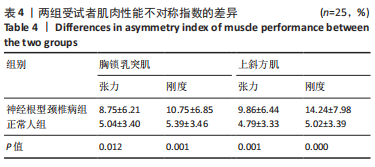
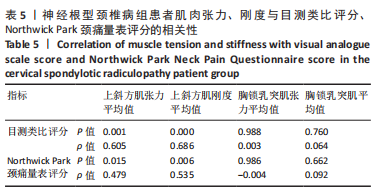
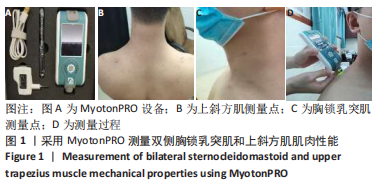
[1] CHEN B, ZHANG C, ZHANG RP, et al. Acupotomy versus acupuncture for cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: protocol of a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e029052.
[2] WOODS BI, HILIBRAND AS. Cervical radiculopathy: epidemiology, etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(5): E251-259.
[3] MENG XW, WANG Y, PIAO SA, et al. Wet Cupping Therapy Improves Local Blood Perfusion and Analgesic Effects in Patients with Nerve-Root Type Cervical Spondylosis. Chin J Integr Med. 2018;24(11):830-834.
[4] 李帅林, 吴嘉容, 严隽陶, 等. 基于筋骨理论探讨手法对颈椎病姿态异常的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2019,34(3):1157-1159.
[5] 徐筱潇, 王楚怀. 非手术脊柱减压牵引对神经根型颈椎病患者颈部肌肉表面肌电信号的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版),2017, 46(3):336-340.
[6] 罗凛, 王振辉, 郭鸿基, 等. 基于颈肌MRI探讨手法治疗椎动脉型颈椎病的起效机制[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(5):14-17.
[7] CHEN G, WU J, CHEN G, et al. Reliability of a portable device for quantifying tone and stiffness of quadriceps femoris and patellar tendon at different knee flexion angles. PLoS One. 2019;14(7): e0220521.
[8] HU X, LEI D, LI L, et al. Quantifying paraspinal muscle tone and stiffness in young adults with chronic low back pain: a reliability study. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14343.
[9] KO CY, CHOI HJ, RYU J, et al. Between-day reliability of MyotonPRO for the non-invasive measurement of muscle material properties in the lower extremities of patients with a chronic spinal cord injury. J Biomech. 2018;73:60-65.
[10] PETALA E, MIRONIDOU-TZOUVELEKI M, NANASSIS K, et al. A study about neck pain on active population who visit Primary Health Centers. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019;22 Suppl 2:41.
[11] LAROCHE DP, COOK SB, MACKALA K. Strength asymmetry increases gait asymmetry and variability in older women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(11):2172-2181.
[12] 张义, 郭长青. 颈肌改变与颈椎病关系的研究进展 [J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2012,21(18):2045-2047.
[13] 程永博, 窦群立, 陈瑞, 等. “筋骨平衡”理论在推拿治疗神经根型颈椎病中的应用 [J]. 中国中医急症,2020,29(9):1686-1688+1692.
[14] 张帅攀, 朱清广, 孔令军, 等. 基于“筋骨平衡”理论探讨推拿治疗颈椎病的生物力学内涵 [J]. 时珍国医国药,2020,31(1):160-162.
[15] 赵勇, 方维, 闫安, 等. 肩胛肌筋膜炎软组织张力与颈椎生理曲度改变相关性探讨 [J]. 中国骨伤,2014,27(5):376-378.
[16] LI H, YIN J, HUANG Y, et al. Establishment of cervical dynamic and static imbalance models and preliminary study on the mechanism of cervical degeneration in rats. Innate Immun. 2020;26(2):107-116.
[17] WANG YJ, SHI Q, LU WW, et al. Cervical intervertebral disc degeneration induced by unbalanced dynamic and static forces: a novel in vivo rat model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(14):1532-1538.
[18] MYŚLIWIEC A, SAULICZ E, KUSZEWSKI M, et al. Assessment of the cervical spine range of motion after the use of the saunders traction device in different positioning of the upper extremities . Adv Clin Exp Med. 2014;23(5):769-774.
[19] 张艺, 李雪松, 孙滨, 等. 牵引态下针刺夹脊穴治疗神经根型颈椎病临床疗效观察及对炎症因子的影响 [J]. 吉林中医药,2018,38(4): 465-467.
[20] 潘胜莲, 郑士立, 周夏慧, 等. 针刺联合颈痛颗粒治疗神经根型颈椎病及对患者IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β和血液流变学指标的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2019,39(12):1274-1278.
[21] LARSSON B, BJöRK J, ELERT J, et al. Fibre type proportion and fibre size in trapezius muscle biopsies from cleaners with and without myalgia and its correlation with ragged red fibres, cytochrome-c-oxidase-negative fibres, biomechanical output, perception of fatigue, and surface electromyography during repetitive forward flexions. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2001;84(6):492-502.
[22] JOHANSSON H, SOJKA P. Pathophysiological mechanisms involved in genesis and spread of muscular tension in occupational muscle pain and in chronic musculoskeletal pain syndromes: a hypothesis. Med Hypotheses. 1991;35(3):196-203.
[23] 程森永. 神经根型颈椎病颈部软组织张力研究[D]. 郑州: 河南中医学院,2015.
[24] 李元石. 长期伏案工作人群肌肉表面肌电信号的特性研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学,2015.
[25] 刘世忠, 梁军, 林乾, 等. 伏案工作人群职业性颈肩肌肉疼痛运动处方的效果[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(7):642-648.
[26] KOCUR P, WILSKI M, GOLIWĄS M, et al. Influence of Forward Head Posture on Myotonometric Measurements of Superficial Neck Muscle Tone, Elasticity, and Stiffness in Asymptomatic Individuals With Sedentary Jobs. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2019;42(3):195-202.
[27] 刘展. 人体动作模式和运动链的理念在运动损伤防护和康复中的应用[J]. 成都体育学院学报,2016,42(6):1-11.
[28] 张明才, 程英武, 詹红生, 等. 神经根型颈椎病椎间孔狭窄因素的影像学分析[J]. 北京中医药大学学报,2009,32(3):199-203.
[29] 罗鹏飞, 李宁, 谢兴文, 等. 基于“筋骨平衡”理论探讨旋转手法治疗颈椎病的生物力学机制研究进展[J]. 中医正骨,2020,32(9): 46-49.
[30] 沈志生. 《内经》经筋理论的再认识[J]. 中国针灸,2006,26(9): 639-640.
[31] 林志刚, 蒋诗超, 程艳彬, 等. 探讨《黄帝内经》“筋骨”理论对中医推拿的指导意义[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2016,31(7):2491-2493.
[32] 徐善达, 孔令军, 朱清广, 等. 颈型颈椎病“筋骨失衡”的运动学特性研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(9):4739-4742.
[33] KOCUR P, WILSKI M, LEWANDOWSKI J, et al. Female office workers with moderate neck pain have increased anterior positioning of the cervical spine and stiffness of upper trapezius myofascial tissue in sitting posture. PM R. 2019;11(5):476-482
[34] 韦以宗. 脊柱机能解剖学研究[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2003(1): 3-11.
[35] 李正祥, 李秀彬, 吴松. 脊柱微调手法联合远近配穴针刺治疗神经根型颈椎病的临床研究[J]. 中医正骨,2020,32(8):1-5.
[36] 曾杨, 林建平, 熊振宇, 等. 推拿对颈型颈椎病患者颈部肌肉协调性的影响[J]. 按摩与康复医学,2018,9(6):50-52.
|