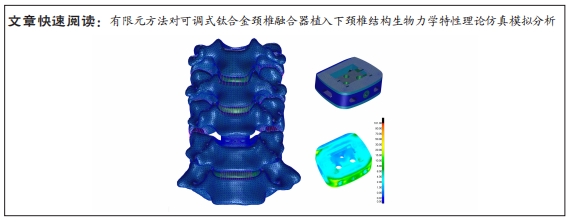
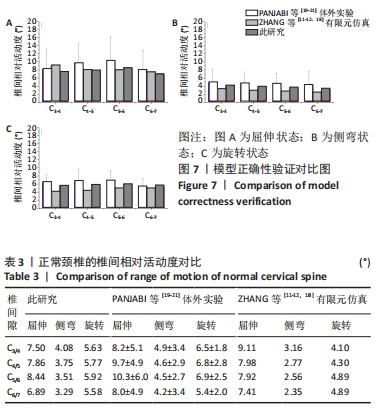
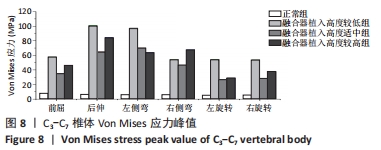
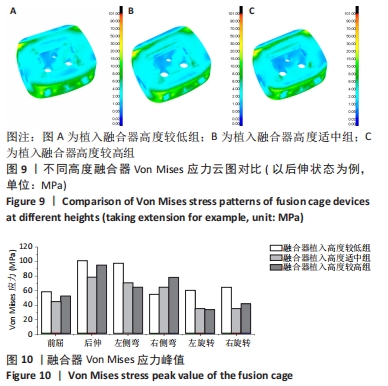
[1] OKUYAMA K, MIYAKOSHI N, SASAKI H, et al. ACDF with a PEEK cage clinically provides a good outcome with minor donor site morbidity despite unsatisfactory radiological findings-A prospective cohort study of a PEEK cage in stand-alone usage. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2017; 1(3):129-134.
[2] CHIN KR, GOHEL NN, ALOISE DM, et al. Effectiveness of a Fully Impregnated Hydroxyapatite Polyetheretherketone Cage on Fusion in Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery. Cureus. 2021;13(8):e17457.
[3] SUN J, WANG Q, CAI D, et al. A lattice topology optimization of cervical interbody fusion cage and finite element comparison with ZK60 and Ti-6Al-4V cages. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):390.
[4] WANG Y, WEI R, SUBEDI D, et al. Tantalum Fusion Device in Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion For Treatment of Cervical Degeneration Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Spine Surg. 2020; 33(3):111-119.
[5] PHAN K, PELLETIER MH, RAO PJ, et al. Integral Fixation Titanium/Polyetheretherketone Cages for Cervical Arthrodesis: Evolution of Cage Design and Early Radiological Outcomes and Fusion Rates. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(1):52-59.
[6] LIU C, ZHANG Y, XIAO L, et al. Vacuum plasma sprayed porous titanium coating on polyetheretherketone for ACDF improves the osteogenic ability: An in vitro and in vivo study. Biomed Microdevices. 2021;23(2):21.
[7] ALHASHASH M, BOEHM H, SHOUSHA M. Management of Symptomatic Cervical Spine Pseudarthrosis: A Suggested Algorithm for Surgical Planning. Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(6):1167-1173.
[8] IGARASHI H, HOSHINO M, OMORI K, et al. Factors Influencing Interbody Cage Subsidence Following Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. Clin Spine Surg. 2019;32(7):297-302.
[9] YIN M, MA J, HUANG Q, et al. The new Zero-P implant can effectively reduce the risk of postoperative dysphagia and complications compared with the traditional anterior cage and plate: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):430.
[10] 卢腾,张廷,董军,等.颈前路融合手术对相邻节段影响的有限元分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2017,37(1):49-55,74.
[11] ZHANG QH, TEO EC, NG HW, et al. Finite element analysis of moment-rotation relationships for human cervical spine. J Biomech. 2006; 39(1):189-193.
[12] ZHANG QH, TEO EC, NG HW. Development and validation of a CO-C7 FE complex for biomechanical study. J Biomech Eng. 2005;127(5):729-735.
[13] BROLIN K, HALLDIN P. Development of a finite element model of the upper cervical spine and a parameter study of ligament characteristics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(4):376-385.
[14] SHIN DS, LEE K, KIM D. Biomechanical study of lumbar spine with dynamic stabilization device using finite element method. Comput Aided Des. 2007;39(7):559-567.
[15] PANZER MB, CRONIN DS. C4-C5 segment finite element model development, validation, and load-sharing investigation. J Biomech. 2009;42(4):480-490.
[16] HA SK. Finite element modeling of multi-level cervical spinal segments (C3-C6) and biomechanical analysis of an elastomer-type prosthetic disc. Med Eng Phys. 2006;28(6):534-541.
[17] 王晨曦,赵改平,柏磊磊,等.动态稳定器植入术后颈椎生物力学的有限元分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2016,33(4):645-651.
[18] 郭群峰,陈方经,倪斌,等.带有颅底的全颈椎三维有限元模型的建立及分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(6):550-554.
[19] PANJABI MM. Cervical spine models for biomechanical research. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(24):2684-2700.
[20] PANJABI MM, NIBU K, CHOLEWICKI J. Whiplash injuries and the potential for mechanical instability. Eur Spine J. 1998;7(6):484-492.
[21] PANJABI MM, CRISCO JJ, VASAVADA A, et al. Mechanical properties of the human cervical spine as shown by three-dimensional load-displacement curves. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(24):2692-2700.
[22] 陆廷盛,罗春山,欧阳北平,等.椎间撑开高度对颈椎前路融合临床结果的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(3):207-210.
[23] 徐锦明,吴强,胡孔和,等.颈前路融合术椎间撑开高度与邻近节段退变的相关性研究[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2017,9(4): 210-217.
[24] BAYLEY JC, YOO JU, KRUGER DM, et al. The role of distraction in improving the space available for the cord in cervical spondylosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(7):771-775.
[25] 张正丰,梅芳瑞.颈椎椎体间撑开对椎间孔面积影响的实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,1999,9(1):20-22.
[26] 田杰.颈椎椎间PLA融合器的有限元分析与实验研究[D].天津:天津理工大学,2019.
[27] PARK JY, CHOI KY, MOON BJ, et al. Subsidence after single-level anterior cervical fusion with a stand-alone cage. J Clin Neurosci. 2016;33:83-88.
[28] 李嘉.颈前路椎间撑开高度对于相邻节段退变影响的相关研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2015.
[29] KOLSTAD F, MYHR G, KVISTAD KA, et al. Degeneration and height of cervical discs classified from MRI compared with precise height measurements from radiographs. Eur J Radiol. 2005;55(3):415-420.
[30] 朱媛君,莫中军,都承斐,等.椎间融合器高度对颈椎生物力学影响[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(3):220-226.
[31] 桂德建,潘宏.颈椎自稳型椎间融合器在颈椎前路减压融合内固定术的应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(4):385-389.
|