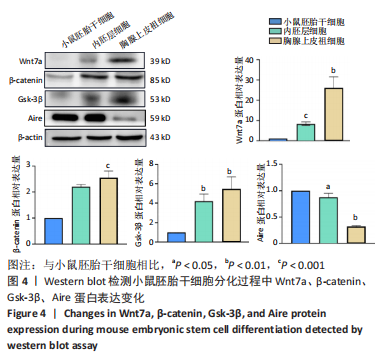
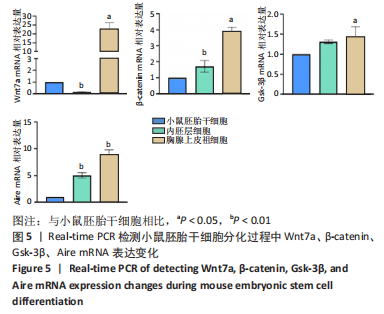
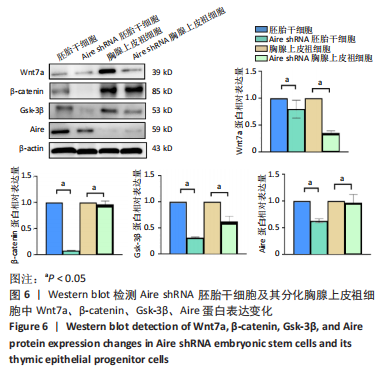
[1] HUR YH, FENG S, WILSON KF, et al. Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Maintain ESC Stemness by Activating FAK. Dev Cell. 2021;56(3):277-291.e6.
[2] KALTSCHMIDT C, GREINER JFW, KALTSCHMIDT B. The Transcription Factor NF-κB in Stem Cells and Development. Cells. 2021;10(8):2042.
[3] NAGAMINE K, PETERSON P, SCOTT HS, et al. Positional cloning of the APECED gene. Nat Genet. 1997;17(4):393-398.
[4] HUBERT FX, KINKEL SA, CREWTHER PE, et al. Aire-deficient C57BL/6 mice mimicking the common human 13-base pair deletion mutation present with only a mild autoimmune phenotype. J Immunol. 2009; 182(6):3902-3918.
[5] NISHIKAWA Y, HIROTA F, YANO M, et al. Biphasic Aire expression in early embryos and in medullary thymic epithelial cells before end-stage terminal differentiation. J Exp Med. 2010;207(5):963-971.
[6] LAAN M, PETERSON P. The many faces of aire in central tolerance. Front Immunol. 2013;4:326.
[7] ABRAMSON J, GIRAUD M, BENOIST C, et al. Aire’s partners in the molecular control of immunological tolerance. Cell. 2010;140(1): 123-135.
[8] FIERABRACCI A. Recent insights into the role and molecular mechanisms of the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10(3):137-143.
[9] ŽUMER K, PLEMENITAŠ A, SAKSELA K, et al. Patient mutation in AIRE disrupts P-TEFb binding and target gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(18):7908-7919.
[10] ANDERSON MS, VENANZI ES, CHEN Z, et al. The cellular mechanism of Aire control of T cell tolerance. Immunity. 2005;23(2):227-239.
[11] DANSO-ABEAM D, HUMBLET-BARON S, DOOLEY J, et al. Models of aire-dependent gene regulation for thymic negative selection. Front Immunol. 2011;2:14.
[12] LI D, ZHAO B, LUO Y, et al. Transplantation of Aire-overexpressing bone marrow-derived dendritic cells delays the onset of type 1 diabetes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;49:13-20.
[13] SIDRAT T, REHMAN ZU, JOO MD, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Pathway-Mediated PPARδ Expression during Embryonic Development Differentiation and Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1854.
[14] LIANG W, HAN P, KIM EH, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling promotes pacemaker cell specification of cardiac mesodermal cells derived from mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2020;38(3): 352-368.
[15] DENG Y, LAO Y, RUAN Q, et al. Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Enhances the Derivation of Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Embryonic Stem Cell-Like Cells. Cell Reprogram. 2020;22(4):217-225.
[16] NAITO AT, SHIOJIMA I, AKAZAWA H, et al. Developmental stage-specific biphasic roles of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cardiomyogenesis and hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(52):19812-19817.
[17] UENO S, WEIDINGER G, OSUGI T, et al. Biphasic role for Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cardiac specification in zebrafish and embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(23):9685-9690.
[18] GORDON J, WILSON VA, BLAIR NF, et al. Functional evidence for a single endodermal origin for the thymic epithelium. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5(5):546-553.
[19] SU M, HU R, JIN J, et al. Efficient in vitro generation of functional thymic epithelial progenitors from human embryonic stem cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9882.
[20] SU M, SONG Y, HE Z, et al. Administration of embryonic stem cell-derived thymic epithelial progenitors expressing MOG induces antigen-specific tolerance and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Autoimmun. 2015;58:36-47.
[21] GILL J, MALIN M, HOLLÄNDER GA, et al. Generation of a complete thymic microenvironment by MTS24(+) thymic epithelial cells. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(7):635-642.
[22] BENNETT AR, FARLEY A, BLAIR NF, et al. Identification and characterization of thymic epithelial progenitor cells. Immunity. 2002; 16(6):803-814.
[23] ROSSI SW, JENKINSON WE, ANDERSON G, et al. Clonal analysis reveals a common progenitor for thymic cortical and medullary epithelium. Nature. 2006;441(7096):988-991.
[24] LAI L, JIN J. Generation of thymic epithelial cell progenitors by mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(12):3012-3020.
[25] KIKUCHI A, YAMAMOTO H, SATO A. Selective activation mechanisms of Wnt signaling pathways. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19(3):119-129.
[26] ANGERS S, MOON RT. Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(7):468-477.
[27] PAIGE SL, OSUGI T, AFANASIEV OK, et al. Endogenous Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is required for cardiac differentiation in human embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2010;5(6):e11134.
[28] SLAWNY NA, O’SHEA KS. Dynamic changes in Wnt signaling are required for neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011;48(3):205-216.
[29] DZOBO K, VOGELSANG M, PARKER MI. Wnt/β-Catenin and MEK-ERK Signaling are Required for Fibroblast-Derived Extracellular Matrix-Mediated Endoderm Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015;11(5):761-773.
[30] LEE H, HALLER C, MANNEVILLE C, et al. Identification of Small Molecules Which Induce Skeletal Muscle Differentiation in Embryonic Stem Cells via Activation of the Wnt and Inhibition of Smad2/3 and Sonic Hedgehog Pathways. Stem Cells. 2016;34(2):299-310.
[31] WANG Q, SONG JW, LIU Y, et al. Involvement of Wnt pathway in ethanol-induced inhibition of mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation. Alcohol. 2017;58:13-18.
[32] 李远迪,马静怡,余佳珊.Wnt7a/β-连环蛋白/自身免疫调节因子信号通路参与1型糖尿病的发生[J].解剖学报,2022,53(4):453-460.
[33] GU B, ZHANG J, CHEN Q, et al. Aire regulates the expression of differentiation-associated genes and self-renewal of embryonic stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394(2):418-423.
[34] KAWANO H, NISHIJIMA H, MORIMOTO J, et al. Aire Expression Is Inherent to Most Medullary Thymic Epithelial Cells during Their Differentiation Program. J Immunol. 2015;195(11):5149-5158.
[35] NISHIJIMA H, KAJIMOTO T, MATSUOKA Y, et al. Paradoxical development of polymyositis-like autoimmunity through augmented expression of autoimmune regulator (AIRE). J Autoimmun. 2018;86:75-92.
[36] SPECK-HERNANDEZ CA, ASSIS AF, FELICIO RF, et al. Aire Disruption Influences the Medullary Thymic Epithelial Cell Transcriptome and Interaction With Thymocytes. Front Immunol. 2018;9:964.
|