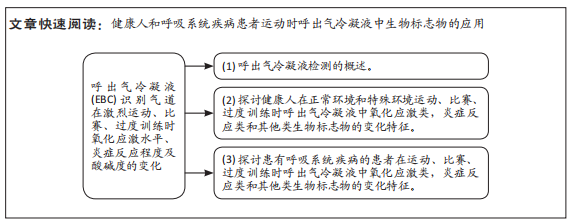
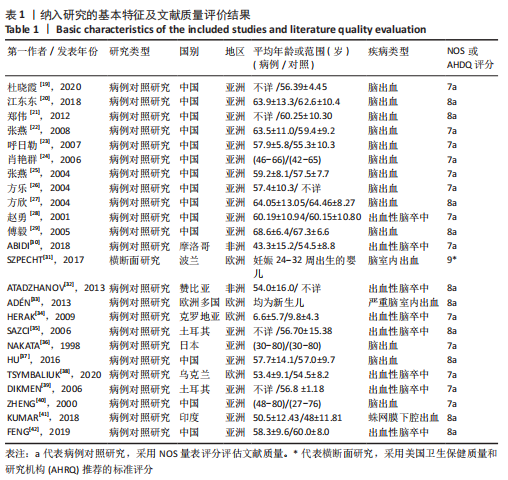
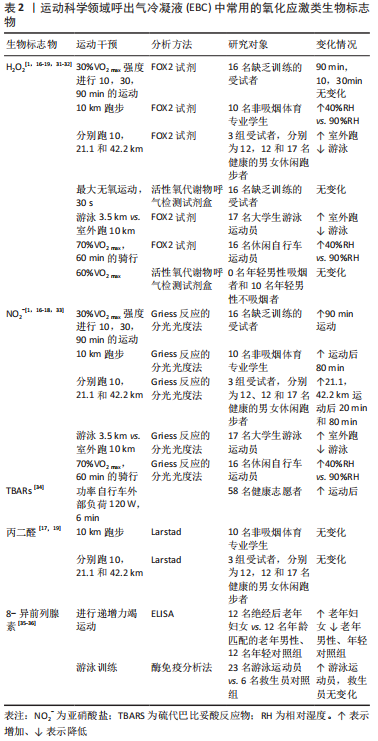
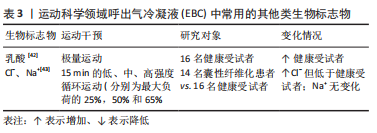
[1] TUESTA M, ALVEAR M, CARBONELL T, et al. Effect of exercise duration on pro-oxidants and pH in exhaled breath condensate in humans. J Physiol Biochem. 2016;72(2):353-360.
[2] DING S, ZHONG C. Exercise and Asthma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1228: 369-380.
[3] ANDERSON SD, KIPPELEN P. Airway injury as a mechanism for exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in elite athletes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122(2):225-235.
[4] CARLSEN KH. Sports in extreme conditions: The impact of exercise in cold temperatures on asthma and bronchial hyper-responsiveness in athletes. Br J Sports Med. 2012;46(11):796-799.
[5] NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HEALTH N H, LUNG, AND BLOOD INSTITUTE. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). http://www.ginasthmaorg, 2006.
[6] MAREK E, VOLKE J, MÜCKENHOFF K, et al. Exercise in cold air and hydrogen peroxide release in exhaled breath condensate. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;756:169-177.
[7] KIPPELEN P, FITCH K D, ANDERSON SD, et al. Respiratory health of elite athletes- preventing airway injury: a critical review. Br J Sports Med. 2012;46(7):471-476.
[8] KUROWSKI M, JURCZYK J, OLSZEWSKA-ZIABER A, et al. A similar pro/anti-inflammatory cytokine balance is present in the airways of competitive athletes and non-exercising asthmatics. Adv Med Sci. 2018;63(1):79-86.
[9] PATSIRIS S, EXARCHOS T, VLAMOS P. Exhaled Breath Condensate(EBC): Is It a Viable Source of Biomarkers for Lung Diseases?. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1195:13-18.
[10] MANISCALCO M, FUSCHILLO S, PARIS D, et al. Clinical metabolomics of exhaled breath condensate in chronic respiratory diseases. Adv Clin Chem. 2019;88:121-149.
[11] 徐百川,李艺婷,赵虎雷,等.呼出气冷凝液生物标志物检测在呼吸系统疾病中的应用现状及前景[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(2): 139-144.
[12] SIDORENKO GI, ZBOROVSKI EI, LEVINA DI. Surface-active properties of the exhaled air condensate (a new method of studying lung function). Ter Arkh. 1980;52(3):65-68.
[13] 孙健,沈巨信.简易呼出气冷凝液收集装置的设计及临床应用[J].实用医学杂志,2010,26(17):3233-3235.
[14] 陈宏,黄莺,余荣环,等.呼出气冷凝液收集器的设计及其临床应用[J].中国临床医学,2013,20(4):498-499.
[15] MATHEUS C, NAKAGAWA NK, DIVA S, et al. Aerobic exercise in polluted urban environments:effects on airway defense mechanisms in young healthy amateur runners. J Breath Res. 2016;10(4):046018.
[16] ARANEDA OF, FELIPE CB, GABRIEL C, et al. Swimming versus running: effects on exhaled breath condensate pro-oxidants and pH. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(11):2319-2329.
[17] ARANEDA OF, GUEVARA AJ, CONTRERAS C, et al. Exhaled breath condensate analysis after long distance races. Int J Sports Med. 2012; 33(12):955-961.
[18] CONTRERAS-BRICEO F, ESPINOSA-RAMIREZ M, VISCOR G, et al. Humidity prevents the exercise-induced formation of hydrogen peroxide and nitrite in exhaled breath condensate in recreational cyclists. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020;120(10):2339-2348.
[19] ARANEDA OF, URBINA-STAGNO R, TUESTA M, et al. Increase of pro-oxidants with no evidence of lipid peroxidation in exhaled breath condensate after a 10-km race in non-athletes. J Physiol Biochem. 2014;70(1):107-115.
[20] CARRARO S, CORRADI M, ZANCONATO S, et al. Exhaled breath condensate cysteinyl leukotrienes are increased in children with exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 115(4):764-770.
[21] Morissette MC, Murray N, Turmel J, et al. Increased exhaled breath condensate 8-isoprostane after a swimming session in competitive swimmers. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(5):569-576.
[22] STELMACH I, ZACZENIUK M, SZTAFIŃSKA A, et al. Serum tryptase level and inflammatory markers in exhaled breath condensate of children with exercise-induced symptoms. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2016;37(5):84-92.
[23] TAHAN F, EKE GH, BICICI E, et al. Increased postexercise lipoxin A4 levels in exhaled breath condensate in asthmatic children with exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2016;26(1):19-24.
[24] CARLSEN KH. Asthma, airway inflammation and epithelial damage in elite athletes. Eur Respir J. 2009;33(4):713-714.
[25] SOMA T, UCHIDA Y, NAKAGOME K, et al. Eicosanoids seasonally impact pulmonary function in asthmatic patients with Japanese cedar pollinosis. Allergol Int. 2020;69(4):594-600.
[26] UCHIDA Y, SOMA T, NAKAGOME K, et al. Implications of prostaglandin D2 and leukotrienes in exhaled breath condensates of asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;123(1):81-88.e1.
[27] KUMAR TC, REDDY KV, ANURADHA D, et al. Enhanced production of LTB4 and free radicals in rat lung by exhaustive physical exercise. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 2010;41(3):641-646.
[28] ALBERCA-CUSTODIO RW, GREIFFO FR, MACKENZIE B, et al. Aerobic Exercise Reduces Asthma Phenotype by Modulation of the Leukotriene Pathway. Front Lmmunol. 2016;7:237.
[29] SERHAN CN. Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxin biosynthesis:an update and role in anti-inflammation and pro-resolution. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002;68:433-455.
[30] NAN C, ARITA M, SERHAN CN. Anti-inflammatory circuitry: lipoxin,aspirin-triggered lipoxins and their receptor ALX. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005;73(3-4):163-177.
[31] TAITO S, SEKIKAWA K, DOMEN S, et al. Pulmonary oxidative stress is induced by maximal exercise in young cigarette smokers. Nicotine Tob Res. 2012;14(2):243-247.
[32] TAITO S, DOMEN S, SEKIKAWA K, et al. Cigarette Smoking does not Induce Plasma or Pulmonary Oxidative Stress after Moderate-intensity Exercise. J Phys Ther Sci. 2014;26(3):413-425.
[33] MAREK E, PLATEN P, VOLKE J, et al. Hydrogen peroxide release and acid-base status in exhaled breath condensate at rest and after maximal exercise in young, healthy subjects. Eur J Med Res. 2009;14(14):134-139.
[34] NOWAK D, KALUCKA S, BIAASIEWICZ P, et al. Exhalation of H2O2 and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARs) by healthy subjects. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001;30(2):178-186.
[35] MORISSETTE MC, MURRAY N, TURMEL J, et al. Increased exhaled breath condensate 8-isoprostane after a swimming session in competitive swimmers. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(5):569-576.
[36] KURTI SP, EMERSON SR, SMITH JR, et al. Older women exhibit greater airway 8-isoprostane responses to strenuous exercise compared with older men and younger controls. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018;43(5): 497-503.
[37] LIANG Y, YELIGAR SM, BROWN L. Exhaled Breath Condensate: A Promising Source for Biomarkers of Lung Disease. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:217518.
[38] RICCIARDOLO FL, STERK PJ, GASTON B, et al. Nitric oxide in health and disease of the respiratory system. Physiol Rev. 2004;84(3):731-765
[39] DEL RIO D, STEWART AJ, PELLEGRINI N. A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2005;15(4):316-328.
[40] FRANKEL EN, NEFF WE. Formation of malonaldehyde from lipid oxidation products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983;754:227.
[41] NIEDERNHOFER LJ, DANIELS JS, ROUZER CA, et al. Malondialdehyde,a product of lipid peroxidation, is mutagenic in human cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(33):31426.
[42] NAKANISHI K, TAJIMA F, NAKAMURA A, et al. Effects of hypobaric hypoxia on antioxidant enzymes in rats. J Physiol. 1995;489(3):869-876.
[43] HENDERSON EM, GASTON B. SNOR and wheeze: the asthma enzyme? Trends Mol Med. 2005;11(11):481-484.
[44] HIRA HS, SHUKLA A, KAUR A, et al. Serum uric acid and lactate levels among patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome:which is a better marker of hypoxemia? Ann Saudi Med. 2012;32(1):37-42.
[45] GHELLI F, PANIZZOLO M, GARZARO G, et al. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath Condensate: A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(17):9820.
[46] HUNT JF, ERWIN E, PALMER L, et al. Expression and activity of pH-regulatory glutaminase in the human airway epithelium. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(1):101-107.
[47] ZHANG J, TONG Z, KIPEN H, et al. Cardiorespiratory biomarker responses in healthy young adults to drastic air quality changes surrounding the 2008 Beijing Olympics. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2013;(174):165-174.
[48] SHOMAN Y, WILD P, HEMMENDINGER M, et al. Reference Ranges of 8-Isoprostane Concentrations in Exhaled Breath Condensate (EBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3822.
[49] FONT-RIBERA L, KOGEVINAS M, ZOCK JP, et al. Short-Term Changes in Respiratory Biomarkers after Swimming in a Chlorinated Pool. Environ Health Pesp. 2010;118(11):1538-1544.
[50] RUNDELL KW, SLEE JB, CAVISTON R, et al. Decreased Lung Function After Inhalation of Ultrafine and Fine Particulate Matter During Exercise is Related to Decreased Total Nitrate in Exhaled Breath Condensate. Inhal Toxicol. 2008;20(1):1-9.
[51] RIEDIKER M, DANUSER B. Exhaled breath condensate pH is increased after moderate exercise. J Aerosol Med. 2007;20(1):13.
[52] GREENWALD R, FERDINANDS JM, TEAGUE WG. Ionic determinants of exhaled breath condensate pH before and after exercise in adolescent athletes. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2010;44(8):768-777.
[53] BIKOV A, LAZAR Z, SCHANDL K, et al. Exercise changes volatiles in exhaled breath assessed by an electronic nose. Acta Physiol Hung. 2011;98(3):321-328.
[54] MERKER MP, PITT BR, CHOI AM, et al. Lung redox homeostasis:emerging concepts. Am J Physiol-Lung C. 2000;279(3):413-417.
[55] FERDINANDS JM, CRAWFORD C, GREENWALD R, et al. Breath acidification in adolescent runners exposed to atmospheric pollution: A prospective, repeated measures observational study. Environ Health. 2008;7:10.
[56] HOSHIKAWA Y, ONO S, SUZUKI S, et al. Generation of oxidative stress contributes to the development of pulmonary hypertension induced by hypoxia. J Appl Physiol. 2001;90(4):1299-1306.
[57] ARANEDA OF, CARBONELL T, TUESTA M. Update on the mechanisms of pulmonary inflammation and oxidative imbalance induced by exercise. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:4868536.
[58] BIKOV A, GALFFY G, TAMASI L, et al. Exhaled breath condensate pH decreases during exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Respirology. 2014;19(4):563-569.
[59] ARANEDA OF, GARCIA C, LAGOS N, et al. Lung oxidative stress as related to exercise and altitude. Lipid peroxidation evidence in exhaled breath condensate:a possible predictor of acute mountain sickness. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2005;95(5-6):383-390.
[60] HEINICKE I, BOEHLER A, RECHSTEINER T, et al. Moderate altitude but not additional endurance training increases markers of oxidative stress in exhaled breath condensate. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009;106(4):599.
[61] 张海婧,徐春雨,胡小键,等.呼出气冷凝液中尿素的高效液相色谱-串联质谱测定法[J].环境与健康杂志,2017,34(2):161-163.
[62] BONSIGNORE MR, GRUTTA SL, CIBELLA F, et al. Effects of exercise training and montelukast in children with mild asthma]. Med Sci Sport Exer. 2008;40(3):405.
[63] ZIETKOWSKI Z, SKIEPKO R, TOMASIAK-LOZOWSKA MM, et al. Endothelin-1 in exhaled breath condensate of allergic asthma patients with exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Resp Res. 2007;82(2):169
[64] MAJAK P, JERZYŃSKA J, BOJO M, et al. Cytokine profiling in exhaled breath condensate after exercise challenge in asthmatic children with post-exercise symptoms. Arch Med Sci. 2016;12:778-784.
[65] WHEATLEY CM, BAKER SE, MORGAN MA, et al. Moderate intensity exercise mediates comparable increases in exhaled chloride as albuterol in individuals with cystic fibrosis. Respir Med. 2015;109(8):1001-1011.
[66] TAITO S, SEKIKAWA K, DOMEN S, et al. Pulmonary oxidative stress is induced by maximal exercise in young cigarette smokers. Nicotine Tob Res. 2012;14(2):243-247.
[67] 吕晓红,陈星海,李洋,等.呼出气冷凝液收集影响因素的探讨[J].中国实验诊断学,2011,15(8):1346-1348.
[68] 吕晓红,李丹,袁海波,等.影响呼出气冷凝液pH值、一氧化氮、过氧化氢测定因素的探讨[J].中国实验诊断学,2012,16(10):1833-1835.
[69] MAREK E, MüCKENHOFF K, STRECKERT HJ, et al. Measurements of L-lactate and H2O2 in exhaled breath condensate at rest and mild to moderate exercise in young and healthy subjects. Pneumologie. 2008;62(9):541.
[70] CHEN X, CHEN W, WANG Y, et al. Responses of healthy young males to fine-particle exposure are modified by exercise habits: a panel study. Environ Health. 2018;17(1):88.
[71] HORVATH I, BARNES PJ, LOUKIDES S, et al. A European Respiratory Society technical standard:exhaled biomarkers in lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2017;26(3):523-548.
[72] RUNDELL KW, SLEE JB. Exercise and other indirect challenges to demonstrate asthma or exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in athletes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122(2):238-246.
[73] 熊小明,童国强,付云杰,等.支气管哮喘-慢性阻塞性肺疾病重叠综合征患者呼出气冷凝液和血清8-isoPG、MPO、LTB4、IL-6的测定及临床意义[J].实用医学杂志,2018,34(4):649-652.
[74] PUCSOK JM, GYOERE I, ARGAY K, et al. Effect of exercise on levels of cyclo-oxygenase mediators in exhaled breath condensate in elite athletes. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2007;47(2):223-227.
[75] LINDSAY A, COSTELLO JT. Realising the potential of urine and saliva as diagnostic tools in sport and exercise medicine. Sports Med. 2016; 47(1):11-31.
[76] CAVALCANTE DE SÁ M, NAKAGAWA NK, SALDIVA DE ANDRÉ CD, et al. Aerobic exercise in polluted urban environments: effects on airway defense mechanisms in young healthy amateur runners. J Breath Res. 2016;10(4):046018.
[77] HORVATH I, BARNES PJ, LOUKIDES S, et al. A European Respiratory Society technical standard:exhaled biomarkers in lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2017;49(4):1600965.
[78] CARPAGNANO GE, LACEDONIA D, FOSCHINO-BARBARO MP. Non-invasive study of airways inflammation in sleep apnea patients. Sleep Med Rev. 2011;15(5):317-326.
[79] MUTLU G, GAREY K, ROBBINS R, et al. Collection and analysis of exhaled breath condensate in humans. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(5):731-737. |