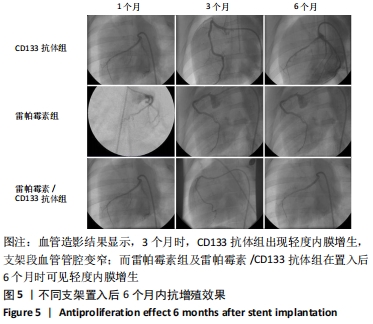
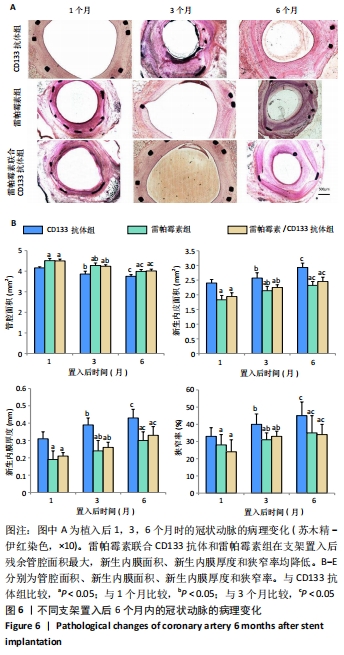
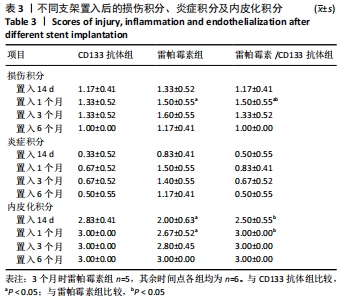
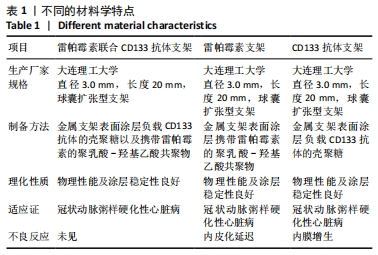
[1] Danese S, Papa A, Saibeni S, et al Inflammation and coagulation in inflammatory bowel disease: The clot thickens. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102(1):174-186.
[2] Kim HS, Rhee TM. Farewell to Drug-Eluting Balloons for In-Stent Restonsis?: Appropriate Technique of Drug-Eluting Balloons Implantation Matters. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11(10):992-994.
[3] Kim J, Song YB, Oh JH, et al. Effects of Prolonged Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in ST-Segment Elevation vs. Non-ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Circ J. 2021;85(6):817-825.
[4] Diaz-Rodriguez S, Rasser C, Mesnier J, et al. Coronary stent CD31-mimetic coating favours endothelialization and reduces local inflammation and neointimal development in vivo. Eur Heart J. 2021; 42(18):1760-1769.
[5] Torii S, Jinnouchi H, Sakamoto A, et al. Drug-eluting coronary stents: insights from preclinical and pathology studies. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(1):37-51.
[6] Sim HW, Thong EH, Tan HC, et al. Clinical Outcomes One Year and Beyond After Combination Sirolimus-Eluting Endothelial Progenitor Cell Capture Stenting During Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2019;20(9):739-743.
[7] Schober A, Hoffmann R, Oprée N, et al. Peripheral CD34+ cells and the risk of in-stent restenosis in patients with coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(8):1116-1122.
[8] Hoesli CA, Tremblay C, Juneau PM, et al. Dynamics of Endothelial Cell Responses to Laminar Shear Stress on Surfaces Functionalized with Fibronectin-Derived Peptides. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(11): 3779-3791.
[9] 杨峰,赵骞,张世轩,等.雷帕霉素联合CD34抗体复合支架快速捕获外周血中内皮祖细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(41): 6694-6698.
[10] Hässler S, Bachelet D, Duhaze J, et al. Clinicogenomic factors of biotherapy immunogenicity in autoimmune disease: A prospective multicohort study of the ABIRISK consortium. PLoS Med. 2020;17(10):e1003348.
[11] Savic V, Stefanovic V, Ardaillou N, et al. Induction of ecto-5’-nucleotidase of rat cultured mesangial cells by interleukin-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Immunology. 1990;70(3):321-326.
[12] Pradhan A, Saran M, Vishwakarma P, et al. Optical Coherence Tomography in In-Stent Restenosis: A Challenge Made Easier. Heart Views. 2019;20(1):28-31.
[13] Yagi S, Kondo D, Ise T, et al. Association of Decreased Docosahexaenoic Acid Level After Statin Therapy and Low Eicosapentaenoic Acid Level with In-Stent Restenosis in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019;26(3):272-281.
[14] Carter AJ, Aggarwal M, Kopia GA, et al. Long-term effects of polymer-based, slow-release, sirolimus-eluting stents in a porcine coronary model. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;63(4):617-624.
[15] Tadano Y, Kotani JI, Kashima Y, et al. Predictors of clinical outcomes after coronary implantation of bioresorbable polymer sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster stents in all-comers: A report of 1,727 cases. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;94(1):91-97.
[16] Sakamoto Y, Yamawaki M, Araki M, et al. Comparison of 12-month angiographic outcomes between repeat drug-eluting stent implantation and drug-coated balloon treatment for restenotic lesion caused by stent fracture. Heart Vessels. 2019;34(10):1589-1594.
[17] Nakazawa G, Granada JF, Alviar CL, et al. Anti-CD34 antibodies immobilized on the surface of sirolimus-eluting stents enhance stent endothelialization. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3(1):68-75.
[18] Yang XS, Zhu HG, Yu ZJ, et al. The union of anti-CD34 antibody can improve the performance of drug-eluting stents. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;79(6):972-978.
[19] 宋现涛,朱华刚,杨兴胜,等.抗CD34抗体抵消雷帕霉素洗脱支架内皮延迟修复研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2011,30(6):539-544.
[20] Fallatah R, Elasfar A, Amoudi O, et al. Endovascular repair of severe aortic coarctation, transcatheter aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis, and percutaneous coronary intervention in an elderly patient with long term follow-up. J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2018;30(3):271-275.
[21] Jeger RV, Farah A, Ohlow MA, et al. Drug-coated balloons for small coronary artery disease (BASKET-SMALL 2): an open-label randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;392(10150):849-856.
[22] Kang HJ, Kim HS, Zhang SY, et al. Effects of intracoronary infusion of peripheral blood stem-cells mobilised with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on left ventricular systolic function and restenosis after coronary stenting in myocardial infarction: the MAGIC cell randomised clinical trial. Lancet. 2004;363(9411):751-756.
[23] Fellows BD, Ghobrial N, Mappus E, et al. In vitro studies of heparin-coated magnetic nanoparticles for use in the treatment of neointimal hyperplasia. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(4):1191-1200.
[24] Liu G, Gong Y, Zhang R, et al. Resolvin E1 attenuates injury-induced vascular neointimal formation by inhibition of inflammatory responses and vascular smooth muscle cell migration. FASEB J. 2018;32(10): 5413-5425.
[25] 韩健,郭富强,张天,等.颅内外动脉狭窄支架成形术后血清 IL-1β、IL-1Ra的变化及与再狭窄的关系[J].中华神经医学杂志, 2010,9(3):277-280.
[26] 金冬霞,胡越成,丛洪良.CD40及CD40配体在介入治疗后再狭窄中的作用[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2012,14(1):98-99.
[27] 凌林,胡名松.地塞米松预防兔移植静脉再狭窄的实验研究[J].中国社区医师,2017,33(14):5,7.
[28] 赵美香,田建会.冠心病患者冠脉支架植入术前后白细胞介素18水平变化[J].实用医药杂志,2007,24(11):1318.
[29] Cilingiroglu M, Elliott J, Patel D, et al. Long-term effects of novel biolimus eluting DEVAX AXXESS plus nitinol self-expanding stent in a porcine coronary model. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2006; 68(2):271-279.
[30] Yeh JS, Oh SJ, Hsueh CM. Frequency of Vascular Inflammation and Impact on Neointimal Proliferation of Drug Eluting Stents in Porcine Coronary Arteries. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2016;32(5):570-577.
|