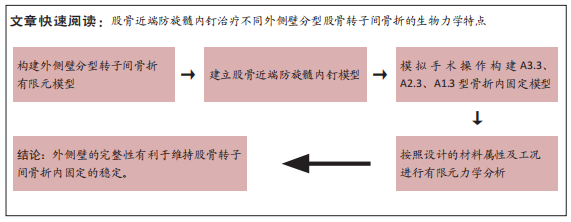
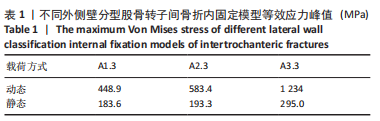
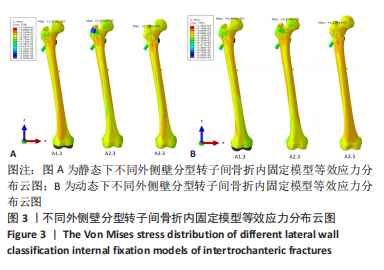
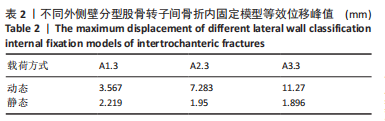
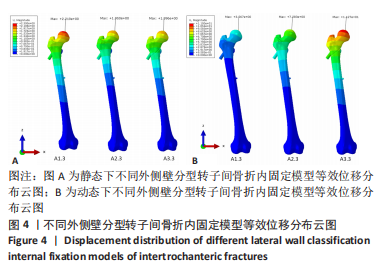
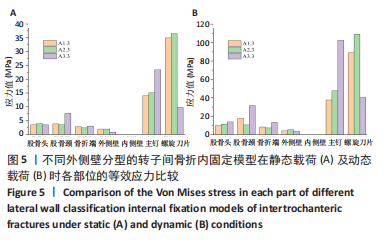
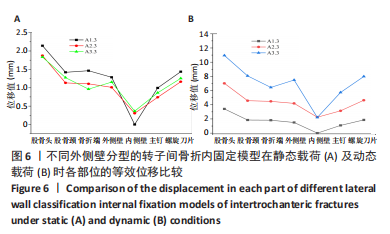
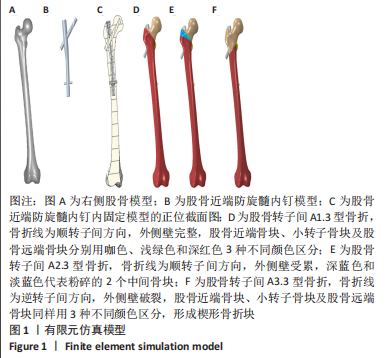
[1] NORRIS R ,PARKER M. Diabetes mellitus and hip fracture: a study of 5966 cases. Injury. 2011;42:1313-1316.
[2] LISK R, YEONG K. Reducing mortality from hip fractures: a systematic quality improvement programme. BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2014;3(1): u205006.w2103.
[3] DYER SM, CROTTY M, FAIRHALL N, et al. A critical review of the long-term disability outcomes following hip fracture. BMC Geriatr. 2016;16(1):158.
[4] BUYUKDOGAN K, CAGLAR O, ISIK S, et al. Risk factors for cut-out of double lag screw fixation in proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2017; 48(2):414-418.
[5] SUN LL, LI Q, CHANG SM. The thickness of proximal lateral femoral wall. Injury. 2016;47(3):784-785.
[6] 郭天庆,薛飞,冯卫.股骨转子间骨折不同外侧壁分型的内固定治疗策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(6):917-923.
[7] HSU CE, SHIH CM, WANG CC, et al. Lateral femoral wall thickness. A reliable predictor of post-operative lateral wall fracture in inter- trochanteric fractures. Bone Joint J. 2013;95- B(8):1134-1138.
[8] GUO Y, YANG HP, DOU QJ, et al. Efficacy of femoral nail anti-rotation of helical blade in unstable intertrochanteric fracture. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(3 Suppl):6-11.
[9] 郑颖捷,李开南.股骨转子间骨折外侧壁的研究进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(2):133-137.
[10] IMERCI A, AYDOGAN NH, TOSUN K. A comparison of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral fail antirotation in the treatment of reverse intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2018;84(2): 123-131.
[11] 陈心敏,罗斯嘉,夏卓伟,等.钉道强化股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年A3.3型股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(27):4265-4271.
[12] YOSIBASH Z, PADAN R, JOSKOWICZ L,et al. A CT-based high-order finite element analysis of the human proximal femur compared to in-vitro experiments. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(3):297-309.
[13] JIANG-JUN Z, MIN Z, YA-BO Y, et al. Finite element analysis of a bone healing model: 1-year follow-up after internal fixation surgery for femoral fracture. Pak J Med Sci. 2014;30(2):343-347.
[14] BERGMANN G, DEURETZBACHER G, HELLER M, et al. Hip contact forces and gait patterns from routine activities. J Biomech. 2001;34(7): 859-871.
[15] CHANG SM, HOU ZY, HU SJ, et al. Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Treatment in Asia: What We Know and What the World Can Learn. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(2):189-205.
[16] GOTFRIED Y. The lateral trochanteric wall: a key element in the reconstruction of unstable pertrochanteric hip fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(425):82-86.
[17] PALM H, JACOBSEN S, SONNE-HOLM S, et al. Integrity of the lateral femoral wall in intertrochanteric hip fractures: an important predictor of a reoperation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(3):470-475.
[18] IM GI, SHIN YW, SONG YJ. Potentially unstable intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(1):5-9.
[19] CHI AS, LONG SS, ZOGA AC, et al. Association of Gluteus Medius and Minimus Muscle Atrophy and Fall-Related Hip Fracture in Older Individuals Using Computed Tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016;40(2):238-242.
[20] HAO Y, ZHANG Z, ZHOU F, et al. Risk factors for implant failure in reverse oblique and transverse intertrochanteric fractures treated with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA). J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1): 350.
[21] VON RÜDEN C, HUNGERER S, AUGAT P,et al. Breakage of cephalomedullary nailing in operative treatment of trochanteric and subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Arch Orthop Taauma Surg. 2015; 135(2):179-185.
[22] GAO Z, LV Y, ZHOU F, et al. Risk factors for implant failure after fixation of proximal femoral fractures with fracture of the lateral femoral wall. Injury. 2018;49(2):315-322.
[23] GADEGONE WM, SHIVASHANKAR B, LOKHANDE V, et al. Augmentation of proximal femoral nail in unstable trochanteric fractures. SICOT J. 2017;3:12.
[24] IMERCI A, AYDOGAN NH, TOSUN K. The effect on outcomes of the application of circumferential cerclage cable following intramedullary nailing in reverse intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(4):835-842.
[25] LEE YK, CHUNG CY, PARK MS, et al. Intramedullary nail versus extramedullary plate fixation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures: decision analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(7):961-968.
[26] 戴寿旺,许兵,余作取,等.髓内固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折中外侧壁的生物力学意义[J].浙江临床医学,2020,22(6):796-798.
[27] 任德新,顾海伦,李赫,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定治疗累及外侧壁的股骨转子间骨折有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018, 20(4):346-351.
[28] MA Z, YAO XZ, CHANG SM. The classification of intertrochanteric fractures based on the integrity of lateral femoral wall: Letter to the editor, Fracture morphology of AO/OTA 31-A trochanteric fractures: A 3D CT study with an emphasis on coronal fragments. Injury. 2017; 48(10):2367-2368.
[29] 顾海伦,杨军,王维,等.不稳定型股骨转子间外侧壁骨折的治疗策略[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(8):679-684.
[30] 张世民,余斌. AO/OTA-2018版股骨转子间骨折分类的解读与讨论[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(7):583-587.
[31] EL’SHEIKH HF, MACDONALD BJ, HASHMI MSJ. Finite element simulation of the hip joint during stumbling:A comparison between static and dynamic loading. J Mat Proc Technol. 2003;143/144(1):249-255.
[32] 颜继英.不同材料赋值下股骨静力学有限元模型的力学仿真分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1390-1394.
|