体15上融合而来,这种人类特异性基因(CHRFAM7A)的失调与神经发育、神经退行性和炎症性疾病有关,并具有重要的拷贝数变化[80-81]。CHRFAM7A基因的转录产生一个1 256 bp的开放阅读框,编码dup-α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,其中来自FAM7的27个氨基酸残基取代了α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体N端细胞外配体结合域的146个氨基酸残基。体外实验表明,dup-α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体形成杂五聚体,显性负调控α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的通道功能[82],通过改变中枢神经系统中的α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体活性、胆碱能抗炎通路的调节和对胆碱酯酶抑制剂的影响发挥根本性作用[36],从而影响人类认知和记忆。单核苷酸多态性可能影响离子通道通透性或烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的稳定性,也可能改变烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的功能,控制下游信号传导。这些单核苷酸多态性可能会影响启动子,从而影响转录途径,诱导蛋白质的不匹配折叠或导致较短的蛋白质的合成。无论是以单核苷酸多态性的形式,还是直接改变一个或多个氨基酸,已被证明会导致对治疗反应的差异[83]。所以,在以α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体为靶点进行阿尔茨海默病的药物研发时,还需要考虑其基因的遗传多态性。
3.3 结论 综上所述,α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与β-淀粉样蛋白特异性结合,通过多信号途径改变突触的可塑性变化、中枢炎症等,在阿尔茨海默病的发生和发展过程中起着非常重要的作用(图4),深入研究α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体的结构、功能及其激动剂和拮抗剂,对于阿尔茨海默病的治疗有着巨大的潜力。然而,由于α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体存在开放概率低、钙通透性高和快速脱敏等现象以及狭窄的活性范围和基因多态性问题[3,18,65,80-81],也使其作为阿尔茨海默病治疗靶点的研究具备一定复杂性。目前,在α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂的研发过程中,尽管有强有力的临床前证据和有希望的早期临床发现,但到目前为止,还没有一种α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体激动剂在临床3期试验中成功[19]。筛选高特异、安全性和以α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体为核心的多靶点结合作用的药物,将成为未来阿尔茨海默病治疗研究的一个方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||