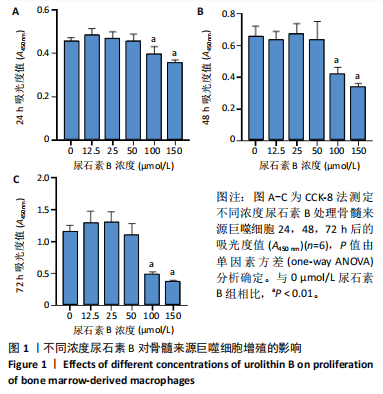
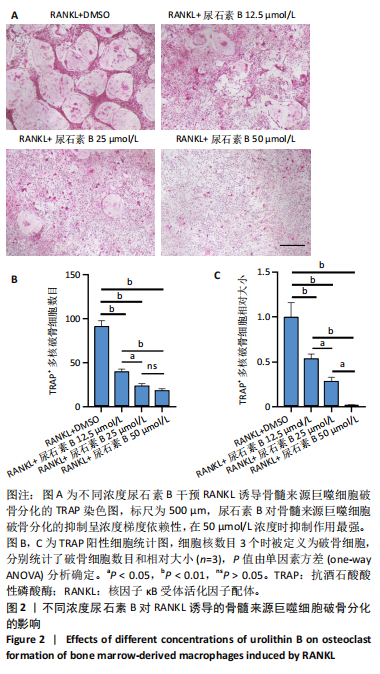
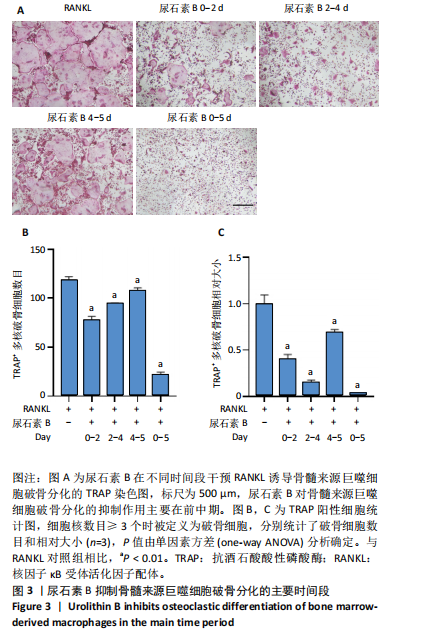
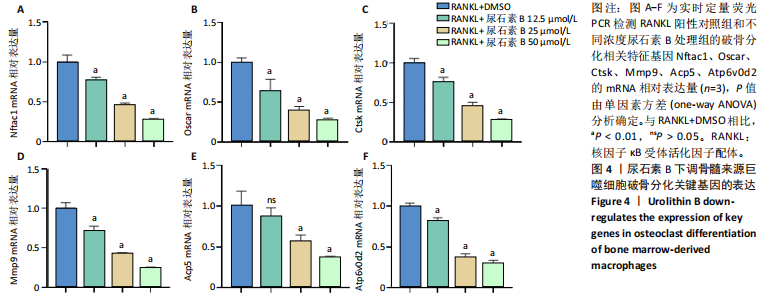
[1] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11):696-711.
[2] TAO H, LI X, WANG Q, et al. Redox signaling and antioxidant defense in osteoclasts. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024;212:403-414.
[3] BOYLE, WILLIAM J, SIMONET W, et al. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature.2003;423(6937):337-342.
[4] BI H, CHEN X, GAO S, et al. Key Triggers of Osteoclast-Related Diseases and Available Strategies for Targeted Therapies: A Review. Front Med. 2017;4:234.
[5] STEGEN S, MOERMANS K, STOCKMANS I, et al. The serine synthesis pathway drives osteoclast differentiation through epigenetic regulation of NFATc1 expression. Nat Metab. 2024;6(1):141-152.
[6] ANESI A, GENERALI L, SANDONI L, et al. From Osteoclast Differentiation to Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: Molecular and Clinical Insights. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4925.
[7] BROWN JP, MORIN S, LESLIE W, et al. Bisphosphonates for treatment of osteoporosis: expected benefits, potential harms, and drug holidays. Can Fam Physician. 2014;60(4):324-333.
[8] DEEKS ED. Denosumab: A Review in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Drugs Aging. 2018;35(2):163-173.
[9] KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis treatment: recent developments and ongoing challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(17):898-907.
[10] REID IR, BILLINGTON EO. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet. 2022;399(10329):1080-1092.
[11] ASADIPOOYA K, WEINSTOCK A. Cardiovascular Outcomes of Romosozumab and Protective Role of Alendronate. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(7):1343-1350.
[12] TAKITO J, NONAKA N. Osteoclasts at Bone Remodeling: Order from Order. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024;71:227-256.
[13] VEIS DJ, O’BRIEN CA. Osteoclasts, Master Sculptors of Bone. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023;18:257-281.
[14] FENG X, TEITELBAUM SL. Osteoclasts: New Insights. Bone Res. 2013; 1(1):11-26.
[15] TAKITO J, NONAKA N. Osteoclasts at Bone Remodeling: Order from Order. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2021;71:227-256.
[16] TAKAYANAGI H. RANKL as the master regulator of osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):13-18.
[17] HE J, ZHENG L, LI X, et al. Obacunone targets macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) to impede osteoclastogenesis and alleviate ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Adv Res. 2023;53:235-248.
[18] TAKAYANAGI H ASAGIRI M. The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 2007;40(2):251-264.
[19] GANDHI GR, ANTONY PJ, CEASAR SA, et al. Health functions and related molecular mechanisms of ellagitannin-derived urolithins. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(2):280-310.
20] ZHENG D, LIU Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Urolithin B, a gut microbiota metabolite, protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via p62/Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res. 2020;153:104655.
[21] REDDY MK, GUPTA SK, JACOB MR, et al. Antioxidant, antimalarial and antimicrobial activities of tannin-rich fractions, ellagitannins and phenolic acids from Punica granatum L. Planta Med. 2007;73(5): 461-467.
[22] WANG ST, CHANG WC, HSU C, et al. Antimelanogenic Effect of Urolithin A and Urolithin B, the Colonic Metabolites of Ellagic Acid, in B16 Melanoma Cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2017;65(32):6870-6876.
[23] AL-HARBI SA, ABDULRAHMAN AO, ZAMZAMI MA, et al. Urolithins: The Gut Based Polyphenol Metabolites of Ellagitannins in Cancer Prevention, a Review. Front Nutr. 2021;8:647582.
[24] LV MY, SHI CJ, PAN FF, et al. Urolithin B suppresses tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma through inducing the inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(10):117273-17282.
[25] XUE H, ZHOU H, LOU Q, et al. Urolithin B reduces cartilage degeneration and alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammation. Food Funct. 2024;15(7):3552-3565.
[26] RAIMUNDO AF, FERREIRA S, POBRE V, et al. Urolithin B: Two-way attack on IAPP proteotoxicity with implications for diabetes. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:1008418.
[27] QU Z, AN H, FENG M, et al. Urolithin B suppresses osteoclastogenesis via inhibiting RANKL-induced signalling pathways and attenuating ROS activities. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(16):4428-4439.
[28] WU Z, LI C, CHEN Y, et al. Chrysin Protects Against Titanium Particle-Induced Osteolysis by Attenuating Osteoclast Formation and Function by Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK Signaling. Front Pharmaco. 2022;13: 793087.
[29] MIAO J, TU Y, JIANG J, et al. VSIG4 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by enhancing Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response against reactive oxygen species production. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024; 260:129357.
[30] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[31] JIANG T, XIA T, QIAO F, et al. Role and Regulation of Transcription Factors in Osteoclastogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(22):16175.
[32] LIU CL, HO TL, FANG SY, et al. Ugonin L inhibits osteoclast formation and promotes osteoclast apoptosis by inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;166:115392.
[33] 梅良伟, 桑文华, 陈富春, 等. RANK 信号调控破骨细胞分化与成熟的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(12):1652-1656.
[34] QIU Z, LI L, HUANG Y, et al. Puerarin specifically disrupts osteoclast activation via blocking integrin-β3 Pyk2/Src/Cbl signaling pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2022;33:55-69.
[35] ZHANG L, YANG Y, LIAO Z, et al. Genetic and pharmacological activation of Hedgehog signaling inhibits osteoclastogenesis and attenuates titanium particle-induced osteolysis partly through suppressing the JNK/c-Fos-NFATc1 cascade. Theranostics. 2020;10(15):6638-6660.
[36] XU H, CHEN F, LIU T, et al. Ellagic acid blocks RANKL-RANK interaction and suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting RANK signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact. 2020;331:109235.
[37] LIN X, YUAN G, LI Z, et al. Ellagic acid protects ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice by inhibiting osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(9):5951-5961.
[38] LI Y, ZHUANG Q, TAO L, et al. Urolithin B suppressed osteoclast activation and reduced bone loss of osteoporosis via inhibiting ERK/ NF-κB pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(10):e13291.
[39] MA L, ZHANG L, LIAO Z, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of protein S-palmitoylation suppresses osteoclastogenesis and ameliorates ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Orthop Translat. 2023;42:1-14.
[40] GHOSH S, HAYDEN MS. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell, 2008;132(3):344-362.
[41] TIAN M, HAN YB, YANG GY, et al. The role of lactoferrin in bone remodeling: evaluation of its potential in targeted delivery and treatment of metabolic bone diseases and orthopedic conditions. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1218148.
[42] YANG Y, LIU Z, WU J, et al. Nrf2 Mitigates RANKL and M-CSF Induced Osteoclast Differentiation via ROS-Dependent Mechanisms. Antioxidants. 2023;12(12):2094.
[43] LUO N, ZHANG L, XIU C, et al. Piperlongumine, a Piper longum-derived amide alkaloid, protects mice from ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis via suppression of p38 and JNK signaling. Food Funct. 2024;15(4):2154-2169.
[44] LIU C, WALTER TS, HUANG P, et al. Structural and functional insights of RANKL-RANK interaction and signaling. J Immunol. 2010;184(12): 6910-6919.
|