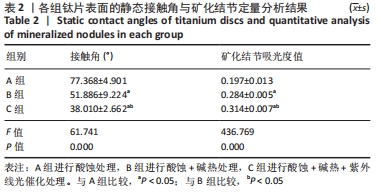
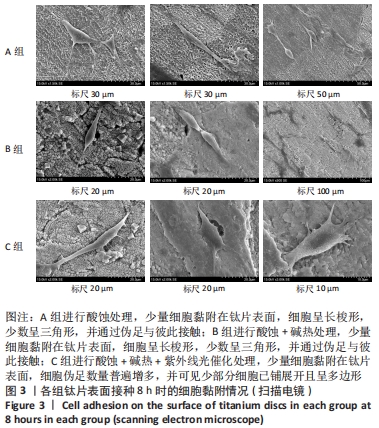
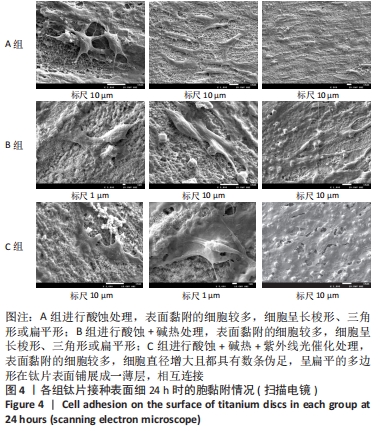
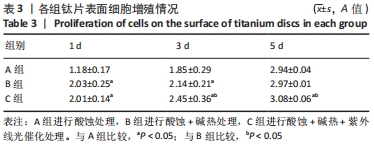
[1] 高岩.不同波长紫外线激发微弧氧化纯钛表面光催化作用的体外生物活性研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2012.
[2] KOKUBO T, YAMAGUCHI S. Bioactive titanate layers formed on titanium and itsalloys by simple chemical and heat treatments. Open Biomed Eng J. 2015;9:29-41.
[3] XING H, KOMASA S, TAGUCHI Y, et al. Osteogenic activity of titanium surfaces with nanonetwork structures. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9: 1741-1755.
[4] SO K, KANEUJI A, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Is the bone-bonding ability of a cementless total hip prosthesis enhanced by alkaline and heat treatments? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(12):3847-3855.
[5] 栗兴超.表面粗化处理不均衡螺纹钛人工牙种植体的生物学性能研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2017.
[6] KOKUBO T, KIM HM, KAWASHITA M, et al. Bioactive metals: preparation and properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004;15(2):99-107.
[7] 韩石磊,赵颖,李大鹏,等.碱热处理联合紫外光照后钛体外活性的研究[J].口腔医学,2017,37(5):408-412.
[8] ZHANG H, KOMASA S, MASHIMO C, et al. Effect of ultraviolet treatment on bacterial attachment and osteogenic activity to alkali-treated titanium with nanonetwork structures. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:4633-4646.
[9] AITA H, HORI N, TAKEUCHI M, et al. The effect of ultraviolet functionalization of titanium on integration with bone.Biomaterials. 2009;30(6):1015-1025.
[10] BUDDY D, ALLAN S, FREDERICK J, et al. Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine. Elsevier Academic Press,1985.
[11] TEXTOR M, SITTIG C, FRAUCHIGER V, et al. Properties and Biological Significance of Natural Oxide Films on Titanium and Its Alloys. In: Titanium in Medicine. Engineering Materials. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. 2001.
[12] CHO SA, PARK KT. The removal torque of titanium screw inserted in rabbit tibia treated by dual acid etching. Biomaterials. 2003;24(20): 3611-3617.
[13] PARK JY, DAVIES JE. Red blood cell and platelet interactions with titanium implant surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11(6):530-539.
[14] COCHRAN DL, BUSER D, TEN BRUGGENKATE CM, et al. The use of reduced healing times on ITI implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched (SLA) surface: early results from clinical trials on ITI SLA implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13(2):144-153.
[16] MAROM R, SHUR I, SOLOMON R, et al. Characterization of adhesion and differentiation markers of osteogenic marrow stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 2005;202(1):41-48.
[17] EHARA A, OGATA K, IMAZATO S, et al. Effects of alpha-TCP and TetCP on MC3T3-E1 proliferation, differentiation and mineralization.Biomaterials. 2003;24(5):831-836.
[18] WONG M, EULENBERGER J, SCHENK R, et al. Effect of surface topology on the osseointegration of implant materials in trabecular bone. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995;29(12):1567-1575.
[19] WEBSTER TJ, ERGUN C, DOREMUS RH, et al. Specific proteins mediate enhanced osteoblast adhesion on nanophase ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51(3):475-483.
[20] KARLSSON M, PÅLSGÅRD E, WILSHAW PR, et al. Initial in vitro interaction of osteoblasts with nano-porous alumina. Biomaterials. 2003;24(18):3039-3046.
[21] 冯智敏.糖尿病对大鼠正畸牙齿移动的影响[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2006.
[22] GOUGH JE, JONES JR, HENCH LL. Nodule formation and mineralisation of human primary osteoblasts cultured on a porous bioactive glass scaffold. Biomaterials. 2004;25(11):2039-2046.
[23] ZHOU J, LI B, LU S, et al. Regulation of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by interrod spacing of Sr-HA nanorods on microporous titania coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(11):5358-5365.
[24] CAI YL, ZHANG JJ, ZHANG S, et al. Osteoblastic cell response on fluoridated hydroxyapatite coatings: the effect of magnesium incorporation. Biomed Mater. 2010;5(5):054114.
[25] LANDI E, TAMPIERI A, MATTIOLI-BELMONTE M, et al. Biomimetic Mg- and Mg,CO3-substituted hydroxyapatites: synthesis characterization and in vitro behaviour. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2006;26(13):2593-2601.
[26] WANG J, ZHAO Y, CHENG X, et al. Effects of different Ca2+ level on fluoride-induced apoptosis pathway of endoplasmic reticulum in the rabbit osteoblast in vitro. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018;116(Pt B):189-195.
[27] DE COLLI M, RADUNOVIC M, ZIZZARI VL, et al. Osteoblastic differentiating potential of dental pulp stem cells in vitro cultured on a chemically modified microrough titanium surface. Dent Mater J. 2018;37(2):197-205.
[28] LEE MN, HWANG HS, OH SH, et al. Elevated extracellular calcium ions promote proliferation and migration of mesenchymal stem cells via increasing osteopontin expression. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(11):1-16.
[29] KOPF BS, RUCH S, BERNER S, et al. The role of nanostructures and hydrophilicity in osseointegration: In-vitro protein-adsorption and blood-interaction studies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(8):2661-2672.
[30] ALBORZI A, MAC K, GLACKIN CA, et al. Endochondral and intramembranous fetal bone development: osteoblastic cell proliferation, and expression of alkaline phosphatase, m-twist, and histone H4. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1996;16(2):94-106.
[31] LOTZ EM, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, BERNER S, et al. Osteogenic response of human MSCs and osteoblasts to hydrophilic and hydrophobic nanostructured titanium implant surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(12):3137-3148.
[32] LOTZ EM, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, et al. Comparable responses of osteoblast lineage cells to microstructured hydrophilic titanium-zirconium and microstructured hydrophilic titanium. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(7):e51-e59.
[33] Hotchkiss KM, Reddy GB, Hyzy SL, et al.Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:425-434.
[34] ALFARSI MA, HAMLET SM, IVANOVSKI S. Titanium surface hydrophilicity enhances platelet activation. Dent Mater J. 2014;33(6):749-756.
|