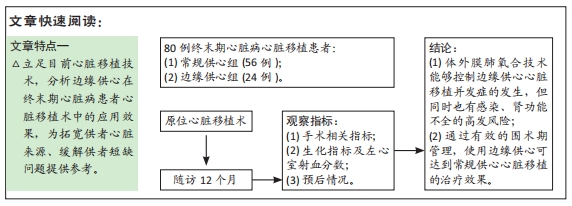
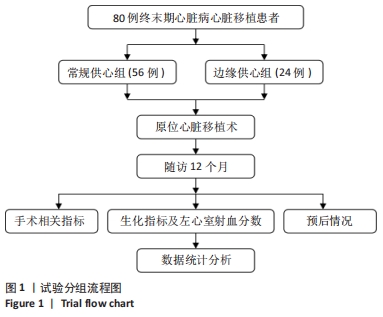
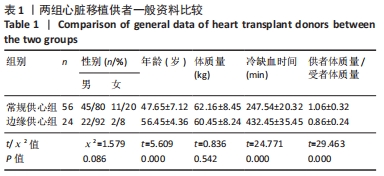
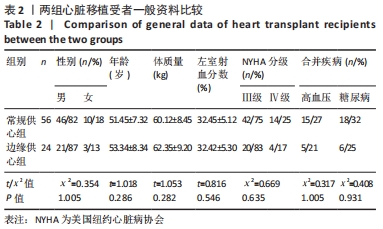
[1] AISSAOUI N, MORSHUIS M, MAOULIDA H, et al. Management of end-stage heart failure patients with or without ventricular assist device: an observational comparison of clinical and economic outcomes. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;53(1):170-177.
[2] 黄洁.国人心脏移植注册数据分析与脑死亡心脏供体的选择和维护[J].实用器官移植电子杂志,2016,4(5):295.
[3] KILIC A, EMANI S, SAI-SUDHAKAR CB, et al. Donor selection in heart transplantation. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6(8):1097-1104.
[4] 吴敏,吴怡锦,吴梅芬,等.125例脑死亡捐献心脏供体的单中心回顾性分析及边缘供心使用探讨[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2019,26(11): 1069-1073.
[5] KAMRAN S, CONTI F, POMEY MP, et al. Patients’ preferences in transplantation from marginal donors: results of a discrete choice experiment. Transpl Int. 2017; 30(6):589-602.
[6] WANG Y, CAI J, SUN Y, et al. Extended donor criteria in heart transplantation: a retrospective study from a single Chinese institution. J Thorac Dis. 2018; 10(4):2153-2165.
[7] 中华医学会器官移植分会.中国心脏移植供心获取与保护技术规范(2019版)[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):8-10.
[8] WILHELM MJ, RUSCHITZKA F, FLAMMER AJ, et al. Fiftieth anniversary of the first heart transplantation in Switzerland in the context of the worldwide history of heart transplantation. Swiss Med Wkly. 2020;150:w20192.
[9] 江文诗,GOMEZ MP,PAEZ G,等.数据之美-聚集全球器官捐献发展趋势[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):28-33.
[10] KOBASHIGAWA J, KHUSH K, COLVIN M, et al. Report From the American Society of Transplantation Conference on Donor Heart Selection in Adult Cardiac Transplantation in the United States. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(10):2559-2566.
[11] MEHRA MR, CANTER CE, HANNAN MM, et al. The 2016 International Society for Heart Lung Transplantation listing criteria for heart transplantation: A 10-year update. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2016;35(1):1-23.
[12] AMMIRATI E, CIPRIANI MG, VARRENTI M, et al. A prospective comparison of mid-term outcomes in patients treated with heart transplantation with advanced age donors versus left ventricular assist device implantation. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016;23(4):584-592.
[13] KAKUTA T, FUKUSHIMA S, SHIMAHARA Y, et al. Benefits of the Modified Bicaval Anastomosis Technique for Orthotopic Heart Transplantation From a Size-Mismatched Marginal Donor. Circ J. 2019;84(1):61-68.
[14] 杨丽静,王古岩,郑哲,等.远隔缺血预后联合后处理对心脏移植术患者心肌损伤的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2016,36(8):918-921.
[15] JAWITZ OK, RAMAN V, BARAC YD, et al. Influence of donor brain death duration on outcomes following heart transplantation: A United Network for Organ Sharing Registry analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020;159(4): 1345-1353.e2.
[16] ZHU C, SU Y, JURIASINGANI S, et al. Supplementing preservation solution with mitochondria-targeted H2 S donor AP39 protects cardiac grafts from prolonged cold ischemia-reperfusion injury in heart transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2019;19(11):3139-3148.
[17] 谢云亮,杨洲,杨卿,等.公民逝世后器官捐献高龄供肝肝移植的临床疗效分析:单中心经验[J].器官移植,2020,11(2):271-275.
[18] BOSSEAU C, LELONG B, PATTIER S, et al. Heart transplantation in selected patients aged 60 years and older: a two-decade retrospective and multicentre analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2017;51(5):893-901.
[19] RAM E, LAVEE J, KOGAN A, et al. Does donor-recipient age difference matter in outcome of heart transplantation? Clin Transplant. 2019;33(7):e13593.
[20] 王怡轩,谢飞,蔡杰,等.单中心回顾性研究心脏移植的边缘供心应用[J].中国循环杂志,2017,32(z1):121-122.
[21] STEHLIK J, KOBASHIGAWA J, HUNT SA, et al. Honoring 50 Years of Clinical Heart Transplantation in Circulation: In-Depth State-of-the-Art Review. Circulation. 2018;137(1):71-87.
[22] BERGENFELDT H, STEHLIK J, HÖGLUND P, et al. Donor-recipient size matching and mortality in heart transplantation: Influence of body mass index and gender. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2017;36(9):940-947.
[23] SHUDO Y, WANG H, LINGALA B, et al. Evaluation of Risk Factors for Heart-Lung Transplant Recipient Outcome: An Analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing Database. Circulation. 2019;140(15):1261-1272.
[24] 吴智勇,王志维,任宗力,等.边缘供心临床应用的单中心效果分析[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2020,36(4):222-226.
[25] 中华医学会器官移植学分会.器官移植病理学技术操作规范(2019版)——心脏移植[J].器官移植,2019,10(4):393-401.
[26] GOSSETT JG, AMDANI S, KHULBEY S, et al. Review of interactions between high-risk pediatric heart transplant recipients and marginal donors including utilization of risk score models. Pediatr Transplant. 2020;24(3):e13665.
[27] YANG Y, LIN H, WEN Z, et al. Keeping donor hearts in completely beating status with normothermic blood perfusion for transplants. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95(6):2028-2034.
[28] 中会医学器官移植学分会.中国心脏移植免疫抑制治疗及排斥反应诊疗规范(2019版)[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):15-20.
[29] 武康,蔡明,许亮,等.不同免疫诱导方案在心脏死亡器官捐献肾移植中的应用研究[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2018,12(1):1-4.
[30] NAM KH, KOH Y, LIM CM, et al. Central Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Bridging of Right-Sided Heart Failure to Lung Transplantation: A Single-Center Experience and Literature Review. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2019;33(7):1873-1876.
[31] 柴军武,王凯,周巍,等.体外膜肺氧合在心脏移植术后心功能衰竭中的应用体会[J].天津医药,2018,46(5):478-481.
|