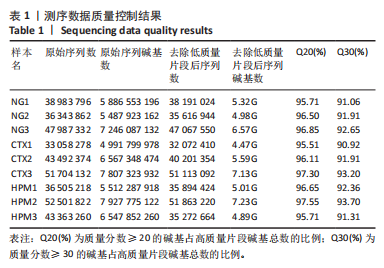
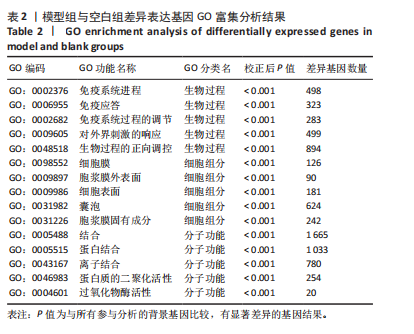
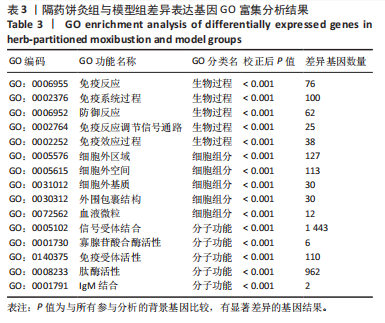
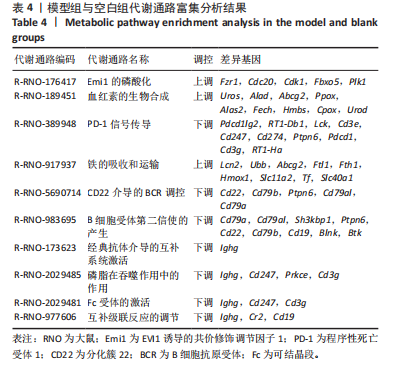
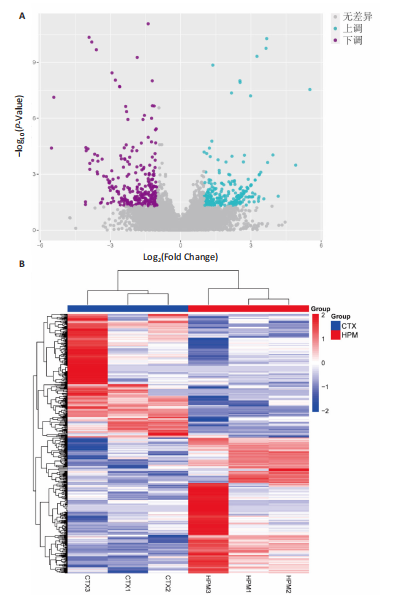
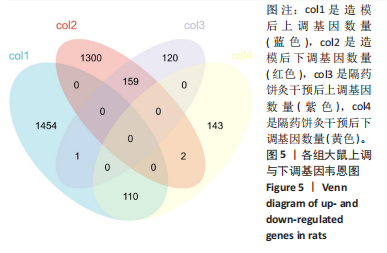
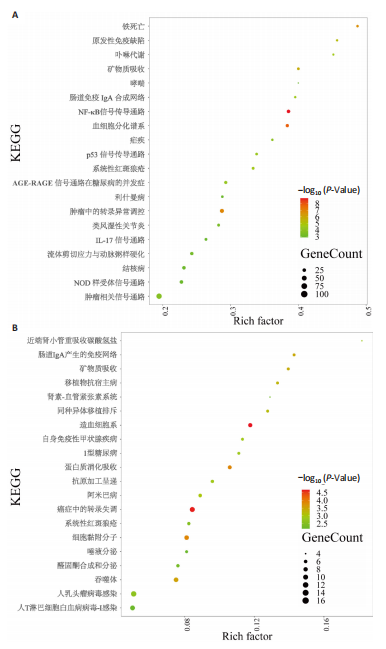
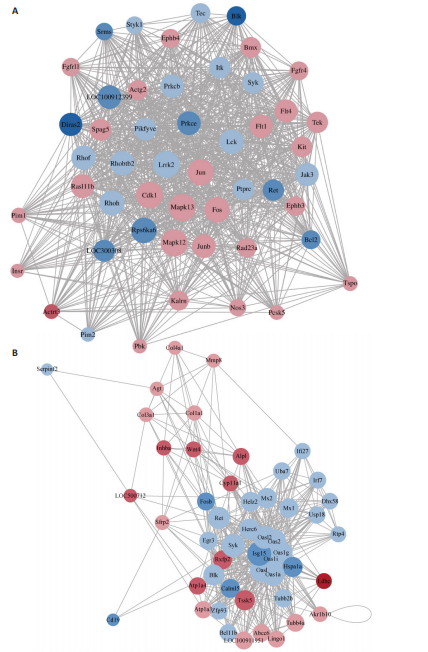
[1] VAN DELFT MAM, HUIZINGA TWJ. An overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102392.
[2] JIANG Q, YANG G, LIU Q, et al. Function and role of regulatory t cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:626193.
[3] JIANG X, WANG J, DENG X, et al. Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol Cancer. 2019; 18(1):10.
[4] 祁云霞,刘永斌,荣威恒.转录组研究新技术:RNA-Seq及其应用[J].遗传,2011,33(11):1191-1202.
[5] FAN Y, LI Y, YAO X, et al. Epithelial SOX9 drives progression and metastases of gastric adenocarcinoma by promoting immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment. Gut. 2023;72(4): 624-637.
[6] ZHU M, ZHANG P, YU S, et al. Targeting ZFP64/GAL-1 axis promotes therapeutic effect of nab-paclitaxel and reverses immunosuppressive microenvironment in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.2022; 41(1):14.
[7] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见[Z].中华人民共和国科学技术部,2006.
[8] 马盼盼,叶军,杨艳芳,等.大鼠免疫抑制长期模型的建立及验证[J].中国药房,2018,29(15):2045-2048.
[9] 崔瑾,严洁.艾灸或针刺膈俞穴对环磷酰胺致白细胞减少大鼠诱生粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(28):5473-5476.
[10] 李忠仁.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2003.
[11] 徐东升,赵硕,崔晶晶,等.绘制实验大鼠腧穴图谱的新尝试[J].针刺研究,2019, 44(1):62-65,79.
[12] 王海军,冀来喜.关于大鼠“神阙”穴的定位[J].针刺研究,2007, 32(5):312.
[13] 何丽,景荣华,顾仁艳.温针灸对卵巢功能减退大鼠TGF-β1/Smads信号通路的影响[J]. 中国性科学,2023,32(10):141-145.
[14] ZHENG S, MA M, CHEN Y, et al. Effects of quercetin on ovarian function and regulation of the ovarian PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signalling pathway and oxidative stress in a rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced premature ovarian failure. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022;130(2):240-253.
[15] HUANG B, DING C, ZOU Q, et al. Cyclophosphamide regulates N6-methyladenosine and m6A RNA enzyme levels in human granulosa cells and in ovaries of a premature ovarian aging mouse model. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:415.
[16] 李佳妮,宋新龙,张乐,等.穿龙薯蓣皂苷对再生障碍性贫血小鼠VEGF、EGFR1表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(9):5186-5190.
[17] 石健菲,焦丹丽,赵琛,等.环磷酰胺联合环孢霉素介导的获得性再生障碍性贫血小鼠模型的建立[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2022, 30(1):222-226.
[18] 王旭,孙妮娜,田岳凤,等.不同灸法对环磷酰胺所致免疫抑制兔脾组织程序性死亡因子-1及其配体表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2020,27(11):66-70.
[19] 毛凯荣,熊罗节,田岳凤,等.隔药饼灸对免疫抑制兔调节性B细胞介导的TIGIT/CD155和JAK2/STAT3信号通路的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2023,30(9):102-107.
[20] 熊罗节,田岳凤,徐小珊,等.隔药饼灸对免疫抑制兔Tim-4及PD-1的泛素化的影响[J].中国针灸,2023,43(5):529-536.
[21] XIONG L, TIAN Y, XU X, et al. Immunopotentiating effects of herb-partitioned moxibustion on the spleens of cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed rats. Chin Med. 2024;19(1):1-21.
[22] XU X, DENG W, ZHANG W, et al. Transcriptome analysis of rat lungs exposed to moxa smoke after acute toxicity testing. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:5107441.
[23] LEE S, CHANG L, JUNG W, et al. OASL phase condensation induces amyloid-like fibrillation of RIPK3 to promote virus-induced necroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2023;25(1):92-107.
[24] 张焕霞,刘春礼,孙晓明,等.艾灸辅助艾速康对HIV/AIDS患者疗效及miR-222、血清CD4+的影响[J].光明中医,2022,37(5):840-843.
[25] HUANG Y, ZHENG Y, ZHOU Y, et al. OAS1, OAS2, and OAS3 contribute to epidermal keratinocyte proliferation by regulating cell cycle and augmenting IFN-1‒induced Jak1‒signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 phosphorylation in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2022; 142(10):2635-2645.e9.
[26] FERNANDEZ T, GARCIA R, ALONSO M, et al. Mx1, Mx2 and Mx3 proteins from the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) show in vitro antiviral activity against RNA and DNA viruses. Mol Immunol. 2013;56(4): 630-636.
[27] HUNTZINGER E, SINTEFF J, MORLET B, et al. HELZ2: a new, interferon-regulated, human 3’-5’exoribonuclease of the RNB family is expressed from a non-canonical initiation codon. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(17): 9279-9293.
[28] LI P, LU G, WANG L, et al. A rare nonsynonymous variant in the lipid metabolic gene HELZ2 related to primary biliary cirrhosis in Chinese Han. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2016;12:14.
[29] TOMARU T, SATOH T, YOSHINO S, et al. Isolation and characterization of a transcriptional cofactor and its novel isoform that bind the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding domain of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ. Endocrinology. 2006;147(1):377-388.
[30] KATANO A, SATOH T, OMARU T, et al. THRAP3 interacts with HELZ2 and plays a novel role in adipocyte differentiation. Mol Endocrinol. 2013;27(5):769-780.
[31] 张其奥,王子路,李佩波,等.USP18介导的蛋白质去ISG化及其在结核病等传染病中的作用[J].遗传,2023,45(11):998-1006.
[32] 何文峰,李琛,李隆熙,等.ISG15基因敲除增加小鼠对脑心肌炎病毒(EMCV)的易感性[J].中国兽医学报,2023,43(9):1873-1880.
[33] 刘欣然,陈桐,张煜,等.泛素样蛋白ISG15抗冠状病毒感染作用的研究进展(英文)[J].华中师范大学学报(自然科学版),2023, 57(5):748-757.
[34] OUDSHOORN D, VAN VAN BOHEEMEN, SANCHEZ A, et al. HERC6 is the main E3 ligase for global ISG15 conjugation in mouse cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29870.
[35] 杜夏琳. E3泛素连接酶HERC5通过介导PTEN的ISG化和降解增强巨噬细胞的抗结核免疫[D].广州:南方医科大学,2021.
[36] MOLLINEDO F. Neutrophil degranulation, plasticity, and cancer metastasis. Trends Immunol. 2019;40(3):228-242.
[37] CHEN Z, SHAO Z, MEI S, et al. Sepsis upregulates CD14 expression in a MyD88-dependent and Trif-independent pathway. Shock. 2018; 49(1):82-89.
[38] MALMHALL B, ANDERSSON K, ERLANDSSON M, et al. Metabolic signature and proteasome activity controls synovial migration of CDC42hiCD14+ cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2023;14: 1187093.
[39] 张娟,张根生,黄雪,等.贝前列素钠片联合当归黄芪汤对糖尿病足溃疡患者创面愈合、血管新生及氧化应激的影响[J/OL].中华中医药学刊,1-12[2024-03-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R.20230915.1700.084.html.
[40] 李晓娜,齐先梅,张田甜,等.沉默Fcgr3降低SiO2诱导的小鼠肺泡巨噬细胞系MH-S炎性因子表达[J].基础医学与临床,2023, 43(6):904-908.
[41] WANG T, RAVETCH J. Functional diversification of IgGs through Fc glycosylation. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(9):3492-3498. |