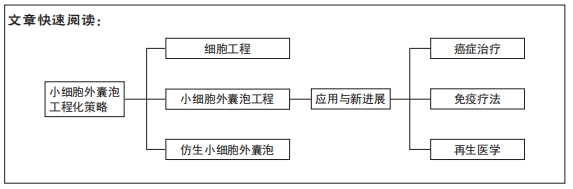
[1] ZHU GY, LU BY, PENG Q, et al. Antibiofilm effect of drug-free and cationic poly (D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles via nano-bacteria interactions. Nanomedicine (Lond.). 2018;13(10):1093-1106.
[2] SHAO XR, WEI XQ, PENG Q, et al. Effects of Micro-environmental pH of Liposome on Chemical Stability of Loaded Drug. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017;12(1):504.
[3] LIU J, DONG J, PENG Q, et al. Graphene-based nanomaterials and their potentials in advanced drug delivery and cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2018;286:64-73.
[4] PENG Q, ZHANG ZR, LIN YF, et al. Nanocomplex based on biocompatible phospholipids and albumin for long-circulation applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(16):13730-13737.
[5] LUAN X, YUAN H, SUN D, et al. Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017; 38(6):754-763.
[6] HAQUE S, WHITTAKER MR, KAMINSKAS LM, et al. Disposition and safety of inhaled biodegradable nanomedicines: Opportunities and challenges. Nanomedicine. 2016;12:1703-1724.
[7] SHAO XR, WEI XQ, PENG Q, et al. Independent effect of polymeric nanoparticle zeta potential/surface charge, on their cytotoxicity and affinity to cells. Cell Prolif. 2015;48(4):465-474.
[8] AHN J, PARK TE, JEON NL, et al. Investigation on vascular cyto-toxicity and extravascular transport of cationic polymer nanoparticles using perfusable 3D microvessel model. Acta Biomater. 2018;76:154-163.
[9] THERY C, AMIGORENA S, CLAYTON A, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;23(1):1-29.
[10] LAI RC, YEO RW, LIM SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin. Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88.
[11] SKOGBERG G, LUNDBERG V, EKWALL O, et al. Human thymic epithelial primary cells produce exosomes carrying tissue-restricted antigens. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015;93(8):727-734.
[12] BENITO-MARTIN A, CEDER S, PEINADO H, et al. The new deal: a potential role for secreted vesicles in innate immunity and tumor progression. Front. Immunol. 2015;6:66.
[13] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88: 487-514.
[14] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750.
[15] 姜承耀,陈文娟,韩树萍,等.母乳外泌体载药用于新生儿相关疾病治疗的研究进展[J].医学综述,2020,26(19):3769-3773+3779.
[16] JAFARI D, FOROUZANDEH MOGHADAM M, SAMADIKUCHAKSARAEI A, et al. Designer Exosomes: A New Platform for Biotechnology Therapeutics. BioDrugs. 2020;34(5):567-586.
[17] VADER P, MOL EA, SCHIFFELERS RM, et al. Extracellular vesicles for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;106(Pt A):148-156.
[18] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, TURBIDE C, et al.Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.
[19] PAOLICELLI RC, BERGAMINI G, RAJENDRAN L. Cell-to-cell communication by extracellular vesicles: focus on microglia. Neuroscience. 2019;405:148-157.
[20] WESTON WW, GANEY T, TEMPLE HT. The relationship between exosomes and cancer: implications for diagnostics and therapeutics. BioDrugs. 2019;33(2):137-158.
[21] ALMIÑANA C, TSIKIS G, BAUERSACHS S, et al. Deciphering the oviductal extracellular vesicles content across the estrous cycle: implications for the gametesoviduct interactions and the environment of the potential embryo. BMC Genom. 2018;19(1):622.
[22] JIANG N, XIANG L, WANG C, et al. Exosomes mediate epithelium-mesenchyme crosstalk in organ development. ACS Nano. 2017;11(8): 7736-7746.
[23] SUN B, PENG J, ZHANG Z, et al. Applications of stem cell-derived exosomes in tissue engineering and neurological diseases. Rev Neurosci. 2018;29(5):531-546.
[24] HUANG CC, ALAPATI S, RAVINDRAN S, et al. Exosomes as biomimetic tools for stem cell diferentiation: applications in dental pulp tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;111:103-115.
[25] TOH WS, ZHANG B, LIM SK, et al. MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018;46:843-853.
[26] UTSUGI-KOBUKAI S, NAKAZAWA M, MINAMI M, et al. MHC class I-mediated exogenous antigen presentation by exosomes secreted from immature and mature bone marrow derived dendritic cells. Immunol Lett. 2003;89(2):125-131.
[27] LAN FM, YU HM, YUE X, et al. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell Oncol. 2018;41(1):25-33.
[28] GOMARI H, MOGHADAM MF, SOLEIMANI M. Targeted cancer therapy using engineered exosome as a natural drug delivery vehicle. OncoTargets Ther. 2018;11:5753.
[29] MATHIYALAGAN P, SAHOO S. Exosomes-based gene therapy for microRNA delivery. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1521:139-152.
[30] JING H, HE X, ZHENG J. Exosomes and regenerative medicine: state of the art and perspectives. Transl Res. 2018;196:1-16.
[31] TAN A, DE LA PEÑA H, SEIFALIAN AM. The application of exosomes as a nanoscale cancer vaccine. Int J Nanomed. 2010;5:889-900.
[32] 晏梓钧,茹楠,蔡梦溪,等.外泌体改造和修饰研究进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2019,40(12):1203-1206.
[33] LU M, XING H, XUN Z, et al. Functionalized extracellular vesicles as advanced therapeutic nanodelivery systems. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;121:34-46.
[34] SANCHO-ALBERO M, ARRUEBO M, MARTÍN-DUQUE P, et al. Exosome origin determines cell targeting and the transfer of therapeutic nanoparticles towards target cells. J Nanobiotechnol. 2019;17(1):16.
[35] OKSVOLD MP, LI M, BRECH A, et al. Expression of B-cell surface antigens in subpopulations of exosomes released from B-cell lymphoma cells. Clin Ther. 2014;36(6):847-862.
[36] SAVVATEEVA EN, TIKHONOV AA, RUBINA AY, et al. Exosomal surface protein markers in diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Mol Biol. 2017;51(5): 752-760.
[37] ZHAO C, BUSCH DJ, VERSHEL CP, et al. Multifunctional Transmembrane Protein Ligands for Cell-Specific Targeting of Plasma Membrane-Derived Vesicles. Small. 2016;12(28):3837-3848.
[38] HARASZTI RA, MILLER R, DUBUKE ML, et al. Serum Deprivation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Exosome Activity and Alters Lipid and Protein Composition. Science. 2019;16:230-241.
[39] ALVAREZ-ERVITI L, LAKHAL S, WOOD MJ, et al. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(4):341.
[40] BELLAVIA D, RAIMONDO S, CALABRESE G, et al. Interleukin 3-receptor targeted exosomes inhibit in vitro and in vivo Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia cell growth. Theranostics. 2017;7(5):1333-1345.
[41] STICKNEY Z, ZHANG Z, LU B, et al. Development of exosome surface display technology in living human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;472(1):53-59.
[42] KOOIJMANS SA, VADER P, SCHIFELERS RM, et al. Display of GPI-anchored anti-EGFR nanobodies on extracellular vesicles promotes tumour cell targeting. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5(1):31053.
[43] OHNO SI, ISHIKAWA A, MATSUYAMA N, et al. Systemically injected exosomes targeted to EGFR deliver antitumor microRNA to breast cancer cells. Mol Ther. 2013;21(1):185-191.
[44] VAN DONGEN HM, WITWER KW, PEGTEL DM, et al. Extracellular vesicles exploit viral entry routes for cargo delivery. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016;80(2):369-386.
[45] RAIBORG C, RUSTEN TE, STENMARK H. Protein sorting into multivesicular endosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003;15:446-455.
[46] STERZENBACH U, PUTZ U, HOWITT J, et al. Engineered Exosomes as Vehicles for Biologically Active Proteins. Mol Ther. 2017;25(6):1269-1278.
[47] YIM N, LEE S, CHOI H, et al. Exosome engineering for efcient intracellular delivery of soluble proteins using optically reversible protein-protein interaction module. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12277.
[48] LI Z, YANG G, YUAN L, et al. In Vitro and in Vivo RNA Inhibition by CD9-HuR Functionalized Exosomes Encapsulated with miRNA or CRISPR/dCas9. Nano Lett. 2019;19(1):19-28.
[49] KIM SM, KIM HS. Engineering of extracellular vesicles as drug delivery vehicles. Stem Cell Investig. 2017;4:74.
[50] MUNAGALA R, AQIL F, GUPTA RC, et al. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016;371(1):48-61.
[51] JOHNSEN KB, GUDBERGSSON JM, MOOS T, et al. Evaluation of electroporation-induced adverse effects on adipose-derived stem cell exosomes. Cytotechnology. 2016;68:2125-2138.
[52] KIM MS, HANEY MJ, KLYACHKO NL, et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomed-Nanotechnol. 2016;12:655-664.
[53] FUHRMANN G, SERIO A, STEVENS MM, et al. Active loading into extracellular vesicles significantly improves the cellular uptake and photodynamic effect of porphyrins. J Control Release. 2015;205:35-44.
[54] HANEY MJ, KLYACHKO NL, HE ZJ, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207: 18-30.
[55] SATO YT, SASAKI Y, HARADA N, et al. Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes. 2016;6:21933.
[56] HOOD JL. Post isolation modification of exosomes for nanomedicine applications. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016;11:1745-1756.
[57] JANG SC, KIM OY, GHO YS, et al. Bioinspired exosome-mimetic nanovesicles for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics to malignant tumors. ACS Nano. 2013;7(9):7698-7710.
[58] HU CM, FANG RH, DEHAINI D, et al. Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking. Nature. 2015;526:118-121.
[59] TOLEDANO FURMAN NE, LETKO N, WEINSTEIN E, et al. Reconstructed stem cell nanoghosts: a natural tumor targeting platform. Nano Lett. 2013;13:3248-3255.
[60] YOON J, JEONG H, PARK J, et al. Generation of nanovesicles with sliced cellular membrane fragments for exogenous material delivery. Biomaterials. 2015;59:12-20.
[61] LEE YS, CHO JA, KIM CW, et al. Introduction of the CIITA gene into tumor cells produces exosomes with enhanced antitumor efects. Exp Mol Med. 2011;43(5):281.
[62] NEDERGAARD MK, HEDEGAARD CJ, POULSEN HS. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in solid tumor malignancies. BioDrugs. 2012;26(2):83-99.
[63] GRAPP M, WREDE A, SNAIDERO N, et al. Choroid plexus transcytosis and exosome shuttling deliver folate into brain parenchyma. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2123.
[64] JIA G, HAN Y, TANG Q, et al. NRP-1 targeted and cargo-loaded exosomes facilitate simultaneous imaging and therapy of glioma in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2018;178:302-316.
[65] XITONG D, XIAORONG ZJG. Targeted therapeutic delivery using engineered exosomes and its applications in cardiovascular diseases. Gene. 2016;575(2):377-384.
[66] WANG X, YU Y, SUN J, et al. Engineered exosomes with ischemic myocardium-targeting peptide for targeted therapy in myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7:15.
[67] KIM H, YUN N, PARK H, et al. Cardiacspecifc delivery by cardiac tissue-targeting peptide-expressing exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;499(4):803-808.
[68] SUN D, MILLER D, ZHANG HG, et al. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol Ther. 2010;18(9):1606-1614.
[69] WU K, WU SY, WATABE K, et al. Extracellular vesicles as emerging targets in cancer: Recent development from bench to bedside. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017;1868(2):538-563.
|