| [1] Jiang Y, Villeneuve PJ, Fenton SS,et al. Liver transplantation and subsequent risk of cancer: findings from a Canadian cohort study. Liver Transpl. 2008;14(11):1588-1597.
[2] Haridass D, Narain N, Ott M. Hepatocyte transplantation: waiting for stem cells. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2008; 13(6):627-632.
[3] Snykers S, De Kock J, Rogiers V,et al. In vitro differentiation of embryonic and adult stem cells into hepatocytes: state of the art.Stem Cells. 2009;27(3):577-605.
[4] 丁鹏,冯忠堂,杨智勇,等.趋化因子SDF-1体外趋化骨髓基质细胞迁移的实验研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2007,6(3):225-227,237.
[5] Shen LH, Li Y, Chen J,et al. Therapeutic benefit of bone marrow stromal cells administered 1 month after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27(1):6-13.
[6] 杨丽萍,马俊勋,袁菊芳,等.HGF,EGF对体外培养大鼠肝脏干细胞增殖的实验研究[J].实验动物与比较医学,2009,29(6): 361-365.
[7] Parekkadan B, van Poll D, Megeed Z,et al. Immunomodulation of activated hepatic stellate cells by mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;363(2):247-252.
[8] 王方,冯淑娴,寇俊峰,等.经门静脉或肝动脉脐带血干细胞移植治疗失代偿期肝硬化的近期疗效与安全性比较[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2013,16(4):327-329.
[9] Lesko E, Majka M. The biological role of HGF-MET axis in tumor growth and development of metastasis. Front Biosci. 2008;13:1271-1280.
[10] Abdel Aziz MT, Atta HM, Mahfouz S,et al. Therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on experimental liver fibrosis. Clin Biochem. 2007;40(12):893-899.
[11] Higashiyama R, Inagaki Y, Hong YY,et al. Bone marrow-derived cells express matrix metalloproteinases and contribute to regression of liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology. 2007;45(1):213-222.
[12] 朱英,刘平.一贯煎对DMN肝纤维化大鼠肝卵圆细胞增殖分化的影响[J].大连医科大学学报,2011,33(1):11-16.
[13] 袁璐萍.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗肝硬化的研究进展[J].浙江临床医学,2011,13(11):1279-1281.
[14] 林荣,吴兵,戴若竹,等.粒细胞集落刺激因子治疗兔急性心肌梗死的时间窗研究[J].中国医药生物技术,2007,2(4):281-285.
[15] 徐旭雯,谭德明,鲁猛厚.粒细胞集落刺激因子对小鼠急性肝衰竭的保护作用[J].中南大学学报:医学版,2006,31(4):543-547.
[16] 卢兴浩,裴雪莲,肖智伟,等.粒细胞集落刺激因子骨髓干细胞动员治疗大鼠肝损伤的实验研究[J].农垦医学,2009,31(6):487-490.
[17] 张善红,姜春萌,李荣宽,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗失代偿期肝硬化的临床研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2012,6(4): 1016-1018.
[18] Barascuk N, Veidal SS, Larsen L,et al. A novel assay for extracellular matrix remodeling associated with liver fibrosis: An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for a MMP-9 proteolytically revealed neo-epitope of type III collagen. Clin Biochem. 2010;43(10-11):899-904.
[19] di Bonzo LV, Ferrero I, Cravanzola C,et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells as a two-edged sword in hepatic regenerative medicine: engraftment and hepatocyte differentiation versus profibrogenic potential. Gut. 2008;57(2): 223-231.
[20] 吴佳羽,尹华发.肝脏干细胞移植治疗肝硬化的研究进展[J].临床医学,2011,31(3):111-113.
[21] 邢全台,孙启龙,李栋,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞样细胞的诱导分化[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2009,17(26): 2654-2661.
[22] Shi XL, Qiu YD, Wu XY,et al. In vitro differentiation of mouse bone marrow mononuclear cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Hepatol Res. 2005 ;31(4):223-231.
[23] Kang XQ, Zang WJ, Song TS,et al. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into hepatocytes in vitro.World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11(22):3479-3484.
[24] Snykers S, Vanhaecke T, Papeleu P,et al. Sequential exposure to cytokines reflecting embryogenesis: the key for in vitro differentiation of adult bone marrow stem cells into functional hepatocyte-like cells.Toxicol Sci. 2006;94(2): 330-341.
[25] Wang PP, Wang JH, Yan ZP,et al. Expression of hepatocyte-like phenotypes in bone marrow stromal cells after HGF induction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 320(3):712-716.
[26] 张刚庆,方驰华,池达智.肝细胞生长因子诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞分化的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志, 2005, 43(11): 716-720.
[27] 丁鹏,冯忠堂,杨智勇,等.趋化因子SDF-1体外趋化骨髓基质细胞迁移的实验研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2007,6(3):225-227,237.
[28] Bhakta S, Hong P, Koc O.The surface adhesion molecule CXCR4 stimulates mesenchymal stem cell migration to stromal cell-derived factor-1 in vitro but does not decrease apoptosis under serum deprivation. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2006;7(1):19-24.
[29] 卢宁,赵龙凤,李红,等.应用全骨髓贴壁法获取高纯度大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的实验研究[J].山西医科大学学报,2010,41(3): 277-280.
[30] Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Gerasimov UV. Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: in vitro cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1987; 20(3):263-272.
[31] 朱建宇,施伟民.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的体外培养和鉴定[J].同济大学学报:医学版,2012,33(5): 45-48.
[32] 张怡,赵连三,唐红.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离与培养[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2004 , 21(5): 746-748.
[33] 王文,李静,王宗仁,等.不同分离方法与培养条件下大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞生长增殖情况比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(3): 482-485,489.
[34] 庄淑波,刘毅,陈克明,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外分离、纯化与培养适宜条件的筛选[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(20): 3886-3991.
[35] 彭德新,陈自谦,白伟,等.不同首次换液模式对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞培养的影响[J].临床军医杂志, 2011, 39(3): 403-406.
[36] 杨丽萍,马俊勋,袁菊芳,等. HGF, EGF对体外培养大鼠肝脏干细胞增殖的实验研究[J].实验动物与比较医学,2009,29(6): 361-365.
[37] 邝郁郁.不同浓度肝细胞生长因子和成纤维细胞生长因子对大鼠肝干细胞的增殖调控[J].国际病理科学与临床杂志, 2010, 30(2):106-109.
[38] 张悦,欧来良,程兆康,等.CXCR4基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞体外迁移实验[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2009, 26(3): 595-600.
[39] Phinney DG, Kopen G, Isaacson RL,et al. Plastic adherent stromal cells from the bone marrow of commonly used strains of inbred mice: variations in yield, growth, and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 1999;72(4):570-585.
[40] 张本斯,王凡,邓力,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离纯化与初步鉴定[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2003,12(2):161-165.
[41] Encina NR, Billotte WG, Hofmann MC. Immunomagnetic isolation of osteoprogenitors from human bone marrow stroma. Lab Invest. 1999;79(4):449-457.
[42] Zohar R, Sodek J, McCulloch CA. Characterization of stromal progenitor cells enriched by flow cytometry. Blood. 1997;90(9): 3471-3481.
[43] Conget PA, Minguell JJ. Phenotypical and functional properties of human bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells. J Cell Physiol. 1999;181(1):67-73.
[44] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[45] Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16(3):1215.
[46] Hayashi SI, Watanabe J, Nakachi K,et al. PCR detection of an A/G polymorphism within exon 7 of the CYP1A1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19(17):4797.
[47] Snykers S, Vanhaecke T, De Becker A,et al. Chromatin remodeling agent trichostatin A: a key-factor in the hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells derived of adult bone marrow. BMC Dev Biol. 2007;7:24.
[48] 李瀚旻,晏雪生,明安萍,等.肝脏细胞条件培养基诱导大鼠骨髓间质细胞分化为肝细胞的作用[J].中西医结合肝病杂志, 2005, 15(1): 28-30. |
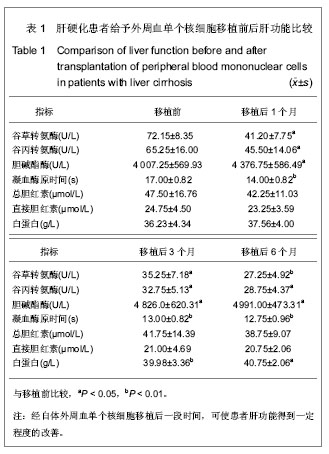
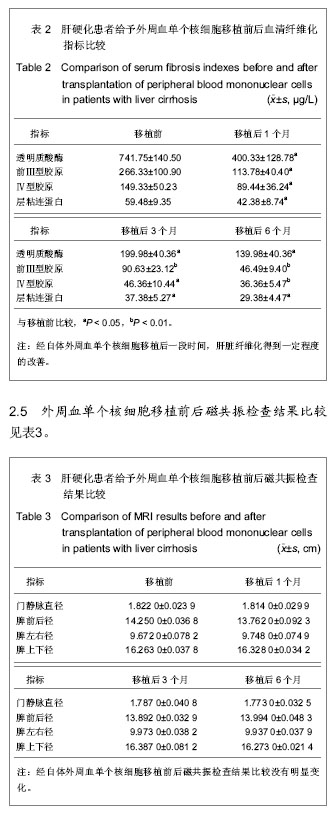

.jpg)
