中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (33): 5403-5412.doi: 10.12307/2024.674
• 植入物相关大数据分析 Implant related big data analysis • 上一篇
外骨骼机器人辅助步行康复治疗脊髓损伤:研究热点的CiteSpace分析
许 轶,邓宇斌
- 中山大学附属第七医院,中山大学(深圳),广东省深圳市 518107
-
收稿日期:2023-09-18接受日期:2023-11-07出版日期:2024-11-28发布日期:2024-01-31 -
通讯作者:邓宇斌,博士,教授,中山大学附属第七医院,中山大学(深圳),广东省深圳市 518107 -
作者简介:许轶,女,广东省广州市人,汉族,2017年中山大学毕业,博士,副主任医师,主要从事骨科康复和神经康复研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(82172548),项目负责人:许轶;深圳科创委基础研究自由探索项目(JCYJ20180307150610733),项目负责人:许轶
Exoskeleton-assisted walking rehabilitation for spinal cord injury: CiteSpace analysis of research hotspots
Xu Yi, Deng Yubin
- Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Sun Yat-sen University (Shenzhen), Shenzhen 518107, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-09-18Accepted:2023-11-07Online:2024-11-28Published:2024-01-31 -
Contact:Deng Yubin, PhD, Professor, Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Sun Yat-sen University (Shenzhen), Shenzhen 518107, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Xu Yi, MD, PhD, Associate chief physician, Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Sun Yat-sen University (Shenzhen), Shenzhen 518107, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82172548 (to XY); Basic Research Free Exploration Project of Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission, No. JCYJ20180307150610733 (to XY)
摘要:

文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是由于创伤性或非创伤性原因对脊髓造成损伤,导致患者出现运动、感觉及大小便等功能障碍的严重致残性疾病,常见引起截瘫,甚至四肢瘫痪。外骨骼机器人辅助步行:是一种新型辅助步行技术,由典型穿戴外骨骼机器人设备执行,患者通过惯性测量单元、压力传感器及驱动器等传达运动意图,与外骨骼形成人机紧耦合系统,控制外骨骼机器人完成对应肢体动作,从而实现康复训练或辅助步行运动。
背景:脊髓损伤危害严重,损伤后步行功能障碍最影响患者的日常生活能力,在该领域运用外骨骼机器人开展辅助步行康复研究日趋活跃。
目的:应用CiteSpace可视化软件绘制脊髓损伤后外骨骼机器人辅助步行为主题的科学知识图谱,并探讨近10年该领域研究现状、热点及未来趋势,为该领域后续科学研究和临床运用提供借鉴。方法:利用Web of Science核心集数据库通过布尔逻辑运算符进行主题词检索,选择语种英语,检索策略:TS=“spinal cord injury OR SCI”AND“walk OR walking”AND“robot OR exoskeleton OR (exoskeleton-assisted walking) OR EAW”,利用知识图谱软件CiteSpace 6.2.R4对去重后获得的高质量文献进行发文量、国家/研究机构合作、高影响力作者/文献共被引、关键词共现/聚类/突现等主题热点、国际前沿趋势可视化分析,并绘制科学知识图谱。
结果与结论:①共纳入544篇高质量文献,近10年该领域发文量、总被引频次呈增长趋势;②发文量排名前3的国家依次是美国、中国、意大利,发文量排名前3研究机构是美国退伍军人事务部、美国退伍军人健康管理局、瑞士联邦理工学院;③被引文献频次最高(167次)和中介中心性最高(0.13)的作者均为美国宾夕法尼亚Esquenazi A团队,在该领域具有较高影响力;④对被引频次、中介中心性前5共被引文献分析显示:目前针对脊髓损伤患者配备动力外骨骼设备步行康复研究重点包括在机构、家庭等真实环境中步行康复训练安全性判断、优势分析、个体化培训计划设计,动力外骨骼设备应用于胸椎及以下节段运动功能完全丧失脊髓损伤患者辅助步行效果优劣、影响因素及应用潜力等;⑤近年该领域研究热点集中于个体化(individuals)、步态(gait)、动力外骨骼( powered exoskeleton)、减重支持(body weight support)、功能性电刺激(functional electrical stimulation)、康复(rehabilitation)、辅助技术(assistive technology)、步行活动(ambulation)、恢复(recovery)等内容;⑥该领域研究早期多应用于脑卒中患者,前沿包括减重支持、往复式步态矫形器及功能性电刺激等技术手段,脊髓损伤外骨骼机器人辅助步行康复研究近年呈现上升趋势,关注点逐渐向以适应性控制为机制的医用下肢外骨骼设备研制、安全性提升、应用潜力挖掘等前沿方向转变,研究检测手段注重联合功能性近红外光谱成像等高端技术,而关注患者生活质量、提升运动训练能力及改善机体结构为该领域未来的研究热点。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7829-6989(许轶);https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2664-8254(邓宇斌)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
许 轶, 邓宇斌 . 外骨骼机器人辅助步行康复治疗脊髓损伤:研究热点的CiteSpace分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(33): 5403-5412.
Xu Yi, Deng Yubin. Exoskeleton-assisted walking rehabilitation for spinal cord injury: CiteSpace analysis of research hotspots[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5403-5412.
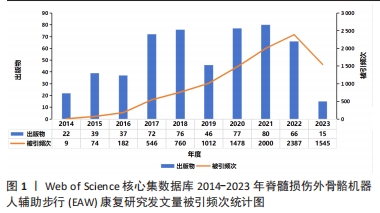
2.1.1 发文量和被引频次统计 通过文献数量变化趋势可有效分析该领域研究发展倾向,预测未来可能发展走势。如图1所示,2014-2023 年,脊髓损伤患者EAW功能康复相关研究年度发文量和被引频次总体呈上升趋势。其中,2021年度发文量最多,达80篇;2022被引频次最高2 387。应用Web of Science核心集数据库创建的引文报告功能分析,出版物合计544,被引文献4 929,去除自引后4 498;被引频次总计9 750次,去除自引后7 384,H 指数(h-index)=51,每篇平均被引17.92次。
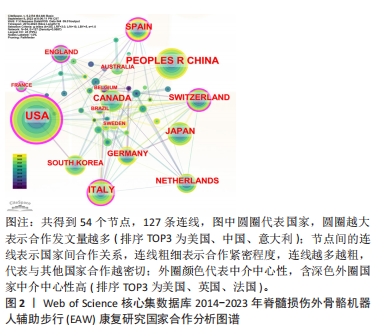
2.1.2 施引文献国家(地区)合作分析 如图2,表2所示,外骨骼机器人应用于脊髓损伤后患者步行功能研究可以看出,2014-2023 年,共有54个国家(地区)发表了该领域相关研究,合作图谱共得到54个节点,127条连线,各国间有良好合作关系。发文数量排名前5国家依次是:美国USA 158篇,中国PEOPLES R CHINA 77篇,意大利ITALY 50篇,日本JAPAN 47篇,加拿大 CANADA 43篇。中介中心性前5国家依次为:美国USA(0.42),英国ENGLAND(0.18),法国FRANCE(0.16),意大利 ITALY (0.14),瑞士SWITZERLAND(0.12)。美国的发文量及中介中心性均最高居于榜首,在此领域处于领军地位。可能由于欧美国家科学技术水平较高、起步较早、认可度高,故中介中心性也较高。中国近几年度发文量提升明显,但可能由于起步相对较晚,中介中心性仍偏低(0.05)。具体见图2。
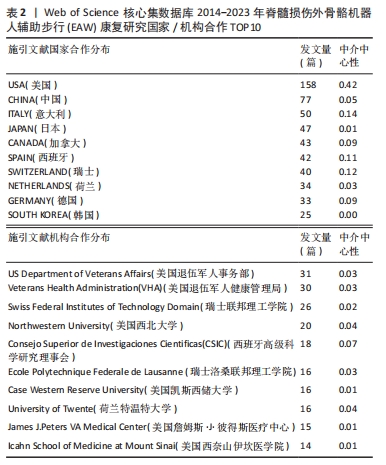
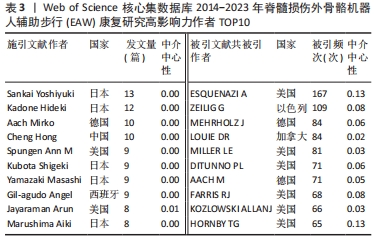
2.1.3 施引文献机构合作分析 如图3,表2所示,在过去近10年共有约240个机构涉及该领域研究,集中于各国大学,具有密切合作关系。发表文章数量排名前5位的机构依次为美国退伍军人事务部US Department of Veterans Affairs 31篇,美国退伍军人健康管理局Veterans Health Administration (VHA) 30篇,瑞士联邦理工学院 Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology Domain 26篇,美国西北大学 Northwestern University 20篇,西班牙国家最高科学研究委员会 Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas (CSIC)18篇 ;就中介中心性而言,排名前5位的机构依次是美国芝加哥Shirley Ryan康复中心(原芝加哥康复研究所)Shirley Ryan Ability Lab 0.08,西班牙国家最高科学研究委员会 Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas (CSIC) 0.07,意大利圣卢西亚基金会 IRCCS Santa Lucia 0.07,美国佐治亚理工学院Georgia Institute of Technology 0.05,美国西北大学 Northwestern University 0.04。与主要研究国家一致,该领域主要研究机构也以欧美国家为主,这些信息可为从事该领域研究专家后续进一步研究、深造、合作提供信息。

2.1.4 高影响力施引文献作者合作与被引文献作者共被引分析 如表3所示,近 10年来多名施引文献作者参与该领域研究,其中4位作者发文量在10篇以上,分别是日本筑波大学Sankai Yoshiyuki教授(13篇)、Kadone Hideki教授(12篇),德国波鸿伯格曼谢尔大学Aach Mirko教授(10篇),中国四川电子科技大学Hong Cheng教授(10篇),但综合而言,作者中介中心性较低,被引用率不高;如表3所示,近 10年被引文献被引频次排序前 5 核心共被引作者依次为美国宾夕法尼亚MossRehab & Albert Einstein医疗中心ESQUENAZI A (167 次)、以色列Chaim Sheba医疗中心ZEILIG G(109次)、德国德累斯顿医学院MEHRHOLZ J (84 次)、加拿大哥伦比亚大学LOUIE DR (84次)、美国北卡罗来纳州Miller科学咨询机构MILLER LE (81次)。被引文献中介中心性排序前 5的核心共被引作者依次为美国宾夕法尼亚MossRehab & Albert Einstein医疗中心ESQUENAZI A(0.13),美国印第安纳大学HORNBY TG (0.13),瑞士苏黎世Hocoma医学GmbH的VENEMAN JF (0.12),美国科罗拉多州恩格尔伍德克雷格医院TEFERTILLER C (0.12),瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院RIENER R (0.11)。其中被引文献共被引频次最多、中介中心性最高作者均为来自美国Pennsylvania大学MossRehab & Albert Einstein Medical Center的Alberto Esquenazi教授,他在脊髓损伤后EAW研究领域涉及的研究主题包括评估脊髓损伤患者使用 ReWalk? 外骨骼行走系统的安全性和耐受性,评估功能性步行测量,并将其与神经脊髓水平、年龄和受伤后持续时间等相关联;并长期致力于外骨骼机器人、肉毒毒素等手段应用于各类步行功能障碍患者的相关研究[11-16]。
2.2 研究热点分析结果
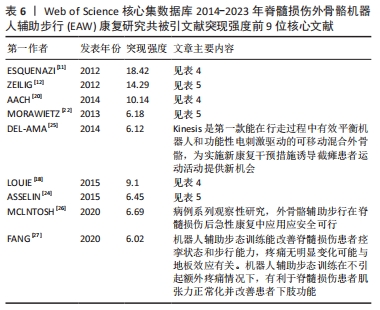
2.2.1 被引核心文献共被引分析结果 文献共被引指1篇文献被≥2篇文献同时引用,可预测研究领域在一定时间范围内研究热点及趋势。图4可见2014-2023年间该领域的研究共涉及297篇共被引核心参考文献。共被引参考文献排名前5位的文献依次是:美国Virginia Tech大学MILLER团队[17]2016年在《Med Devices-Evid Res》发表文献,共被引次数(53次)最高,加拿大温哥华大学LOUIE团队[18]于2015年发表于《J Neuroeng Rehabil》的文献,共被引51次;丹麦Rigshospitalet脊髓损伤诊所BAUNSGAARD团队[19]2018年发表于《Spinal Cord》的文献,共被引45次;美国宾夕法尼亚MossRehab & Albert Einstein医疗中心ESQUENAZI团队[11]2012年发表于《Am J Phys Med Rehab》的文献,共被引41次;德国BG大学AACH 团队[20]2014年发表于《Spine J》的文献,共被引39次,频次前5位文献主要研究内容:脊髓损伤患者配备电动外骨骼设备真实环境中行走的安全性及优势;以及设备应用于胸椎及以下水平运动功能完全损伤的脊髓损伤患者辅助步行效果、影响因素及应用潜力等,具体见表4。
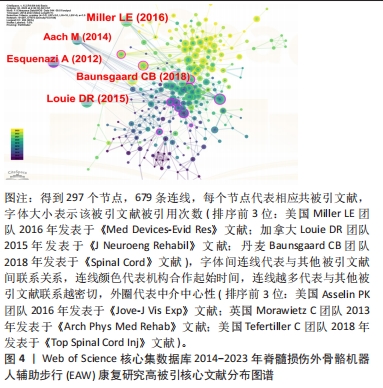
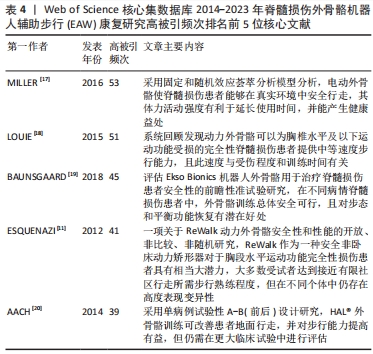
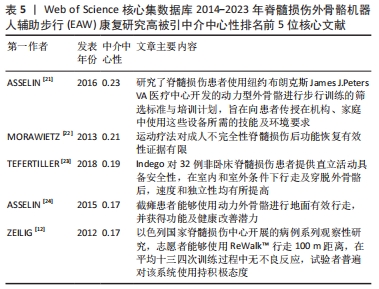
最佳中介中心性(0.23)以美国退伍军人事务部Asselin PK团队在《JOVE-J VIS EXP》发表文献“Training Persons with Spinal Cord Injury to Ambulate Using a Powered Exoskeleton”获得,他们重点研究了脊髓损伤患者使用动力型外骨骼筛选标准与培训计划[21];其他高中介中心性被引参考文献尚包括英国格拉斯哥喀里多尼亚大学 MORAWIETZ团队[22]2013年发表于《ARCH PHYS MED》文献,中介中心性0.21;美国科罗拉多州恩格尔伍德克雷格医院TEFERTILLER团队 [23]2018年发表于《 TOP SPINAL CORD INJ》文献,中介中心性0.19;美国退伍军人事务部ASSELIN团队[24]2015年发表于《J REHABIL RES DEV》文献,中介中心性 0.17;以色列Chaim Sheba医疗中心ZEILIG团队[12]2012年发表于《J SPINAL CORD MED》文献,中介中心性 0.17 ,具体见表5。
2.2.2 高被引文献突现强度排序 突现强度可以较好地展现研究领域在一定时间范围内研究前沿,呈现该领域聚焦热点及趋势。图5可见2014-2023年该领域高被引文献突现强度排序情况。运行 CiteSpace 得到共被引文献知识图谱[11-12,18,20,22,24-27],被引文献突现强度情况及具体信息见图5,表6。
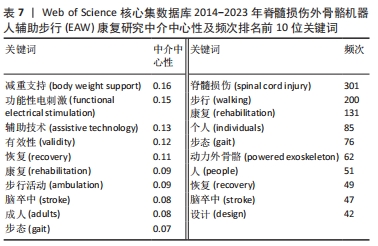
2.2.3 关键词共现分析结果 文献主要内容一般可被凝炼成关键词,故关键词共同出现次数越多则代表该领域在一定时间范围内研究主题热度越高,主要以中介中心性为衡量量化指标(0-1),数值越大影响力越大,若其≥0.1 说明中介中心性较高,如表7,图6,中介中心性排名前10的关键词依次是:body weight support (减重支持),Functional electrical stimulation (功能性电刺激),assistive technology(辅助技术),validity (有效性), recovery(恢复),rehabilitation(康复),ambulation(步行活动),stroke(脑卒中),adults(成人),gait(步态)。除去与主题相关的关键词——Spinal cord injury(脊髓损伤),walking(步行),rehabilitation(康复),共现出现频次前10的关键词尚包括Individuals (个人),gait(步态),Powered exoskeleton(动力外骨骼),people(人),recovery(恢复),stroke(脑卒中),design(设计)。
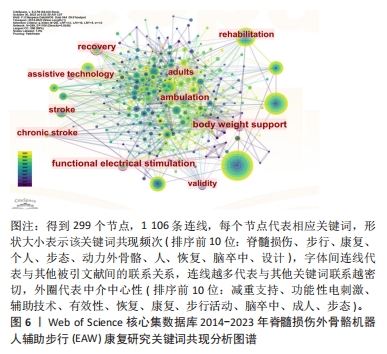
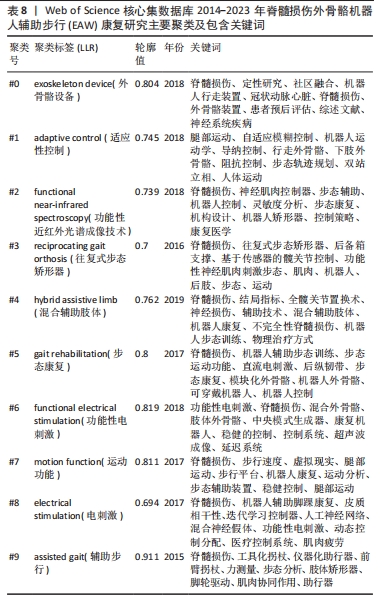
2.2.4 关键词共现聚类分析结果 关键词聚类分析是将关联密切关键词汇聚成一类,并观察一定时间范围内研究领域形成的具体研究类团(聚类号),号数越小则类团包含关键词数量越多,轮廓值则表示类团内部关键词间紧密程度,一般认为> 0.7 时聚类较成功。进一步通过对上述关键词进行对数似然比(log-likelihood ratio,LLR)聚类分析,得到聚类图7。其中,聚类模块化Q 值Modularity为0.489 8(> 0.3,表示聚类结构显著),平均轮廓S 值Silhouette 值为0.775 2(一般认为S值> 0.5聚类即合理,S值> 0.7意味聚结果令人信服),提示聚类结构显著,同质性高。如图7,排名前10的聚类与相应轮廓值分别为#0 exoskeleton device(外骨骼设备,0.804 ),#1 adaptive control(适应性控制,0.745),#2 functional near-infrared spectroscopy(功能性近红外光谱成像技术 0.739),#3 reciprocating gait orthosis (往复式步态矫形器,0.7),#4 hybrid assistive limb (混合辅助肢体,0.762),#5 gait rehabilitation(步态康复,0.8),#6 functional electrical stimulation(功能性电刺激,0.819),#7 motion function(运动功能 0.811),#8 electrical stimulation(电刺激,0.694),#9 assisted gait(辅助步行,0.911)。将上述信息进一步进行聚类列表处理,自聚类Clusters-聚类列表Summary Table中白名单Whitelist获得关键词具体相关信息,具体见表8。由聚类结果及其所含关键词可知,脊髓损伤患者步态功能康复近年研究主要聚焦于外骨骼设备技术,作用机制以适应性控制为主,既往促进步行功能改善方法还包括往复式步态矫形器、混合辅助肢体、功能性电刺激等康复工程技术,目前研究倾向联合功能性近红外光谱成像等智能高端技术。
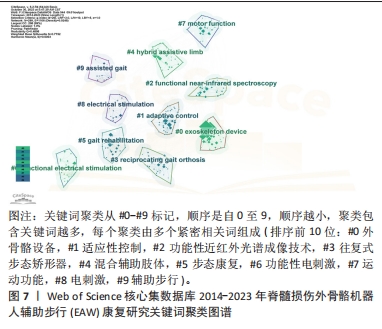
2.2.5 关键词突现分析和时间线图分析结果 关键词突现分析指对一定时间范围内文献中突然大量出现的特定词语分析研究,可用于发现某一领域研究呈现演化趋势,回顾预测关键分支技术成为热点的时间范围,更好地展现该领域研究前沿,并帮助判断未来延续爆发趋势;图谱中Strength代表关键词爆发强度,数值越大代表爆发强度越大。关键词时间线图分析则指进一步观察单一聚类里关键词随时间演化分布趋势与状况。如图8,9,该研究领域关键词突现情况大致分3个时间段:

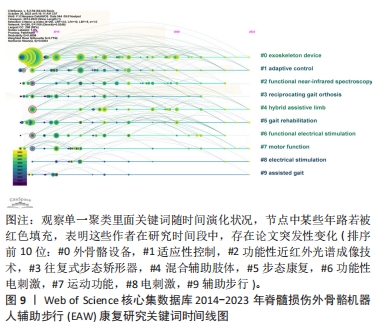
(1) 2014-2018年热点: stroke(脑卒中),2014-2017时间段针对步态异常康复机器人设备更偏重对脑卒中类患者进行尝试与研究;mobility (行走能力)与system(系统)。
(2) 2016-2018年热点:研究强调提升患者步行能力及综合系统对待病患具体问题; functional electrical stimulation (功能性电刺激),2017-2018时间段内研究偏重功能性电刺激使用对脊髓损伤患者功效。
(3)2019-2020 研究热点:逐渐转向 locomotor training(步行训练)作为干预手段改善脊髓损伤患者步行功能。
(4) 2020-2023年热点:突变热点转变为quality of life (生活质量),exercise(运动训练)、body composition(身体结构)、legged locomotion(腿部运动)等,突变系数较高且至今仍保持较高发文量,应是该领域研究热点与前沿方向,其中,尤其以quality of life 突变系数最高,可见围绕脊髓损伤患者步态康复阶段各项评估内容中,患者生活质量的重要性日益受到关注。在功能恢复中,运动训练扮演着至关重要的角色。研究人员也致力于改善机体结构,以促进康复和功能恢复。
进一步对关键词聚类进行时间线图分析,可见#0 exoskeleton device(外骨骼设备)一直是脊髓损伤患者步行功能康复研究热点与重点,尤其近几年呈现热度持续增高趋势,也是后续被持续关注目标方向;#4 hybrid assistive limb (混合辅助肢体)、#7 motion function(运动功能)也是近年研究热点聚类;相反,#3 reciprocating gait orthosis (往复式步态矫形器),#6 FES(功能性电刺激)虽在早年关注度较高,但近年呈下降趋势,具体见图9。

| [1] YUAN S, SHI Z, CAO F, et al. Epidemiological features of spinal cord injury in china: a systematic review. Front Neurol. 2018;9:683. [2] JAZAYERI SB, MAROUFI SF, MOHAMMADI E, et al. Incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury worldwide: a systematic review, data integration, and update. World Neurosurg X. 2023;18:100171. [3] WEST CR, ALYAHYA A, LAHER I, et al. Peripheral vascular function in spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Spinal Cord. 2013;51(1):10-19. [4] KOYAMA S, TANABE S, SAITOH E, et al. Characterization of unexpected postural changes during robot-assisted gait training in paraplegic patients. Spinal Cord. 2016;54(2):120-125. [5] KHAN AS, LIVINGSTONE DC, HURD CL, et al. Retraining walking over ground in a powered exoskeleton after spinal cord injury: a prospective cohort study to examine functional gains and neuroplasticity. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2019;16(1):145. [6] NAM KY, KIM HJ, KWON BS, et al. Robot-assisted gait training (Lokomat) improves walking function and activity in people with spinal cord injury: a systematic review. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017;14(1):24. [7] XIANG XN, DING MF, ZONG HY, et al. The safety and feasibility of a new rehabilitation robotic exoskeleton for assisting individuals with lower extremity motor complete lesions following spinal cord injury (SCI): an observational study. Spinal Cord. 2020;58(7):787-794. [8] TSAI CY, DELGADO AD, WEINRAUCH WJ, et al. Exoskeletal-assisted walking during acute inpatient rehabilitation leads to motor and functional improvement in persons with spinal cord injury: a pilot study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(4):607-612. [9] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1): 5303-5310. [10] CHEN C, SONG M. Visualizing a field of research: a methodology of systematic scientometric reviews. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e0223994. [11] ESQUENAZI A, TALATY M, PACKEL A, et al. The ReWalk powered exoskeleton to restore ambulatory function to individuals with thoracic-level motor-complete spinal cord injury. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012; 91(11):911-921. [12] ZEILIG G, WEINGARDEN H, ZWECKER M, et al. Safety and tolerance of the ReWalk exoskeleton suit for ambulation by people with complete spinal cord injury: a pilot study. J Spinal Cord Med. 2012;35(2):96-101. [13] SALGA M, GATIN L, DELTOMBE T, et al. International recommendations to manage poststroke equinovarus foot deformity validated by a panel of experts using delphi. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(3):372-379. [14] ESQUENAZI A, BRASHEAR A, DELTOMBE T, et al. The effect of repeated abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport(R)) injections on walking velocity in persons with spastic hemiparesis caused by stroke or traumatic brain injury. PM R. 2021;13(5):488-495. [15] AWAD LN, ESQUENAZI A, FRANCISCO GE, et al. The ReWalk ReStore soft robotic exosuit: a multi-site clinical trial of the safety, reliability, and feasibility of exosuit-augmented post-stroke gait rehabilitation. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020;17(1):80. [16] ESQUENAZI A, TALATY M. Robotics for Lower Limb Rehabilitation. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2019;30(2):385-397. [17] MILLER LE, ZIMMERMANN AK, HERBERT WG. Clinical effectiveness and safety of powered exoskeleton-assisted walking in patients with spinal cord injury: systematic review with meta-analysis. Med Devices (Auckl). 2016;9:455-466. [18] LOUIE DR, ENG JJ, LAM T, et al. Gait speed using powered robotic exoskeletons after spinal cord injury: a systematic review and correlational study. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015;12:82. [19] BAUNSGAARD CB, NISSEN UV, BRUST AK, et al. Exoskeleton gait training after spinal cord injury: an exploratory study on secondary health conditions. J Rehabil Med. 2018;50(9):806-813. [20] AACH M, CRUCIGER O, SCZESNY-KAISER M, et al. Voluntary driven exoskeleton as a new tool for rehabilitation in chronic spinal cord injury: a pilot study. Spine J. 2014;14(12):2847-2853. [21] ASSELIN PK, AVEDISSIAN M, KNEZEVIC S, et al. Training persons with spinal cord injury to ambulate using a powered exoskeleton. J Vis Exp. 2016. doi: 10.3791/54071. [22] MORAWIETZ C, MOFFAT F. Effects of locomotor training after incomplete spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;94(11): 2297-2308. [23] TEFERTILLER C, HAYS K, JONES J, et al. Initial outcomes from a multicenter study utilizing the indego powered exoskeleton in spinal cord injury. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2018;24(1):78-85. [24] ASSELIN P, KNEZEVIC S, KORNFELD S, et al. Heart rate and oxygen demand of powered exoskeleton-assisted walking in persons with paraplegia. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2015;52(2):147-158. [25] DEL-AMA AJ, GIL-AGUDO A, PONS JL, et al. Hybrid FES-robot cooperative control of ambulatory gait rehabilitation exoskeleton. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2014;11:27. [26] MCINTOSH K, CHARBONNEAU R, BENSAADA Y, et al. The safety and feasibility of exoskeletal-assisted walking in acute rehabilitation after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(1):113-120. [27] FANG CY, TSAI JL, LI GS, et al. Effects of robot-assisted gait training in individuals with spinal cord injury: a meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:2102785. [28] KWON SH, LEE BS, LEE HJ, et al. Energy efficiency and patient satisfaction of gait with knee-ankle-foot orthosis and robot (ReWalk)-assisted gait in patients with spinal cord injury. Ann Rehabil Med. 2020;44(2):131-141. [29] EDWARDS DJ, FORREST G, CORTES M, et al. Walking improvement in chronic incomplete spinal cord injury with exoskeleton robotic training (WISE): a randomized controlled trial. Spinal Cord. 2022;60(6):522-532. [30] OKAWARA H, TASHIRO S, SAWADA T, et al. Neurorehabilitation using a voluntary driven exoskeletal robot improves trunk function in patients with chronic spinal cord injury: a single-arm study. Neural Regen Res. 2022; 17(2):427-432. [31] KOSEKI K, TAKAHASHI K, YAMAMOTO S, et al. Use of robot-assisted ankle training in a patient with an incomplete spinal cord injury: a case report. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2023;8(1):301. [32] EZAKI S, KADONE H, KUBOTA S, et al. Analysis of gait motion changes by intervention using robot suit hybrid assistive limb (HAL) in myelopathy patients after decompression surgery for ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament. Front Neurorobot. 2021;15:650118. [33] TAMBURELLA F, TAGLIAMONTE NL, PISOTTA I, et al. Neuromuscular controller embedded in a powered ankle exoskeleton: effects on gait, clinical features and subjective perspective of incomplete spinal cord injured subjects. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2020;28(5):1157-1167. [34] HONG E, GORMAN PH, FORREST GF, et al. Mobility skills with exoskeletal-assisted walking in persons with SCI: results from a three center randomized clinical trial. Front Robot AI. 2020;7:93. [35] JANG YC, PARK HK, HAN JY, et al. Cardiopulmonary function after robotic exoskeleton-assisted over-ground walking training of a patient with an incomplete spinal cord injury: Case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(50):e18286. [36] WU CH, MAO HF, HU JS, et al. The effects of gait training using powered lower limb exoskeleton robot on individuals with complete spinal cord injury. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2018;15(1):14. [37] SUTOR TW, GHATAS MP, GOETZ LL, et al. Exoskeleton training and trans-spinal stimulation for physical activity enhancement after spinal cord injury (EXTra-SCI): an exploratory study. Front Rehabil Sci. 2022;2:789422. [38] YANG A, ASSELIN P, KNEZEVIC S, et al. Assessment of in-hospital walking velocity and level of assistance in a powered exoskeleton in persons with spinal cord injury. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2015;21(2):100-109. [39] GUANZIROLI E, CAZZANIGA M, COLOMBO L, et al. Assistive powered exoskeleton for complete spinal cord injury: correlations between walking ability and exoskeleton control. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019;55(2): 209-216. [40] MOLTEDO M, BACEK T, SERRIEN B, et al. Walking with a powered ankle-foot orthosis: the effects of actuation timing and stiffness level on healthy users. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020;17(1):98. [41] ANTONELLIS P, MOHAMMADZADEH GONABADI A, MYERS SA, et al. Metabolically efficient walking assistance using optimized timed forces at the waist. Sci Robot. 2022;7(64):eabh1925. [42] KIM HS, PARK JH, LEE HS, et al. Effects of wearable powered exoskeletal training on functional mobility, physiological health and quality of life in non-ambulatory spinal cord injury patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(12):e80. [43] TANG X, WANG X, JI X, et al. A wearable lower limb exoskeleton: reducing the energy cost of human movement. Micromachines (Basel). 2022; 13(6):900. [44] RAITHATHA R, CARRICO C, POWELL ES, et al. Non-invasive brain stimulation and robot-assisted gait training after incomplete spinal cord injury: a randomized pilot study. NeuroRehabilitation. 2016;38(1):15-25. [45] YOZBATIRAN N, KESER Z, DAVIS M, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) of the primary motor cortex and robot-assisted arm training in chronic incomplete cervical spinal cord injury: a proof of concept sham-randomized clinical study. NeuroRehabilitation. 2016;39(3):401-411. [46] CUI Z, LI Y, HUANG S, et al. BCI system with lower-limb robot improves rehabilitation in spinal cord injury patients through short-term training: a pilot study. Cogn Neurodyn. 2022;16(6):1283-1301. [47] KRENN MJ, WHITE JM, STOKIC DS, et al. Neuromodulation with transcutaneous spinal stimulation reveals different groups of motor profiles during robot-guided stepping in humans with incomplete spinal cord injury. Exp Brain Res. 2023;241(2):365-382. [48] LI Y, WEI B, ZHONG Y, et al. A bibliometric analysis of global research on spinal cord injury: 1999-2019. Spinal Cord. 2022;60(4):281-287. [49] LIU S, SONG L, DAI W, et al. Worldwide productivity and research trend of publications concerning electroactive materials and spinal cord injury: a bibliometric study. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1094059. [50] RODRIGUEZ-FERNANDEZ A, LOBO-PRAT J, FONT-LLAGUNES JM. Systematic review on wearable lower-limb exoskeletons for gait training in neuromuscular impairments. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021;18(1):22. [51] RAJASEKARAN V, LOPEZ-LARRAZ E, TRINCADO-ALONSO F, et al. Volition-adaptive control for gait training using wearable exoskeleton: preliminary tests with incomplete spinal cord injury individuals. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2018;15(1):4. [52] WU AR. Human biomechanics perspective on robotics for gait assistance: challenges and potential solutions. Proc Biol Sci. 2021;288(1956):20211197. [53] ZHAO D, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Double-target neural circuit-magnetic stimulation improves motor function in spinal cord injury by attenuating astrocyte activation. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):1062-1066. [54] SUTOR TW, KURA J, MATTINGLY AJ, et al. The effects of exercise and activity-based physical therapy on bone after spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020608. [55] MICKENS MN, PERRIN P, GOLDSMITH JA, et al. Leisure-time physical activity, anthropometrics, and body composition as predictors of quality of life domains after spinal cord injury: an exploratory cross-sectional study. Neural Regen Res. 2022n;17(6):1369-1375. [56] GORACZKO A, ZUREK G, LACHOWICZ M, et al. Quality of life after spinal cord injury: a multiple case study examination of elite athletes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(20):7437. [57] NIZEYIMANA E, JOSEPH C, PHILLIPS J. Quality of life after traumatic spinal cord injury in a developing context: the influence of contextual factors and injury characteristics. Disabil Rehabil. 2022;44(10):2020-2026. [58] JO HJ, PEREZ MA. Corticospinal-motor neuronal plasticity promotes exercise-mediated recovery in humans with spinal cord injury. Brain. 2020; 143(5):1368-1382. [59] SANTAMARIA V, LUNA TD, AGRAWAL SK. Feasibility and tolerance of a robotic postural training to improve standing in a person with ambulatory spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2021;7(1):94. [60] SUN T, DAI Z, MANOONPONG P. Robust and reusable self-organized locomotion of legged robots under adaptive physical and neural communications. Front Neural Circuits. 2023;17:1111285. [61] XIANG XN, ZONG HY, OU Y, et al. Exoskeleton-assisted walking improves pulmonary function and walking parameters among individuals with spinal cord injury: a randomized controlled pilot study.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021;18:86. [62] CHEN SJ, WANG ZB, LI YQ, et al. Safety and feasibility of a novel exoskeleton for locomotor rehabilitation of subjects with spinal cord injury: a prospective, multi-center, and cross-over clinical trial. Front Neurorobot. 2022;16:848443. [63] NISTOR-CSEPPENTO CD, GHERLE A, NEGRUT N, et al. The outcomes of robotic rehabilitation assisted devices following spinal cord injury and the prevention of secondary associated complications. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(10):1447. [64] GIL-AGUDO A, MEGIA-GARCIA A, PONS JL, et al. Exoskeleton-based training improves walking independence in incomplete spinal cord injury patients: results from a randomized controlled trial. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2023;20:36. |
| [1] | 宋佳婷, 陈建敏, 王柯文, 黄蓝莹, 徐森明, 桂裕昌, 许建文. 创伤性脊髓损伤患者血清和尿液的代谢组学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | 周邦瑜, 李 杰, 阮玉山, 耿福能, 李绍波. 美洲大蠊研粉干预脊髓半横断大鼠运动功能和自噬蛋白Beclin-1的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1223-1228. |
| [3] | 徐灿丽, 何文星, 汪 磊, 吴芳婷, 王佳慧, 段雪琳, 赵铁建, 赵 斌, 郑 洋. 肝脏类器官研究的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104. |
| [4] | 孙宇康, 宋丽娟, 温春丽, 丁智斌, 田 昊, 马 东, 马存根, 翟晓艳. 基于Web of Science近十年干细胞治疗心肌梗死的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1143-1148. |
| [5] | 曾凡卓, 李雨欣, 孙嘉晨, 谷欣阳, 文 山, 田 鹤, 梅晰凡. 脊髓损伤模型小胶质细胞的高效移植替换策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [6] | 刘 涛, 张文凯, 马子谦, 张 焱, 陈学明. 利鲁唑干预脊髓损伤大鼠小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体的活化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1036-1042. |
| [7] | 陈泽鹏, 侯永辉, 陈树东, 侯 宇, 林定坤. 牛磺熊去氧胆酸干预缺糖缺氧条件下脊髓神经元的凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [8] | 张 明, 王 斌, 贾 凡, 陈 杰, 唐 玮. 基于脑电图的脑机接口技术在脑卒中患者上肢运动功能康复中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 581-586. |
| [9] | 高永昌, 付彦涛, 赵 昕, 崔庆峰, 张志峰, 陈世斌. 步行运动下缺血性坏死股骨头力学性能及塌陷风险预测[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(33): 5265-5269. |
| [10] | 袁艳丽, 潘月军, 关天民, 程 楷, 王相恒. 中外脊柱侧弯矫形器的文献计量学与可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(33): 5396-5402. |
| [11] | 宋佳婷, 陈建敏, 王柯文, 黄蓝莹, 徐森明, 桂裕昌, 许建文. 创伤性脊髓损伤患者血清和尿液的代谢组学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(32): 5085-5090. |
| [12] | 闫 杰, 周 静, 赵敬璞, 张清芳, 周明超, 王玉龙. 高精度经颅直流电刺激研究热点的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(32): 5110-5115. |
| [13] | 滕益霖, 席德双, 冯彦斌, 梁 宇, 邓 豪, 曾高峰, 宗少晖. 吲哚丙酸抑制小胶质细胞M1极化治疗脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(31): 5010-5016. |
| [14] | 张 妍, 张文凯, 张雯秀, 刘 涛, 马子谦, 陈学明. Circ0005512促进雌性大鼠脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞焦亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(31): 5029-5035. |
| [15] | 陶广义, 王琳梓, 杨 彬, 黄俊卿. 人工智能在脊柱畸形领域研究热点的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(30): 4915-4920. |
CiteSpace是一款基于JAVA 语言开发的文献分析软件,可通过采集时间信息显示学科前沿动态变化并集中展现于网络图谱,从而实现将某个知识领域演进历程可视化[9]。该软件一经开发成功,即受到医学界、教育学界等学界关注。文章利用 CiteSpace 6.2.R4软件对Web of Science核心数据库中2014-2023年脊髓损伤后EAW康复研究热点、高影响力国家(地区)、机构、高被引作者、高被引文献、高频关键词及突变术语等内容进行可视化处理,对国内外脊髓损伤后步行功能康复研究热点与前沿趋势进行分析和追踪,为今后该领域科学研究工作探究提供思路和依据。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在 2023年9月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时限限制为 2014-01-01/2023-09-01。
1.1.3 检索数据库 Web of Science核心集数据库。1997年由美国Thomson公司将SCI(Science Citation Index),SSCI(Social Science Citation Index)及AHCI(Arts & Humanities Citation Index)整合创建,是全球最大、覆盖学科最多综合性学术信息资源,收录包括自然科学、工程技术及生物医学等各研究领域最具影响力的近1.4万种核心学术期刊(尚包括2.8万种电子期刊,1 079万条研究数据等)。Web of Science推出的影响因子(Impact Factor,IF)已成为国际通用期刊有用性、显示度、学术水平与论文质量评价标杆。网址:https://www.webofscience.com/wos/alldb/basic-search。
1.1.4 检索词 主题词包括“Spinal Cord Injury,SCI”“walk”“robot”等内容,按设计主题词检索方式进行检索,具体参见表1。

1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 选择 Web of Science核心合集,基于布尔逻辑运算符号——逻辑与“AND”、逻辑或“OR”、逻辑非“NOT”等进行检索,选择主题TS,搜索框中输入“robot OR exoskeleton OR (exoskeleton-assisted walking) OR EAW”,检索策略见表1,检索全部文献共670篇,进一步将出版年设置为 2014-01-01/2023-09-01,检索文献类型按“论文、会议录论文、综述论文、在线发表”进行限制,共剔除126篇文献,最后纳入研究文献数目为544篇。
1.2 入组标准1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与脊髓损伤后外骨骼机器人辅助步行康复研究相关文献;②所纳入文献论点、论据可靠;③文献来源于JCR分区Q1、Q2、Q3、Q4收录的期刊文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 与文章内容相关度不高或不相关文献。
1.3 数据分析
1.3.1 数据操作处理流程 将纳入文献设定为“全记录与引用的参考文献”,并以纯文本形式导出,以“download_1-500.txt,download_501-X.txt”等专用文件名(每500条记录合计为一个输出文本)存于指定“input”文件夹中,然后应用 CiteSpace 6.2.R4 软件绘制科学知识图谱。打开软件后主界面中选择“Agree”,并进入操作界面,选择“New新建”,弹出“New Project”界面,自行命名“Title”“Project Home”中输入原指定储存“input”文件夹,“Data Directory”中输入与“input”同一路径另一命名为“Output”的空白文件夹路径;“Data Source”选择“WOS”(Web of Science),“Preterred Language”选择“English”,而后保存Save。保存后页面自动返回至原“New”界面。依次进行具体参数设置,设置完成后点击“Go!”运行,系统将自行运行分析处理数据,弹出“Your Options”界面,确定“Visualize可视化”处理。系统继续可视化处理并弹出分析图谱界面,展示“Spotlight 关键路径”“Burst热点”等信息,操作者可根据具体分析内容通过控制面板、图谱界面上端工具栏工具进行进一步精细化处理,结果可以“Save as PNG”“Save as PDF”等格式进行保存。
1.3.2 参数设置 ①Time Slicing (时区划分): 设定为 2014 年 1 月至2023 年9月,默认1年为 1 个时区段;②Term Source (主题词术语来源) :默认全选;③Node Types (节点类型):可分别选择Country(施引文献国家合作分析)、Institution(施引文献机构合作分析)、Author(施引文献作者合作分析)、Keyword (施引文献关键词分析);Reference(被引文献共被引分析)、Cited Author(被引文献作者共被引分析)、Cited Journal(被引文献期刊共被引分析)逐一分析处理;④Selection Criteria(节点筛选方式)中 g-index中“k”值可根据数据处理后保证全部数据均纳入处理环节(即网络大小)动态增减比例参数k(k值越大,网络越大),系统默认值为25;Top N(阈值)指每个时区划分中提取N个被引次数最高的文献,N越大生成网络相对更全面一些,系统默认设置选择 Top N=50;⑤Pruning (剪裁方式) 选择:对作者与机构科学合作网络进行分析时,可选择:Pathfinder(开拓者,作用简化网络突出重要结构特征);系统同步自动勾选Pruning sliced networks(每个网络);对关键词共现、被引作者和被引文献共被引分析,可选择Minimum Spanning Tree (最小生成树精简算法),Pruning merged networks(综合网络)。
1.3.3 研究热点分析 文章热点分析策略[10]:①被引文献共被引分析:是1篇文献被 2 篇或多篇文献同时参考引用,可用于预测该领域在一定时间范围内研究热点及趋势;②关键词共现分析:关键词是文章主要内容提炼,出现次数越多代表研究主题热度越高,对关键词进行共现分析,可体现该领域研究热点,以中介中心性(Betweenness centrality)为衡量依据,中介中心性是衡量文献关键词重要性的一个量化指标,取值为0-1,中心性越高则表示影响力越大,中介中心性超过0.1的节点称为关键节点;③关键词聚类分析:可提供该领域研究类团情况,即将关联紧密的关键词聚成一类,观察目前该技术/学科领域形成了哪些研究类团,聚类号越小则类团中成员数量越多;轮廓值表示类团内部成员间紧密程度,当其> 0.7 时表示紧密良好或类团成员类似,聚类比较成功;④关键词突现分析:关键词突现指某一时期文献中突然大量出现特定词语,可用于发现某一领域研究呈现从宏观到微观、从单一到多元化演化趋势,回顾或预测关键分支技术成为热点事件,甚至未来延续爆发趋势;⑤关键词时间线图分析:指观察单一聚类里关键词随时间演化状况。
1.4 主要观察指标 包括施引文献国家/机构/作者合作分析,施引文献关键词分析,被引文献文献/作者/期刊共被引分析等,利用综合可视化图谱及Web of Science核心集数据库文献计量学功能进行分析结果。
首先,从机制角度研究发现目前研究重点为适应性控制为主,具体方式可能包括:①EAW可能对脊髓损伤患者躯干肌群有适应性控制继而激活作用,并与损伤程度密切相关。OKAWARA等[30]研究发现对患有慢性脊髓损伤的9例老年患者在采用自主驱动外骨骼的减重支持跑步训练20次后,患者躯干肌肉力量得到很大改善、核心适应性控制能力增强。证明外骨骼机器人步行训练方法可能对脊髓损伤患者(尤其老年)躯干肌群具有适应性控制及激活作用。除此之外,有研究为一例ASIA C级不完全性脊髓损伤患者提供单关节混合辅助肢体踝关节单元康复治疗,还发现外骨骼医用机器人也可诱导激活患者下肢肌群出现自主肌肉电位活动,即EAW可能通过促进神经电活动变化加强机体适应性控制下肢肌肉运动的能力[31]。在中国,XIANG等[7]对15-75岁28例胸腰椎完全性脊髓损伤患者进行外骨骼辅助步行训练2周,发现患者下肢运动评分(LEMS)均无改善,但Hoffe步行能力分级、脊髓独立性评分和脊髓损伤 II步行指数均发生变化,提示采用新型机器人外骨骼计划也可能为完全性脊髓损伤患者提供潜在的有意义的行动能力改善。②EAW对脊髓损伤患者下肢肌力、关节活动范围、痉挛程度、疼痛评分等可能有一定改善作用。有研究对15例诊断为后纵韧带骨化减压术后脊髓损伤患者进行混合辅助肢体(HAL)干预,结果显示患者组步态速度、步幅距离都有显著改善,患者组双侧髋、膝关节活动范围(ROM)也显著增加[32]。此外,TAMBURELLA等[33]研究证实动力外骨骼Achilles可改善不完全性脊髓损伤患者自由步行速度、提高肌力评分,进而改善肢体痉挛MAS评分、减少疼痛感觉目测类比评分。这些研究均进一步证实EAW康复干预对于促进脊髓损伤后患者中枢神经可塑性提高、躯干下肢适应性控制至关重要。
其次,随着科学技术不断进步发展,研究者们将各类外骨骼机器人产品越来越多投入实践,尤其在医学康复领域实现临床应用。例如,对EAW作用于脊髓损伤患者改善下肢步行运动功能方面进行过较多临床实践研究:HONG 等[34]通过试验确定了为达到足够EAW技能和速度至少所需训练的数量频次与质量效能百分比——建议每周至少进行36次训练,并力争12周内完成,百分比应达到62%及以上。TSAI等[8]则将试验推进至脊髓损伤急性阶段进行研究,他们对10例符合运动训练条件的急性脊髓损伤患者进行了EAW干预,结果证实将EAW纳入脊髓损伤急性住院康复流程对促进患者运动功能恢复可能有助益。此外,临床研究还发现EAW也可能通过其他机制改善脊髓损伤患者运动功能及代谢指标。既往研究证实EAW可达到脊髓损伤患者中等强度运动预期效果并有效降低运动负荷,例如,JANG等[35]对1例诊断为C3/4不完全脊髓损伤患者训练6周后,发现其在计时起跑试验中步速提高,通过代谢当量和VO2试验测量的心功能也增强,证实使用外骨骼机器人进行步行训练可改善不完全慢性颈髓损伤患者心肺功能。FANG等[28]Meta综述研究证实机器人辅助步态训练能改善脊髓损伤患者痉挛状态及步行能力,与TAMBURELLA等[33]研究不同,该研究认为机器人辅助步态训练后疼痛并无明显变化,且可能原因是地板效应;KWON等[28]对13例完全性脊髓损伤患者进行穿着膝踝足矫形器KAFO与机器人辅助步态对比,结果显示与KAFO相比,机器人使截瘫患者能够以更低能耗步行活动,但二者满意度并无差异。WU等[36]对2例完全性脊髓损伤受试者进行为期8周的动力外骨骼步态训练,结果提示训练后患者骨矿密度有所增加;SUTOR等[37]研究发现,12周EAW训练可显著降低脊髓损伤患者肥胖标志物。因此,EAW对脊髓损伤患者步行运动支持应是综合性效果。
此外,与文章关键词共现聚类分析研究一致,研究者既往对不同类型外骨骼机器人具体功效差异也开展较多研究。
(1)从驱动设计角度分类:①传统Lokomat®、Rewalk®及混合辅助肢体(医用型下肢外骨骼设备)等主要采用刚性电机驱动设计,能承重、行走安全性较有保障,但舒适性欠佳。YANG等[38]证实ReWalk®是一种安全院内行走设备;GUANZIROLI等[39]证实ReWalk®可以让慢性完全性脊髓损伤患者安全进行地面行走,并发现外骨骼下肢运动控制平稳性是促进人机交互、提高受试者行走能力关键因素;②新型EAWExosuit®及XoSoft®等使用柔性气压驱动结构,具有结构轻便舒适特点,但承重能力不足,相较刚性驱动设备更存在跌倒风险[40-41]。
(2)按有无动力源分类:①动力型:将电机、气动及液压驱动等作为动力来源,借助生物或机械传感器在自动控制策略下完成辅助步行。WU等[36]研究发现完全型脊髓损伤患者经8周步态训练可独立使用动力型下肢外骨骼机器人;KIM等[42]证实动力型医疗外骨骼H-MEX训练对非卧床脊髓损伤患者下肢功能、移动能力、生理健康和生活质量均具有积极影响,但也存在质量大、结构臃肿及人机协调性差等缺陷,制约其进一步发展。②无动力型:无需外部能源,可将自身重力势能或运动动能转换到弹性元件并辅助下肢运动,在续航能力、质量、体积及成本等方面具有固有优势,是机器人外骨骼新发展方向[43]。
最后,正如文章关键词共现聚类分析结果,目前研究倾向联合功能性近红外光谱、经颅直流电刺激、脑机接口等高端检测治疗技术,研究者将EAW与功能性近红外光谱、经颅直流电刺激等检测治疗手段联合应用以观察治疗成效。例如,RAITHATHA等[44]将经颅直流电刺激与机器人辅助步态矫形器(LT-RGO)结合,证实二者联用可以较单独使用更有效改善脊髓损伤患者下肢运动功能;YOZBATIRAN等[45]在一项平行组、双盲、随机对照试验中发现,与假刺激和机器人辅助训练联合相比,真性经颅直流电刺激可能通过刺激阳极初级运动皮质(M1)调节皮质脊髓束使得脊髓回路兴奋性增强进而能够更好地改善不完全性四肢瘫患者对侧上肢与手部运动功能,这可能是一项颇有前途的研究策略,后续也可考虑应用于脊髓损伤患者下肢运动功能恢复潜在机制探索;此外,CUI等[46]证实将带有下肢机器人的脑-机接口系统引入脊髓损伤患者短期训练后患者下肢关键肌肉力量得到改善、AISA评级改善,表明下肢机器人脑机接口系统临床应用应是安全可行的,对脊髓损伤患者具有潜在积极影响;KRENN等[47]证实在一定频率范围内应用连续腰骶部经皮脊髓刺激作为改善步态治疗干预时,需更好理解和描述脊髓损伤患者运动控制特征。总之,EAW技术可单独实施,也可与不同技术协同运用[6],对未来临床康复实践、干预措施选择等均有较大价值,值得进一步加大投入研究力度。
3.2 脊髓损伤的EAW研究国家/机构分布、高影响力作者/文献共被引分析 近年来,EAW设备数量、品种、效应逐年增高,通过年度发文量统计可以从宏观上了解外骨骼机器人辅助脊髓损伤患者步行康复训练研究现状。2014年至今,脊髓损伤后EAW康复相关研究文献年度发文量及被引频次总体呈上升趋势,提示EAW在脊髓损伤患者下肢功能康复领域越来越受到重视。国家分布以美国、中国和意大利等国文献数量最多,机构分布以美国退伍军人事务部、美国退伍军人健康管理局、瑞士联邦理工学院居多。 国家分布中介中心性以美国、英国、法国等国居前,芝加哥Shirley Ryan康复中心、西班牙国家最高科学研究委员会CSIC等机构中介中心性排名前列,各国机构间具有良好合作关系。综上所述,美国以发文量、中介中心性均最高居于榜首。中国发文量排全球第二,但因起步晚、研究机构相对分散等缘故,中介中心性方面影响力仍不足。被引文章频次最多、中介中心性最高的作者是美国Pennsylvania大学Alberto Esquenazi A教授。
根据高影响力作者/文献共被引分析,目前在脊髓损伤患者配备动力外骨骼设备进行步行康复方面的研究主要集中在以下几个方面:①真实环境中步行康复训练安全性判断:研究者关注如何在机构、家庭等真实环境中进行步行训练,以确保患者的安全。这方面的研究旨在找到合适的步行训练方法,并评估其对患者的安全性;美国Virginia Tech大学Miller LE所著文献共被引次数最高,文献主要对动力外骨骼辅助步行治疗脊髓损伤临床疗效和安全性进行Meta分析系统评价,结果展示电动外骨骼使脊髓损伤患者能够在真实环境中安全行走,体力活动强度有利于延长使用时间,并有益健康[17]。ASSELIN教授团队[21]最佳中介中心性视频论文则介绍了美国退伍军人事务部对脊髓损伤患者步行功能恢复所设计的个体化康复培训方案,向患者及家属传授在机构、家庭或社区环境中使用动力外骨骼设备所需技能。②优势分析:BAUNSGAARD等[19]及AACH等[20]研究者试图确定动力外骨骼设备在脊髓损伤患者康复过程中的优势。这方面的研究包括比较动力外骨骼设备与传统治疗方法之间的差异,以及评估动力外骨骼设备是否能够提供更好的康复效果和生活质量。③个体化培训计划设计:针对不同的患者个体特点和需求,研究人员致力于设计个体化的培训计划[17]。这方面的研究旨在找到最适合患者的步行训练方案,以实现最佳的康复效果。④动力外骨骼设备在胸椎及以下节段运动功能完全丧失脊髓损伤患者中的辅助步行效果优劣:MILLER等 [17]系统回顾关注动力外骨骼设备在完全性脊髓损伤患者中的辅助步行效果,这方面研究旨在评估动力外骨骼设备对患者行走能力的提升程度,并比较不同设备效果。⑤影响因素及应用潜力:TEFERTILLER等[23]及MCLNTOSH等[26]研究人员还致力于探索影响动力外骨骼设备应用效果的因素,例如设备的质量及患者身体状况等。此外,MORAWIETZ等[22]也在研究动力外骨骼设备在其他领域的潜在应用,以拓展其康复应用的范围。以上研究方向将进一步推动脊髓损伤患者配备动力外骨骼设备进行步行康复的发展和应用。
CiteSpace软件具有“图”“谱”双重性质与特征,文章针对脊髓损伤后外骨骼机器人应用于步态康复方面的研究前沿表征集中展现于结果部分的网络图谱中,图谱上已自动标识作为知识基础的引文节点文献数量、分析对象间相互关联关系、关联密切程度、关联时间范围、关键词共现聚类/突现强度所表征的研究热点前沿等多重信息展示[48-49]。
3.3 脊髓损伤的EAW康复研究热点、前沿与趋势 根据关键词共现聚类分析的结果,近年来脊髓损伤患者步态功能康复研究主要聚焦于外骨骼机器人行走装置设备定性研究。在作用机制方面,适应性控制被广泛应用。目前,外骨骼技术与功能性近红外光谱成像检测的联合研究或成为最新热点方向。此外,往复式步态矫形器、混合辅助肢体和功能性电刺激等多种康复工程技术也被用于促进脊髓损伤患者的步行功能康复。目前最新研究热点方向为外骨骼技术同步功能性近红外光谱成像检测等联合研究。促进脊髓损伤患者步行功能康复方法还包括往复式步态矫形器、混合辅助肢体、功能性电刺激等多种康复工程技术。
(1)目前,脊髓损伤患者外骨骼机器人设备的设计配置趋向于向社区和家庭应用发展[21]。根据KHAN等[5]研究,ReWalk®外骨骼机器人大约需要进行45次训练才能重建严重脊髓损伤患者的步行能力;RODRIGUEZ-FERNANDEZ等[50]对87项临床研究进行综述后发现,可穿戴外骨骼机器人具有多种应用潜力,包括早期康复、促进体育锻炼、在家和社区进行日常生活活动、改善非流动人群的行动能力和独立性等。
(2)对脊髓损伤外骨骼机器人设计具体辅助技术主要着力于适应性控制技术改善,通过应用自适应模糊控制、导纳控制、阻抗控制、步态轨迹规划等理论作为基础[51],对脊髓损伤患者步行运动过程中站立相腿部运动进行调整优化。例如,RAJASEKARAN 等[51]研究发现:基于人类矫形器交互力矩和修改关节阻抗特性,患者特定自适应控制可应用于可穿戴机器人。由大脑直接控制的启动允许将患者意图与外骨骼运动提供的传入刺激同步,最大限度地提高系统在神经康复治疗中的潜力。WU等[52]认为:机器人设备技术进步有可能通过步态辅助改变人类行动能力,但将物理硬件、软件控制算法与患者集成以帮助步态受损仍存在挑战。
(3)脊髓损伤患者进行外骨骼步态辅助机器人设计时可结合经颅磁刺激、近红外光谱成像(fNRI)等技术进行机制分析、控制策略设计、临床应用等研究,这被认为是可穿戴外骨骼机器人未来的研究发展新趋势[47-53]。
(4)脊髓损伤后外骨骼机器人设计仍需考虑参考早期应用于脑卒中患者的传统减重支持、往复式步态矫形器、功能性神经肌肉电刺激、中央模式发生器等步态激活机制与模式[54]。
文章通过关键词突现及时间线图分析发现2020-2023年研究前沿是Quality of life(生活质量)、exercise(运动训练)、body composition(身体结构)等 [50-55]。对脊髓损伤患者而言,提高其生活质量是患者及其家属重点关注的方面[56-57]。KIM等[42]发现新开发可穿戴外骨骼H-MEX对非卧床脊髓损伤患者安全可行,并可能通过辅助两足行走提高患者日常生活质量。研究者可能通过使用智能康复机器人设备、虚拟现实技术等多种手段帮助患者更好管理病情,提供定制化康复方案,改善心理健康。运动训练也在脊髓损伤患者康复过程中起着重要作用,JO等[58]研究表明,对脊髓损伤患者进行针对性非侵入性脊髓突触刺激并结合个体化运动训练可能是促进不同程度瘫痪和脊髓损伤患者运动介导功能恢复的有效策略。预计未来研究将集中于开发创新的运动训练方法和工具,以提高患者运动能力和功能恢复速度,这可能包括使用机器学习算法来优化运动控制和指导系统,以及设计智能化的康复设备和辅助工具。研究人员还将致力于改善机体结构,以促进康复和功能恢复。例如,SANTAMARIA等[59]讨论使用机器人姿势训练改善脊髓损伤患者站立姿势及体态结构的可行性和耐受性。后续研究可能包括使用生物材料和组织工程技术来重建受损的组织和神经,以及开发新的治疗方法、药物、新手术方式等来促进机体结构的修复和再生。这些研究都将有助于提高患者的整体康复效果和生活质量。综上,学科交叉领域研究在脊髓损伤患者个体化下肢步行功能康复中得到重点关注[60]。
3.4 中国脊髓损伤患者EAW康复发展现状及挑战 近年来,脊髓损伤患者EAW康复领域取得显著进展。中国已涌现一批如电子科技大学机器人研究中心、中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院、北航生物医学工程高精尖创新中心等高水平智能型康复机器人研究团队,同时也出现一批拥有包括成都布法罗、北京大艾、深圳迈步及上海傅利叶等自主知识产权的康复机器人制造企业[61-62]。例如,XIANG团队[61]采用前瞻性、单中心、单盲随机对照方法,应用中国成都布法罗公司生产的第四代TEAIDER(瘫痪患者辅助装置)驱动机器人外骨骼对18例脊髓损伤患者进行历时4周共16次50-60 min步行训练,结果证实与常规训练相比,EAW训练对脊髓损伤下胸神经水平个体的肺功能参数有潜在改善作用。CHEN团队[62]采用前瞻性、多中心、交叉临床试验,通过对比国产北京大艾公司生产Aiwalker、Ailegs与定制无动力髋膝踝足矫形器(HKAFO)对T6-L2节段脊髓损伤截瘫患者进行步行训练,结果证实T6以下截瘫患者使用Ai-Robot能够安全、有效地行走。然而,同国际发展现状类似[63-64],中国在该领域实际研发、应用过程中同样面临较多挑战和问题,包括:①设备使用安全性衡量:例如,CHEN团队[62]临床试验发现可能由于缺乏使用外骨骼系统经验,患者参与试验过程中可出现皮肤损伤、压疮和骨折等方面不良事件,因此,人工智能机器人使用应在有经验医务人员指导下学习;②外骨骼机器人应用潜力探索:包括上文提及的与应用机制相关的驱动动力源设计选择,如何与其他检测治疗手段结合,外骨骼机器人设计辅助技术优化等诸多问题,例如,有研究团队综述提示,外骨骼机器人的使用极大促进患者更好、更大自主权,以及最佳社会融合,因此如何不断挖掘设备应用潜力仍应是后续工作重中之重[63];③脊髓损伤患者治疗方案选择:近年来,脊髓损伤患者治疗方案选择一直是研究者们关注重点,有研究对脊髓损伤后机器人康复辅助装置的疗效及继发性并发症的预防进行综述研究发现:为增加神经运动康复机会并获得满意结果,机器人、康复及药物等治疗相结合可能是最佳选择之一[63]。与文章关键词突现分析一致,该领域未来研究热点、重点与前沿可能将继续聚焦于提升患者生活质量、增强运动训练能力和改善机体结构。
3.5 研究的局限性 ①文章只纳入了Web of Science核心集数据库,未包括KCI-Korean Journal Database等普通数据库,可能造成小部分相关领域文献未被全面纳入,存在一定局限性;②文章类型主要为英文论文、综述,可能忽略该领域在其他语种(如法语、德语及日语等)及其他形式(如专利等)方面高质量成果,文献检索结果可能不全面;③进行文献检索主题词设计时,可能存在不全及遗漏;④使用CiteSpace软件生成可视化图谱流程中,节点筛选方式、阈值设置、剪裁方式及关键词聚类等信息处理均根据实际情况设定,处理结果可能存在一定程度偏倚现象。
3.6 结论及展望 文章采用Web of Science核心数据库和CiteSpace软件,对国际脊髓损伤后外骨骼机器人辅助步行康复训练研究进行文献计量和可视化分析,尝试总结该领域研究热点,积极预测领域未来研究趋势,为今后相关领域研究提供一定的数据参考。
外骨骼机器人辅助步行康复研究最初主要应用于脑卒中患者。近年来,脊髓损伤后BAW康复研究逐渐受到关注,年度发文量及被引频次呈现上升趋势。在研究技术手段方面,减重支持、往复式步态矫形器和功能性电刺激等技术早期被广泛运用。近年,研究逐步注重EAW联合功能性近红外光谱成像等高端检测技术等应用,研究重点逐渐转向以适应性控制为机制的医用下肢外骨骼设备的研制、安全性提升、应用潜力挖掘等多个前沿方向。该领域未来研究热点、重点与前沿可能将持续聚焦于提升患者生活质量、增强运动训练能力和改善机体结构。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是由于创伤性或非创伤性原因对脊髓造成损伤,导致患者出现运动、感觉及大小便等功能障碍的严重致残性疾病,常见引起截瘫,甚至四肢瘫痪。外骨骼机器人辅助步行:是一种新型辅助步行技术,由典型穿戴外骨骼机器人设备执行,患者通过惯性测量单元、压力传感器及驱动器等传达运动意图,与外骨骼形成人机紧耦合系统,控制外骨骼机器人完成对应肢体动作,从而实现康复训练或辅助步行运动。
文章利用Web of Science核心数据库,通过CiteSpace可视化分析软件绘制与发文量、国家/机构合作、高影响力作者/文献共被引、关键词共现/聚类/突现等信息相关科学知识图谱,结合既往研究证据,探讨近10年运用外骨骼机器人对脊髓损伤患者开展辅助步行康复的研究现状、热点和未来发展趋势。研究清晰展示各关键内容间关联性和发展动态,为研究人员提供全面而准确的信息基础,以便更好地指导未来研究方向和临床实践。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||