中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 1346-1351.doi: 10.12307/2023.252
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
基于虚拟现实技术的旋提手法下颈椎间孔结构变化动态分析
刘广伟1,冯敏山1,2,朱立国1,2,尹逊路2,陈焯贤2
- 中国中医科学院望京医院,1中医正骨技术北京市重点实验室,2脊柱二科,北京市 100102
Dynamic analysis of structural changes in the lower cervical intervertebral foramen during rotation-traction manipulation by virtual reality technology
Liu Guangwei1, Feng Minshan1, 2, Zhu Liguo1, 2, Yin Xunlu2, Chen Zhuoxian2
- 1Beijing Key Laboratory of Manipulative Technique, 2Second Department of Spine, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China
摘要:
文题释义:
旋提手法:是一种定位牵引的颈椎治疗手法,患者在治疗前经过适度的颈部放松,在医生的指导下自主完成极限位的旋转-屈曲-再旋转,使颈椎处于关节绞索状态,医生使用手臂固定患者头部,依靠自身力量迅速完成预牵引、提扳等动作,以达到颈椎治疗的目的。
运动捕捉:是一种用于准确测量运动物体在三维空间运动状况的技术,其工作原理是在运动物体的关键部位设置跟踪器(Marker点),经计算机处理得到三维运动数据,具有精度高、可实现动态三维运动分析的特点,被广泛应用于虚拟现实、人体工程学、模拟训练、生物力学、运动学等研究方面。
背景:神经根型颈椎病是一类临床常见病,旋提手法是治疗神经根型颈椎病的有效手段,椎间孔的测量是临床上重要的参考标准。
目的:分析不同状态下旋提手法对下颈椎间孔结构变化的影响,探讨旋提手法的生物力学作用机制。
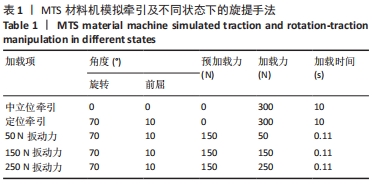
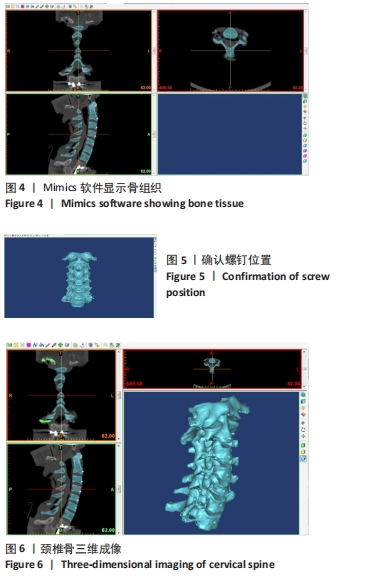
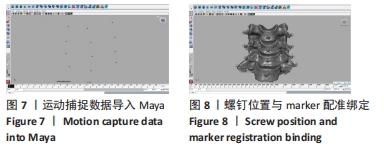
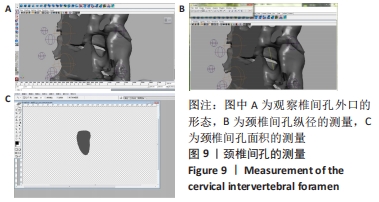
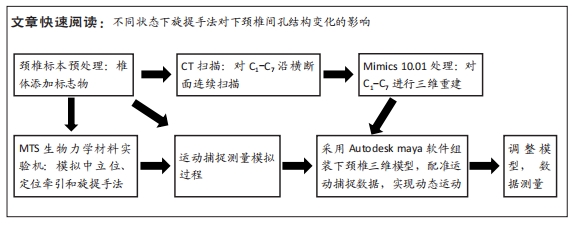
方法:颈椎标本置入螺钉方便CT成像时定位,首先应用MTS材料机在新鲜颈段标本上模拟不同状态下的旋提手法,同时利用运动捕捉技术获取旋提手法过程中Marker点的运动轨迹;然后,通过螺旋CT薄层扫描颈椎标本,运用Mimics软件进行三维颈椎实体重建,依据旋提手法过程下颈椎体的运动轨迹,通过Autodesk maya软件进行多模医学图像三维配准实现动态虚拟现实仿真,进行动态图像处理;最后,分别采用ImageJ软件及Adobe photoshop软件测量旋提手法前后下颈椎间孔的纵径及面积。
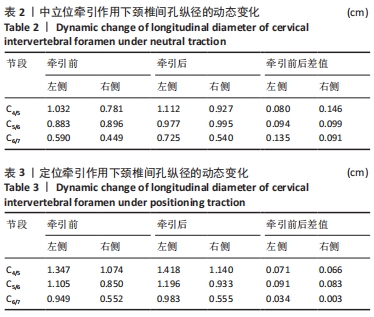
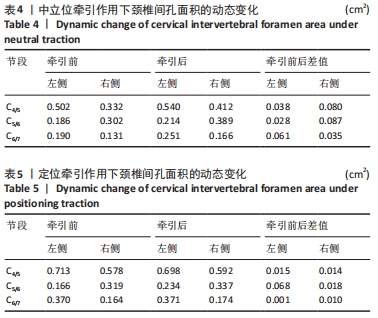
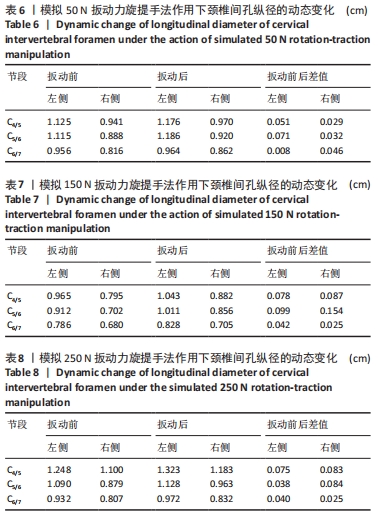
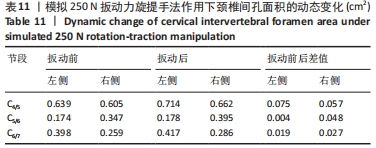
结果与结论:①定位牵引有利于提前打开下颈椎间孔,牵引效果略差于中立位牵引,但定位牵引具有更好的安全性;②扳动力在150 N以内,旋提手法的扳动力越小,颈椎间孔的纵径及面积的增加幅度也越小;扳动力超过150 N之后,颈椎间孔纵径及面积的增加幅度影响不大;③旋提手法通过增大下颈椎间孔可能有助于松解椎间孔周缘的粘连,从而缓解神经根刺激症状。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3753-2081 (刘广伟)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: