[1] KORINTH MC. Treatment of cervical degenerative disc disease: current status and trends. Zentralbl Neurochir. 2008;69(3):113-124.
[2] KOLSTAD F, NYGAARD ØP, ANDRESEN H, et al. Anterior cervical arthrodesis using a “stand alone” cylindrical titanium cage:prospective analysis of radiographic parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(16): 1545-1550.
[3] HILIBRAND AS, ROBBINS M. Adjacent segment degeneration and adjacent segment disease: the consequences of spinal fusion? Spine J. 2004;4(6 Suppl):190-194.
[4] BAZAZ R, LEE MJ, YOO JU. Incidence of Dysphagia After Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery: a prospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(22):2453-2458.
[5] 李玉伟,王海蛟,严晓云,等.颈前路减压零切迹椎间融合器与钉板系统内固定治疗脊髓型颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(11):1136-1141.
[6] SCHOLZ M, SCHNAKE KJ, PINGEL A, et al.A New Zero-profile Implant for Stand-alone Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3):666-673.
[7] MIAO J, SHEN Y, KUANG Y, et al. Early Follow-up Outcomes of a New Zero-profile Implant Used in Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(5):193-197.
[8] 贾连顺.脊髓型颈椎病的早期诊断与治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 1999,6(5):3-5.
[9] SUK SI, LEE CK, KIM WJ, et al. Adding posterio r lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(2): 210-220.
[10] CHRISTENSEN FB, LAURSEN M, GELINECK J, et al. Interobserver and intraobserver agreement of radiograph interpretation with and without pedicle screw implants:the need for a detailed classification sy stem in posterolateral spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(5):538-544.
[11] KANDZIORA F, PFLUGMACHER R, SCHOLZ M, et al. Bioabsorbable interbody cages in a sheep cervical spine fusion model. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(17):1845-1855.
[12] BAZAZ R, LEE MJ, YOO JU. Incidence of dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a prospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(27): 2453-2458.
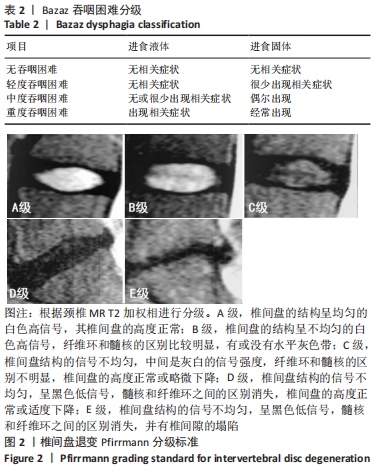
[13] PFIRRMANN CWA, METZDORF A, ZANETTI M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneraion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(17):1873-1878.
[14] REIS MT, REYES PM, CRAWFORD NR, et al. Biomechanical Assessment of Anchored Cervical Interbody Cages: Comparison of 2-Screw and 4-Screw Designs. Neurosurgery. 2014;10:412-417.
[15] 梁跃伟,张帆,李全,等.新一代零切迹内固定系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病的早期疗效[J].昆明医科大学学报,2017,38(6):113-117.
[16] 曹胜,孔令伟,徐昆,等.颈椎矢状位序列参数在评估颈前路椎间盘切除融合术疗效中的价值[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(6):761-764.
[17] NADERI S, OZGEN S, PAMIR MN, et al. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: surgical results and factors affecting prognosis. Neurosurgery. 1998; 43:43-50.
[18] VANEK P, BRADAC O, DELACY P, et al. Anterior interbody fusion of the cervical spine with Zero-P spacer: Prospective comparative study -clinical and radiological results at a minimum 2 years after surgery. Spine. 2013;38(13):792-797.
[19] VILLAVICENCIO AT, BABUSKA JM, ASHTON A, et al. Prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical study evaluating the correlation of clinical outcomes and cervical sagittal alignment. Neurosurgery. 2011;68:1309-1316,1316.
[20] GUERIN P, OBEID I, GILLE O, et al. Sagittal alignment after single cervical disc arthroplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25:10-16.
[21] 曾昭勇,魏鲁青,张健平.颈椎Zero-P与传统颈椎前路内固定治疗颈椎病的对比研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2016,15(10): 1010-1013.
[22] OPSENAK R, HANKO M, SNOPKO P, et al.Subsidence of anchored cage after anterior cervical discectomy. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2019;120(5): 356-361.
[23] JOAQUIM AF, MURAR J, SAVAGE JW, et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a systematic review of potential preventative measures. Spine J. 2014;14(9):2246-2260.
[24] KEPLER CK, RIHN JA, BENNETT JD, et al. Dysphagia and soft-tissue swelling after anterior cervical surgery: a radiographic analysis. Spine J. 2012;12(8):639-644.
[25] SISKA PA, PONNAPPAN RK, HOHL JB, et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery:a prospective study using the swallowingquality of life questionnaire and analysis of patient comorbidities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(17):1387-1391.
[26] 彭爱明,刘果,俞勇,等.颈椎前路减压cage与zero-p椎间植骨融合内固定治疗单节段脊髓型颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(11):1121-1123.
[27] 余彬,彭银虓,薛力,等.零切迹椎间融合固定器与传统颈前路钢板Cage融合内固定治疗双节段颈椎病的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1342-1347.
[28] MOSTAFA AG, ELISABETH T, AMOL PY, et al. Improved Dysphagia Outcomes in Anchored Spacers Versus Plate-Screw Systems in Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: A Systematic Review. Global Spine J. 2020;10(8):1057-1065.
[29] WANG F, HOU HT, WANG P, et al. Symptomatic adjacent segment disease after single-lever anterior cervical discectomy and fusion:Incidence and risk factors. Medicine. 2017;96(47):e8663.
[30] HILIBRAND AS, CARLSON GD, PALUMBO MA, et al. Radiculopathy and myelopathy at segments adjacent to the site of a previous anterior cervical arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(4):519-528.
[31] LEE JC, LEE SH, PETERS C, et al. Adjacent segment pathology requiring reoperation after anterior cervical arthrodesis:the influence of smoking, sex,and number of operated levels. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(10):571-577.
[32] VIRK SS, NIEDERMEIER S, YU E, et al. Adjacent segment disease. Orthopedics.2014;37(8):547-555.
[33] PARK JB, WATTHANAAPHISIT T, RIEW KD. Timing of development of adjacent-level ossification after anterior cervical arthrodesis with plates. Spine J. 2007;7(6):633-636.
[34] ECK JC, HUMPHREYS SC, LIM TH, et al. Biomechanical study on the effect of cervical spine fusion on adjacent-level intradiscal pressure and segmental motion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(22):2431-4243.
|