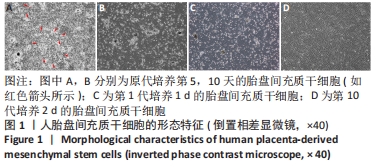
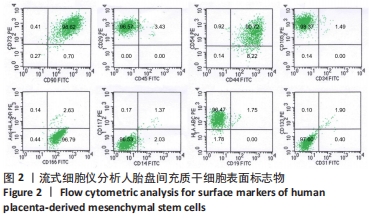
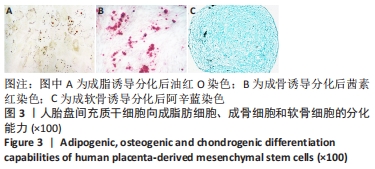
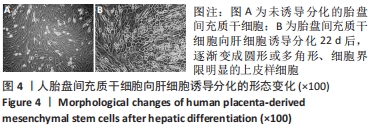
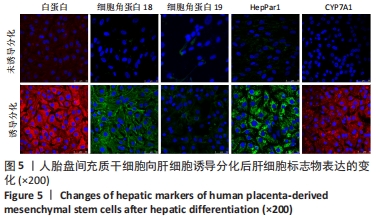
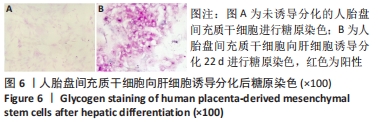
[1] ZERN MA. Cell transplantation to replace whole liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):767-769.
[2] TERATANI T, YAMAMOTO H, AOYAGI K, et al. Direct hepatic fate specification from mouse embryonic stem cells. Hepatology. 2005;41(4):836-846.
[3] DWYER BJ, MACMILLAN MT, BRENNAN PN, et al. Cell therapy for advanced liver diseases: Repair or rebuild. J Hepatol. 2021;74(1):185-199.
[4] 孙婷,李凡,杜联芳.间充质干细胞治疗急性肝损伤:肝脏归巢率及定向分化能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1):125-131.
[5] QIAO Y, XU Z, YU Y, et al. Single cell derived spheres of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance cell stemness properties, survival ability and therapeutic potential on liver failure. Biomaterials. 2020;227:119573.
[6] CHEN L, ZHANG J, YANG L, et al. The Effects of Conditioned Medium Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cocultured with Hepatocytes on Damaged Hepatocytes and Acute Liver Failure in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:9156560.
[7] ZHANG S, LIU P, CHEN L, et al. The effects of spheroid formation of adipose-derived stem cells in a microgravity bioreactor on stemness properties and therapeutic potential. Biomaterials. 2015;41:15-25.
[8] ZHANG S, CHEN L, LIU T, et al. Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells efficiently rescue acute liver failure through paracrine effects rather than hepatic differentiation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(13-14):1352-1364.
[9] WEI T, LV Y. Immediate intraportal transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells prevents death from fulminant hepatic failure in pigs. Hepatology. 2013;58(1):451-452.
[10] WANG YH, WU DB, CHEN B, et al. Progress in mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for acute liver failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):227.
[11] FU Y, DENG J, JIANG Q, et al. Rapid generation of functional hepatocyte-like cells from human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):105.
[12] CUI L, SHI Y, ZHOU X, et al. A set of microRNAs mediate direct conversion of human umbilical cord lining-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(11):e918.
[13] JI R, ZHANG N, YOU N, et al. The differentiation of MSCs into functional hepatocyte-like cells in a liver biomatrix scaffold and their transplantation into liver-fibrotic mice. Biomaterials. 2012;33(35):8995-9008.
[14] STOCK P, BRÜCKNER S, EBENSING S, et al. The generation of hepatocytes from mesenchymal stem cells and engraftment into murine liver. Nat Protoc. 2010; 5(4):617-627.
[15] AURICH H, SGODDA M, KALTWASSER P, et al. Hepatocyte differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue in vitro promotes hepatic integration in vivo. Gut. 2009;58(4):570-581.
[16] YEN MH, WU YY, LIU YS, et al. Efficient generation of hepatic cells from mesenchymal stromal cells by an innovative bio-microfluidic cell culture device. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):120.
[17] BHARTI D, SHIVAKUMAR SB, PARK JK, et al. Comparative analysis of human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells derived from different parts of the same umbilical cord. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;372(1):51-65.
[18] STANKO P, KAISEROVA K, ALTANEROVA V, et al. Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp, bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue by gene expression. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014;158(3):373-377.
[19] 赵姝灿,郑桂纯,林连蓬,等.人羊水、脐带、胎盘来源间充质干细胞体外增殖、分化、运输和免疫学特性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(25): 4028-4034.
[20] CHIEN CC, YEN BL, LEE FK, et al. In vitro differentiation of human placenta-derived multipotent cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(7):1759-1768.
[21] LEE CW, CHEN YF, WU HH, et al. Historical Perspectives and Advances in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Research for the Treatment of Liver Diseases. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(1):46-56.
[22] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[23] LEE KD, KUO TK, WHANG-PENG J, et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275-1284.
[24] DI CAMPLI C, PISCAGLIA AC, PIERELLI L, et al. A human umbilical cord stem cell rescue therapy in a murine model of toxic liver injury. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36(9): 603-613.
[25] 马晨,李晓国,徐明均,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞的扩增与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(33):5293-5299.
[26] ULLAH I, SEO K, WI H, et al. Induction of the differentiation of porcine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into premature hepatocyte-like cells in an indirect coculture system with primary hepatocytes. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2020;24(5):289-298.
[27] REBELO SP, COSTA R, SILVA MM, et al. Three-dimensional co-culture of human hepatocytes and mesenchymal stem cells: improved functionality in long-term bioreactor cultures. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(7):2034-2045.
[28] OUYANG JF, LOU J, YAN C, et al. In-vitro promoted differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards hepatocytes induced by salidroside. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010; 62(4):530-538.
[29] VOLAREVIC V, NURKOVIC J, ARSENIJEVIC N, et al. Concise review: Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of acute liver failure and cirrhosis. Stem Cells. 2014;32(11):2818-2823.
[30] CAMPARD D, LYSY PA, NAJIMI M, et al. Native umbilical cord matrix stem cells express hepatic markers and differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(3):833-848.
[31] AFSHARI A, SHAMDANI S, UZAN G, et al. Different approaches for transformation of mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):54.
[32] YU J, SU X, ZHU C, et al. GFP Labeling and Hepatic Differentiation Potential of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35(6):2299-2308.
[33] PASSARETTA F, BOSCO D, CENTURIONE L, et al. Differential response to hepatic differentiation stimuli of amniotic epithelial cells isolated from four regions of the amniotic membrane. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(7):4350-4355.
[34] FORTE G, MINIERI M, COSSA P, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor effects on mesenchymal stem cells: proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Stem Cells. 2006;24(1):23-33.
[35] ZHANG S, ZHANG Y, CHEN L, et al. Efficient large-scale generation of functional hepatocytes from mouse embryonic stem cells grown in a rotating bioreactor with exogenous growth factors and hormones. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(6):145.
[36] SAHABIAN A, DAHLMANN J, MARTIN U, et al. Production and cryopreservation of definitive endoderm from human pluripotent stem cells under defined and scalable culture conditions. Nat Protoc. 2021;16(3):1581-1599.
|