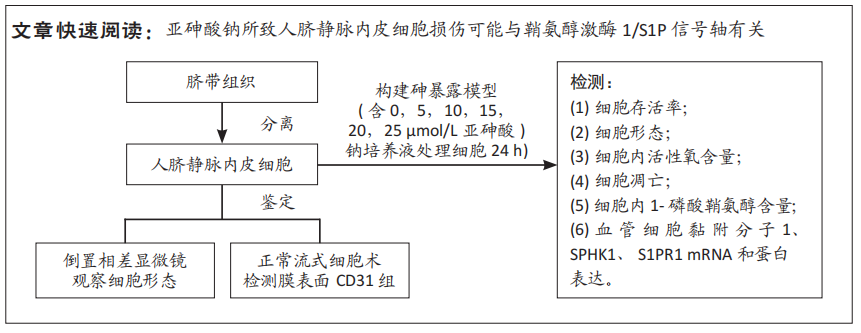
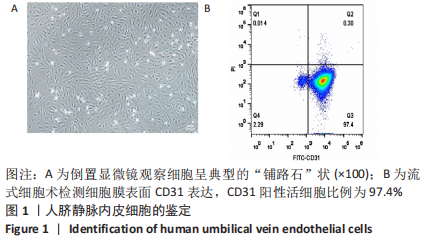
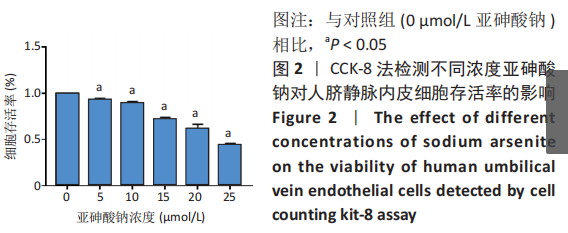
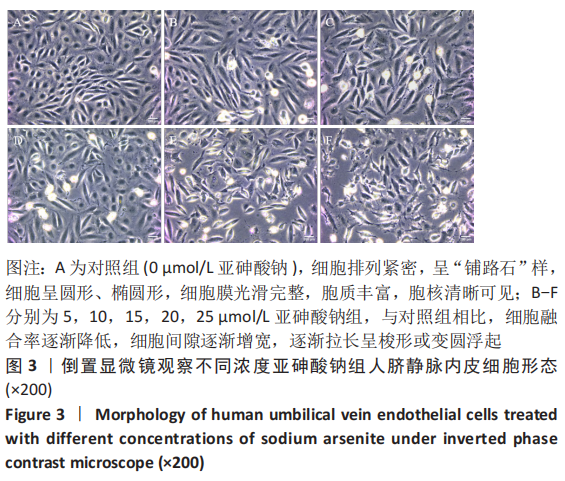
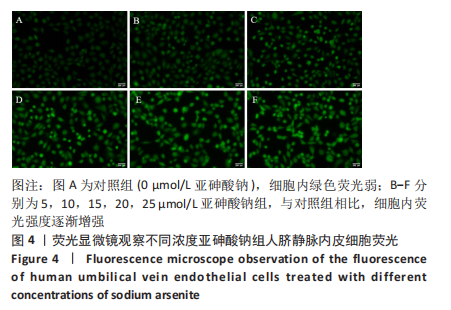
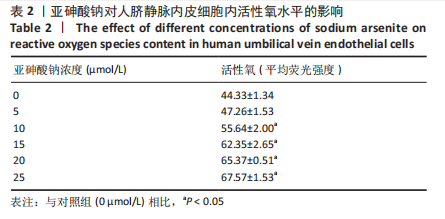
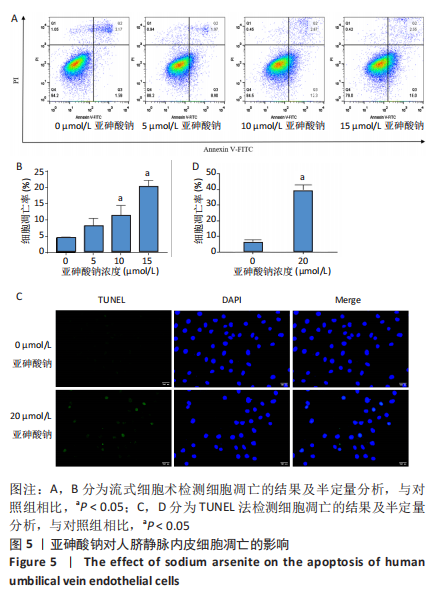
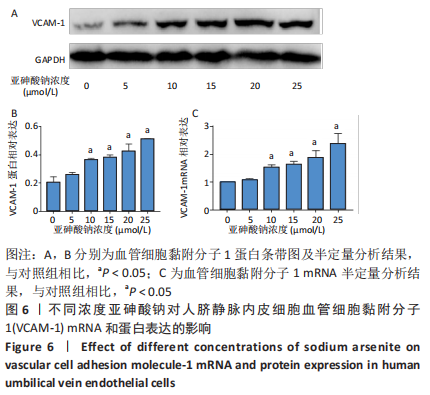
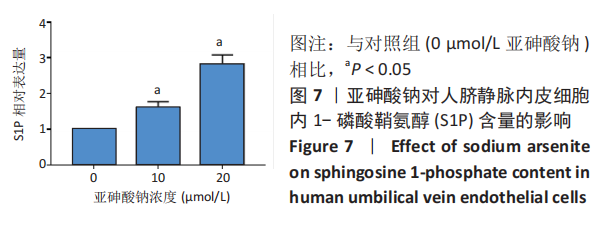
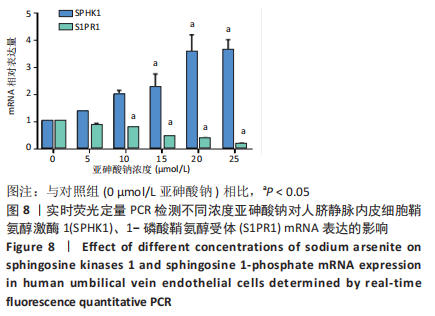
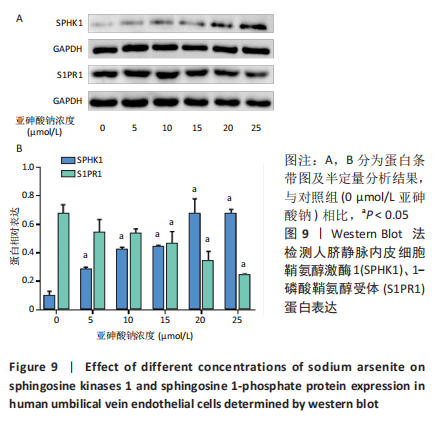
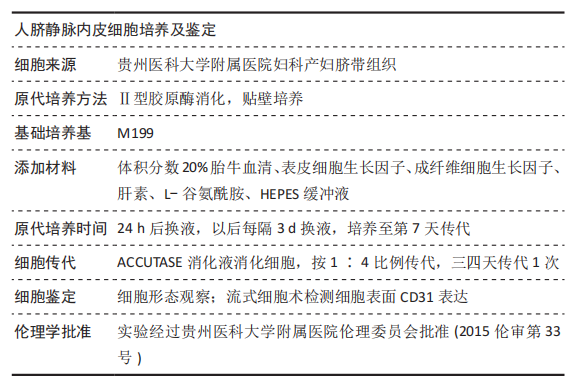
[1] PALMA-LARA I, MARTINEZ-CASTILLO M, QUINTANA-PEREZ JC, et al. Arsenic exposure: A public health problem leading to several cancers. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.2020;110:104539.
[2] SOBEL MH, SANCHEZ TR, JONES MR, et al. Rice Intake, Arsenic Exposure, and Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease Among US Adults in MESA. J Am Heart Assoc.2020;9(4):e15658.
[3] FARZAN SF, EUNUS HM, HAQUE SE, et al. Arsenic exposure from drinking water and endothelial dysfunction in Bangladeshi adolescents. Environ Res.2022;208:112697.
[4] XU S, ILYAS I, LITTLE PJ, et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases and Beyond: From Mechanism to Pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol Rev.2021;73(3):924-967.
[5] GUO X, LIU X, WANG J, et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) ameliorates arsenic-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction in rats and toxicity in endothelial EA.hy926 cells. Environ Res. 2020;186:109506.
[6] LIU P, XUE Y, ZHENG B, et al. Crocetin attenuates the oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosisin arsenic trioxide-induced nephrotoxic rats: Implication of PI3K/AKT pathway. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020,88:106959.
[7] KORNER C, FROHLICH F. Compartmentation and functions of sphingolipids. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2022;74:104-111.
[8] CARTIER A, HLA T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate: Lipid signaling in pathology and therapy. Science. 2019;366(6463):eaar5551.
[9] OGRETMEN B. Sphingolipid metabolism in cancer signalling and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(1):33-50.
[10] SATTAR R, SUMI MP, NIMISHA, et al. S1P signaling, its interactions and cross-talks with other partners and therapeutic importance in colorectal cancer. Cell Signal.2021;86:110080.
[11] ZOU J, MA X, ZHANG G, et al. Evaluation of the change in sphingolipids in the human multiple myeloma cell line U266 and gastric cancer cell line MGC-803 treated with arsenic trioxide. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2015;1004:98-107.
[12] LIU P, CHEN Z, MA X. Arsenic trioxide inhibits the activity of SphK1 by decreasing the level of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidic acid in the human gastric cancer cell line MGC-803. BIOCELL. 2022;46(3):737-743.
[13] CRAMPTON SP, DAVIS J, HUGHES CC. Isolation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC)[J]. J Vis Exp. 2007;(3):183.
[14] 陈小翠, 陈邦党, 杨毅宁,等. 人脐静脉内皮细胞分离培养和鉴定[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2016,32(3):328-331.
[15] ZHENG B, YANG Y, LI J, et al. Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate Alleviates Arsenic Trioxide-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Contribution of Nrf2 and TLR4/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:543-556.
[16] HU Y, LI J, LOU B, et al. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Arsenic Toxicity. Biomolecules. 2020,10(2):240.
[17] HARIJITH A, PENDYALA S, REDDY NM, et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 deficiency confers protection against hyperoxia-induced bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a murine model: role of S1P signaling and Nox proteins. Am J Pathol.2013;183(4):1169-1182.
[18] HUANG LS, SUDHADEVI T, FU P, et al. Sphingosine Kinase 1/S1P Signaling Contributes to Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating Hippo/YAP Pathway and Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species in Lung Fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2064.
[19] COOPER KL, VOLK LB, DOMINGUEZ DR, et al. Contribution of NADPH oxidase to the retention of UVR-induced DNA damage by arsenic. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2022;434:115799.
[20] TSAI CL, TSAI CW, CHANG WS, et al. Protective Effects of Baicalin on Arsenic Trioxide-induced Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. In Vivo. 2021;35(1):155-162.
[21] TSAI CL, TSAI CW, CHANG WS, et al. Protective Effects of Crocetin on Arsenic Trioxide-induced Oxidative Stress in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. In Vivo.2021;35(6):3157-3163.
[22] JOZEFCZUK E, GUZIK T J, SIEDLINSKI M. Significance of sphingosine-1-phosphate in cardiovascular physiology and pathology. Pharmacol Res.2020;156:104793.
[23] DAVAILLE J, GALLOIS C, HABIB A, et al. Antiproliferative properties of sphingosine 1-phosphate in human hepatic myofibroblasts. A cyclooxygenase-2 mediated pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(44):34628-34633.
[24] DAVAILLE J, LI L, MALLAT A, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate triggers both apoptotic and survival signals for human hepatic myofibroblasts. J Biol Chem.2002;277(40):37323-37330.
[25] YANG CC, HSIAO LD, SHIH YF, et al. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate-Upregulated COX-2/PGE2 System Contributes to Human Cardiac Fibroblast Apoptosis: Involvement of MMP-9-Dependent Transactivation of EGFR Cascade. Oxid Med Cell Longev.2022;2022:7664290.
[26] YANG CC, HSIAO LD, SU MH, et al. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Induces Cyclooxygenase-2/Prostaglandin E2 Expression via PKC alpha-dependent Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and NF-kappaB Cascade in Human Cardiac Fibroblasts. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:569802.
[27] NATARAJAN V, HA AW, DONG Y, et al. Expression profiling of genes regulated by sphingosine kinase1 signaling in a murine model of hyperoxia induced neonatal bronchopulmonary dysplasia. BMC Genomics.2017;18(1):664.
[28] BUNDERSON M, COFFIN JD, BEALL HD. Arsenic induces peroxynitrite generation and cyclooxygenase-2 protein expression in aortic endothelial cells: possible role in atherosclerosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002;184(1):11-18.
[29] WANG L, HITRON JA, WISE JT, et al. Ethanol enhances arsenic-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression via both NFAT and NF-kappaB signalings in colorectal cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015;288(2):232-239.
[30] OOKI A, BEGUM A, MARCHIONNI L, et al. Arsenic promotes the COX2/PGE2-SOX2 axis to increase the malignant stemness properties of urothelial cells. Int J Cancer.2018;143(1):113-126.
[31] 王甜, 赵哲仪, 穆银贵, 等. 亚砷酸钠所致L-02人肝细胞损伤与p14ARF表达下调及MDM2、p53表达增加有关[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2020,36(6):507-512.
[32] 赵哲仪, 王正蓉, 方兴艳, 等. 亚砷酸钠对AML12肝细胞氧化应激、凋亡损伤及Hippo信号通路的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022,26(26):4186-4191.
[33] ZHONG G, HU T, TANG L, et al. Arsenic causes mitochondrial biogenesis obstacles by inhibiting the AMPK/PGC-1alpha signaling pathway and also induces apoptosis and dysregulated mitophagy in the duck liver. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.2021;230:113117.
[34] TRONCOSO M F, ORTIZ-QUINTERO J, GARRIDO-MORENO V, et al. VCAM-1 as a predictor biomarker in cardiovascular disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.2021;1867(9):166170.
[35] OBINATA H, HLA T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and inflammation. Int Immunol.2019;31(9):617-625.
[36] ALVAREZ SE, HARIKUMAR KB, HAIT NC, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2. Nature.2010;465(7301):1084-1088.
[37] XIA P, WANG L, MORETTI PA, et al. Sphingosine kinase interacts with TRAF2 and dissects tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling. J Biol Chem.2002;277(10):7996-8003.
[38] WANG L, XING X P, HOLMES A, et al. Activation of the sphingosine kinase-signaling pathway by high glucose mediates the proinflammatory phenotype of endothelial cells. Circ Res.2005;97(9):891-899.
[39] ROSEN H, GONZALEZ-CABRERA PJ, SANNA MG, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor signaling. Annu Rev Biochem.2009;78:743-768.
[40] REN K, LU YJ, MO ZC, et al. ApoA-I/SR-BI modulates S1P/S1PR2-mediated inflammation through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in HUVECs. J Physiol Biochem.2017;73(2):287-296.
[41] YANG Y, WANG Q, WANG W, et al. Semaphorin 4A antibody alleviates arsenic-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via inhibition of AKT2/NF-kappaB inflammatory signaling.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021;410:115364.
[42] ZHANG C, FERRARI R, BEEZHOLD K, et al. Arsenic Promotes NF-Kappab-Mediated Fibroblast Dysfunction and Matrix Remodeling to Impair Muscle Stem Cell Function. Stem Cells, 2016,34(3):732-742.
[43] ANWAR M, MEHTA D. Post-translational modifications of S1PR1 and endothelial barrier regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids.2020;1865(9):158760.
[44] GAENGEL K, NIAUDET C, HAGIKURA K, et al. The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1PR1 restricts sprouting angiogenesis by regulating the interplay between VE-cadherin and VEGFR2. Dev Cell. 2012;23(3):587-599.
[45] GALVANI S, SANSON M, BLAHO VA, et al. HDL-bound sphingosine 1-phosphate acts as a biased agonist for the endothelial cell receptor S1P1 to limit vascular inflammation. Sci Signal.2015;8(389):a79.
[46] CAI Z, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Use of a Mouse Model and Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells to Investigate the Effect of Arsenic Exposure on Vascular Endothelial Function and the Associated Role of Calpains. Environ Health Perspect.2019;127(7):77003. |