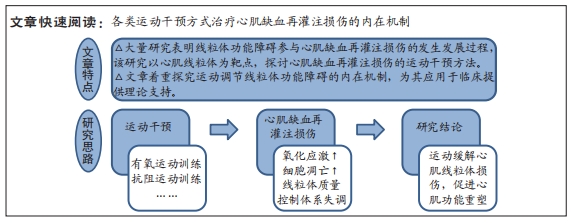
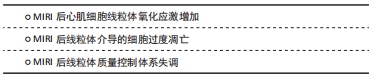
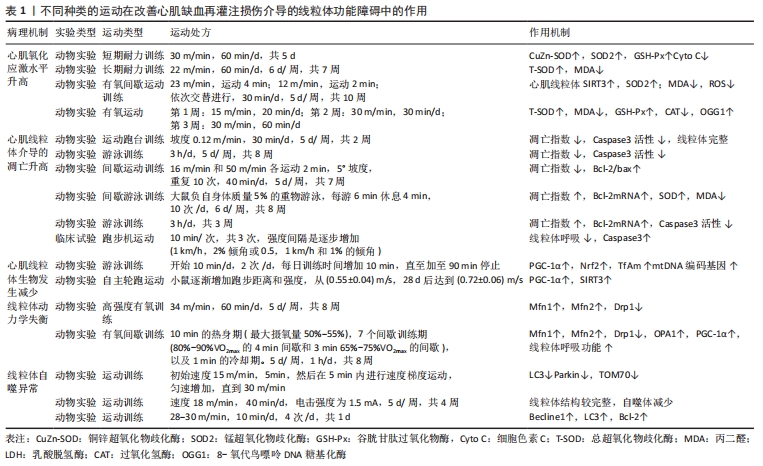
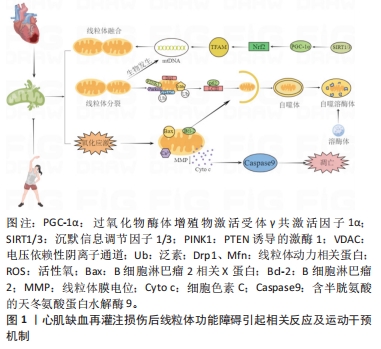
[1] BOATENG S, SANBORN T. Acute myocardial infarction. Dis Mon. 2013; 59(3):83-96.
[2] FERNANDEZ RICO C, KONATE K, JOSSE E, et al. Therapeutic Peptides to Treat Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:792885.
[3] 田野.活性氧在急性心肌梗死心肌再灌注损伤中的作用和机制[J].临床心血管病杂志,2017,33(7):611-614.
[4] WANG J, TOAN S, ZHOU H. Mitochondrial quality control in cardiac microvascular ischemia-reperfusion injury: New insights into the mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Pharmacol Res. 2020;156: 104771.
[5] XU T, DING W, AO X, et al. ARC regulates programmed necrosis and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the inhibition of mPTP opening. Redox Biol. 2019;20:414-426.
[6] KURIAN GA, RAJAGOPAL R, VEDANTHAM S, et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury and Remodeling: Revisited. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:1656450.
[7] ZHOU M, YU Y, LUO X, et al. Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Therapeutics from a Mitochondria-Centric Perspective. Cardiology. 2021;146(6):781-92.
[8] WU Y, LENG Y, MENG Q, et al. Suppression of Excessive Histone Deacetylases Activity in Diabetic Hearts Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Mitochondria Apoptosis Pathway. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:8208065.
[9] MUI D, ZHANG Y. Mitochondrial scenario: roles of mitochondrial dynamics in acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2021;41(1):1-5.
[10] YANG M, LINN BS, ZHANG Y, et,al. Mitophagy and mitochondrial integrity in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(9):2293-2302.
[11] TAO L, BEI Y, LIN S, et al. Exercise Training Protects Against Acute Myocardial Infarction via Improving Myocardial Energy Metabolism and Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(1):162-175.
[12] CORONADO M, FAJARDO G, NGUYEN K, et al. Physiological Mitochondrial Fragmentation Is a Normal Cardiac Adaptation to Increased Energy Demand. Circ Res. 2018;122(2):282-295.
[13] KUZNETSOV AV, JAVADOV S, MARGREITER R, et al. The Role of Mitochondria in the Mechanisms of Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(10):454.
[14] PIZZINO G, IRRERA N, CUCINOTTA M, et al. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:8416763.
[15] BUGGER H, PFEIL K. Mitochondrial ROS in myocardial ischemia reperfusion and remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020; 1866(7):165768.
[16] ANDREADOU I, SCHULZ R, PAPAPETROPOULOS A, et al. The role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, NO and H(2) S in ischaemia/reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(12): 6510-6522.
[17] WANG L, NIU H, ZHANG J. Homocysteine induces mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through stimulating ROS production and the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(2):938-944.
[18] BRADLEY JM, LI Z, ORGAN CL, et al. A novel mtDNA repair fusion protein attenuates maladaptive remodeling and preserves cardiac function in heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;314(2):H311-h321.
[19] CHEN Q, YOUNUS M, THOMPSON J, et al. Intermediary metabolism and fatty acid oxidation: novel targets of electron transport chain-driven injury during ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;314(4):H787-h795
[20] XU X, LAI Y, HUA ZC. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(1):BSR20180992.
[21] LI Y, LIU X. Novel insights into the role of mitochondrial fusion and fission in cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(8):5589-5597.
[22] GRANCARA S, OHKUBO S, ARTICO M, et al. Milestones and recent discoveries on cell death mediated by mitochondria and their interactions with biologically active amines. Amino Acids. 2016;48(10): 2313-2326.
[23] ZHOU H, ZHANG Y, HU S, et al. Melatonin protects cardiac microvasculature against ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of mitochondrial fission-VDAC1-HK2-mPTP-mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res. 2017;63(1):e12413.
[24] FANG R, ZHANG LL, ZHANG LZ, et al. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Postconditioning Protects Against Myocardial Ischemia/reperfusion Injury in Rats via Mitochondrial Signaling and Akt-Gsk3β Phosphorylation. Arch Med Res. 2017;48(2):147-155.
[25] WANG Y, YUAN Y, WANG X, et al. Tilianin Post-Conditioning Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Mitochondrial Protection and Inhibition of Apoptosis. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:4490-4499.
[26] LI J, HU HP, LI Y, et al. Influences of remifentanil on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and the expressions of Bax and Bcl-2 in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(24):8951-8960.
[27] LUO Y, WAN Q, XU M, et al. Nutritional preconditioning induced by astragaloside Ⅳ on isolated hearts and cardiomyocytes against myocardial ischemia injury via improving Bcl-2-mediated mitochondrial function. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;309:108723.
[28] YUAN Y, CAO W, HONG Y, et al. Tilianin pretreatment prevents myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via preservation of mitochondrial function in rat heart. Phytomedicine. 2017;34:106-114.
[29] 张坦,孙易,丁树哲.运动介导AMPK调控线粒体质量控制的机制研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2018,54(6):97-102.
[30] JIN Q, LI R, HU N, et al. DUSP1 alleviates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing the Mff-required mitochondrial fission and Bnip3-related mitophagy via the JNK pathways. Redox Biol. 2018;14:576-587.
[31] POPOV LD. Mitochondrial biogenesis: An update. J Cell Mol Med. 2020; 24(9):4892-4899.
[32] YUE R, XIA X, JIANG J, et al. Mitochondrial DNA oxidative damage contributes to cardiomyocyte ischemia/reperfusion-injury in rats: cardioprotective role of lycopene. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(9):2128-2141.
[33] QI X, WANG J. Melatonin improves mitochondrial biogenesis through the AMPK/PGC1α pathway to attenuate ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial damage. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):7299-7312.
[34] SHANMUGAM K, RAVINDRAN S, KURIAN GA, et al. Fisetin Confers Cardioprotection against Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Inhibiting Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β Activity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:9173436.
[35] DORN GW, 2ND, KITSIS RN. The mitochondrial dynamism-mitophagy-cell death interactome: multiple roles performed by members of a mitochondrial molecular ensemble. Circ Res. 2015;116(1):167-182.
[36] MANEECHOTE C, PALEE S, KERDPHOO S, et al. Balancing mitochondrial dynamics via increasing mitochondrial fusion attenuates infarct size and left ventricular dysfunction in rats with cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019;133(3):497-513.
[37] YANG Y, ZHAO L, MA J. Penehyclidine hydrochloride preconditioning provides cardiac protection in a rat model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via the mechanism of mitochondrial dynamics mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;813:130-139.
[38] ZINGARELLI B, CUZZOCREA S, ZSENGELLÉR Z, et al. Protection against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by 3-aminobenzamide, an inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase. Cardiovasc Res. 1997;36(2): 205-215.
[39] ZHOU XL, WU X, XU QR, et al. Notch1 provides myocardial protection by improving mitochondrial quality control. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7): 11835-11841.
[40] ONISHI M, YAMANO K, SATO M, et al. Molecular mechanisms and physiological functions of mitophagy. Embo J. 2021;40(3):e104705.
[41] ZHU W, LIU F, WANG L, et al. pPolyHb protects myocardial H9C2 cells against ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the Pink1-Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy pathway. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1248-1255.
[42] ZHANG X, LI Q, SUN Y, et al. Chondroitin sulfate from sturgeon bone protects rat chondrocytes from hydrogen peroxide-induced damage by maintaining cellular homeostasis through enhanced autophagy. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:2761-8.
[43] TANG L, LI YP, HU J, et al. Dexpramipexole attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through upregulation of mitophagy. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;899:173962.
[44] XIAO Y, CHEN W, ZHONG Z, et al. Electroacupuncture preconditioning attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitophagy mediated by the mTORC1-ULK1-FUNDC1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110148.
[45] RANJBAR K, ZARRINKALAM E, SALEHI I, et al. Cardioprotective effect of resistance training and Crataegus oxyacantha extract on ischemia reperfusion–induced oxidative stress in diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;100:455-460.
[46] LEE Y, MIN K, TALBERT EE, et al. Exercise protects cardiac mitochondria against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(3): 397-405.
[47] 许思毛,刘书,王第亮,等.较大强度耐力运动预处理对I/R心肌SOD2表达及其活性影响的研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2014,37(11): 73-78
[48] 李丽,仝武军,方立,等.间歇有氧运动训练改善肥胖小鼠缺血后心脏功能恢复[J].心脏杂志,2017,29(3):281-285
[49] RUI F, CAI M, WANG X, et al. Early Aerobic Exercise Combined with Hydrogen-Rich Saline as Preconditioning Protects Myocardial Injury Induced by Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;187(3):663-676.
[50] FRENCH JP, HAMILTON KL, QUINDRY JC, et al. Exercise-induced protection against myocardial apoptosis and necrosis: MnSOD, calcium-handling proteins, and calpain. FASEB J. 2008;22(8):2862-2871.
[51] 于新彦,杨省利.有氧运动训练对大鼠心肌缺血/再灌注损伤致心肌细胞凋亡的作用[J].心脏杂志,2015,27(6):659-661+665.
[52] ZHANG KR, LIU HT, ZHANG HF, et al. Long-term aerobic exercise protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury via PI3 kinase-dependent and Akt-mediated mechanism. Apoptosis. 2007;12(9): 1579-1588.
[53] 彭峰林,张林,彭玉宇,等. 间歇运动对I/R损伤大鼠心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].广西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2009,27(4):119-123.
[54] 刘志梅,于珊珊,贾佳,等. 间歇游泳训练对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 新乡医学院学报,2015,32(9):817-820.
[55] LAI CC, TANG CY, FU SK, et al. Effects of swimming training on myocardial protection in rats. Biomed Rep. 2022;16(3):1-13.
[56] SMENES BT, BÆKKERUD FH, SLAGSVOLD KH, et al. Acute exercise is not cardioprotective and may induce apoptotic signalling in heart surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018;27(1):95-101.
[57] YOUSEF D, FARH GS, GHIASSIE R, et al. Effect of Resistance Exercise on Cardiac Apoptosis Following of Ischemic/Reperfusion. Journal of Animal Veterinary Advances. 2011;10(19):2561-2566.
[58] TAO L, BEI Y, ZHANG H, et al. Exercise Training Protects Against Acute Myocardial Infarction via Improving Myocardial Energy Metabolism and Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(1):162-175.
[59] BUDIONO BP, HOE L, PEART JN, et al. Effects of voluntary exercise duration on myocardial ischaemic tolerance, kinase signaling and gene expression. Life Sci. 2021;(3):119253.
[60] ZANINI G, DE GAETANO A, SELLERI V, et al. Mitochondrial DNA and Exercise: Implications for Health and Injuries in Sports. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2575.
[61] GHAHREMANI R, DAMIRCHI A, SALEHI I, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics as an underlying mechanism involved in aerobic exercise training-induced cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 2018;213:102-108.
[62] MISHRA J, KWOK WM, FITTS RH, et al. Exercise induced Increase in Hexokinase II itochondria Association Reduces Cardiac Ischemia in eperfusion Injury in Rats. FASEB J. 2020;34(S1):1-1.
[63] JIANG HK, WANG YH, SUN L, et al. Aerobic interval training attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction in rats post-myocardial infarction: roles of mitochondrial network dynamics. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):5304-5322.
[64] MUI D, ZHANG Y. Mitochondrial scenario: roles of mitochondrial dynamics in acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2021;41(1):1-5.
[65] YUAN Y, PAN SS. Parkin Mediates Mitophagy to Participate in Cardioprotection Induced by Late Exercise Preconditioning but Bnip3 Does Not. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2018;71(5):303-316.
[66] 唐强,张继瑶,李宏玉,等.基于细胞自噬探讨运动预处理对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 康复学报,2019,29(5):40-45.
[67] LIU H T, PAN SS. Late Exercise Preconditioning Promotes Autophagy against Exhaustive Exercise-Induced Myocardial Injury through the Activation of the AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:5697380.
[68] 李宏玉,张继瑶,张钰,等.运动预处理对心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠自噬相关蛋白表达及心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(8):903-907.
|