中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1712-1718.doi: 10.12307/2023.956
• 脊柱组织构建 spinal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
miR-206对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠髓核炎症、镇痛及自噬相关蛋白的作用机制
王 美,索 娜,于 欢,杨建博
- 哈励逊国际和平医院,河北省衡水市 053000
Mechanism of miR-206 on inflammation, analgesia and autophagy related proteins in nucleus pulposus of rats with lumbar disc herniation
Wang Mei, Suo Na, Yu Huan, Yang Jianbo
- Harrison International Peace Hospital, Hengshui 053000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
自噬:是由 Ashford 和 Porter 在 1962年发现细胞内有“自己吃自己”的现象后提出的,是指从粗面内质网的无核糖体附着区脱落的双层膜包裹部分胞质和细胞内需降解的细胞器、蛋白质等成分形成自噬体(autophagosome),并与溶酶体融合形成自噬溶酶体,降解其所包裹的内容物,以实现细胞本身的代谢需要和某些细胞器的更新。miRNA:是一类内生的、长度为20-24个核苷酸的小RNA,其在细胞内具有多种重要的调节作用。miRNA不仅在基因位置上保守,序列上也呈现出高度的同源性。miRNA高度的保守性与其功能的重要性有密切的关系,与其靶基因的进化有密切的联系,研究其进化历史有助于进一步了解其作用机制和功能。
背景:研究发现,腰椎间盘突出症患者的疼痛机制与炎症相关,自噬与椎间盘疾病及炎症反应密切相关,miR-206表达异常可促进骨骼疾病的发生。
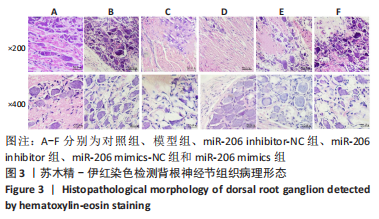
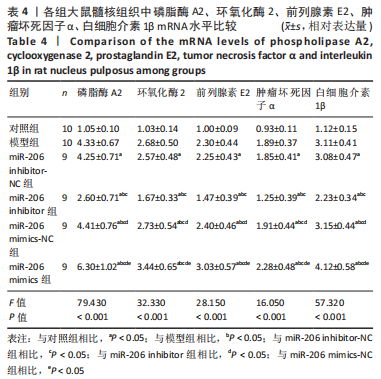
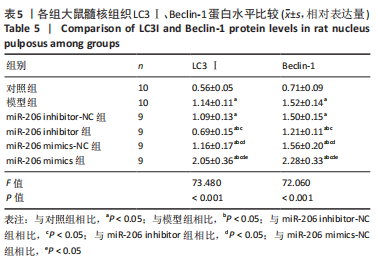
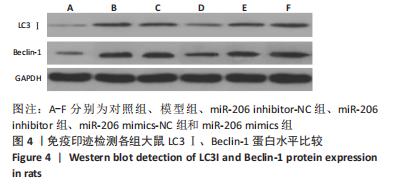
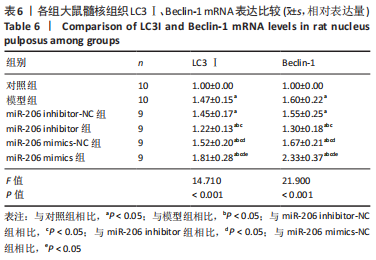
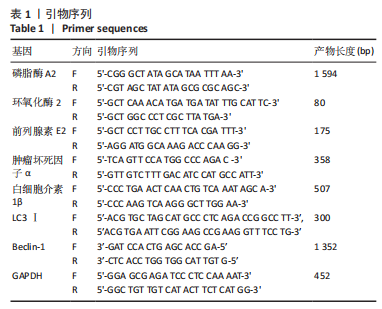
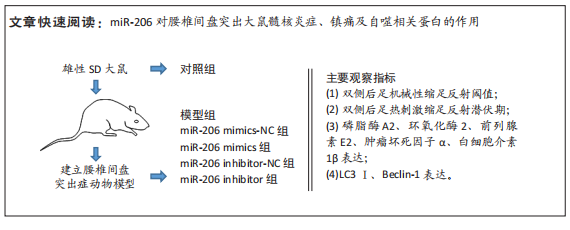
目的:探讨miR-206对腰椎间盘突出大鼠髓核炎症、镇痛及自噬相关蛋白的作用机制。方法: SPF级雄性SD大鼠60只按照随机数字方法分为对照组、模型组、miR-206 mimics-NC组、miR-206 mimics组、miR-206 inhibitor-NC组及miR-206 inhibitor组。除对照组外均建立腰椎间盘突出症大鼠模型,建模后第10天miR-206 mimics-NC组、miR-206 mimics组、miR-206 inhibitor-NC组及miR-206 inhibitor组分别在损伤处注射miR-206 mimics-NC、miR-206 mimics(miR-206模拟物)、miR-206 inhibitor-NC及miR-206 inhibitor(miR-206抑制物),均20 μmol/L,10 μL,1次/d,连续注射4 d;对照组及模型组均注射等剂量生理盐水。Von Frey 纤维丝测定大鼠双侧后足机械性缩足反射阈值,热痛测试仪检测大鼠双侧后足热刺激缩足反射潜伏期;苏木精-伊红染色观察背根神经节组织形态;qPCR检测各组大鼠髓核组织炎症因子磷脂酶A2、环氧化酶2、前列腺素E2、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β表达;免疫印迹检测自噬相关蛋白LC3Ⅰ、Beclin-1表达。
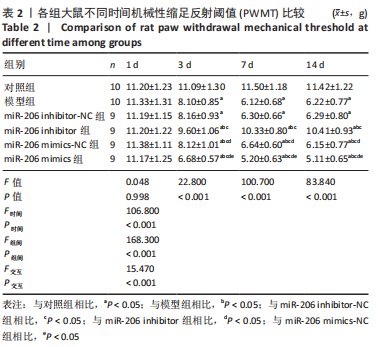
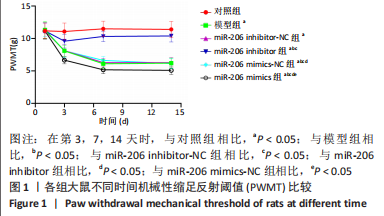
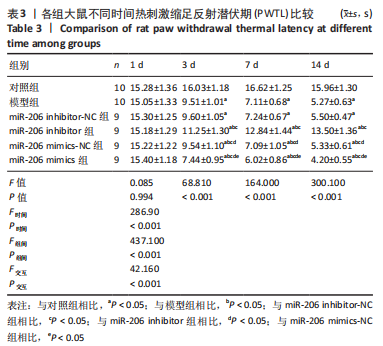
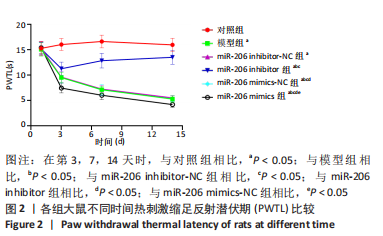
结果与结论:①造模后3,7及14 d时,与对照组相比,模型组大鼠机械性缩足反射阈值、热刺激缩足反射潜伏期降低,磷脂酶A2、环氧化酶2、前列腺素E2、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、LC3Ⅰ、Beclin-1表达升高(P < 0.05);miR-206 inhibitor-NC组、miR-206 mimics-NC组上述指标与模型组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②与miR-206 mimics-NC组相比,miR-206 mimics组大鼠机械性缩足反射阈值、热刺激缩足反射潜伏期降低,磷脂酶A2、环氧化酶2、前列腺素E2、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、LC3Ⅰ、Beclin-1水平升高(P < 0.05);与miR-206 inhibitor-NC组相比,miR-206 inhibitor组大鼠上述指标呈相反变化,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③结果说明,抑制miR-206可以显著改善腰椎间盘突出症大鼠髓核炎症因子水平,提高疼痛阈值,降低细胞自噬,其作用机制与抑制LC3Ⅰ、Beclin-1表达相关。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4759-6150(王美)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: