中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 1051-1056.doi: 10.12307/2022.143
• 牙髓及牙周膜干细胞 Dental pulp and periodontal ligament stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
柚皮素干预人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化能力
罗小玲1,张 丽1,杨茂桦1,徐 洁2,徐晓梅2
- 1西南医科大学口颌面修复重建和再生实验室,四川省泸州市 646000;2西南医科大学附属口腔医院正畸科,四川省泸州市 646000
Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells
Luo Xiaoling1, Zhang Li1, Yang Maohua1, Xu Jie2, Xu Xiaomei2
- 1Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration Laboratory, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Orthodontics, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
柚皮素:是广泛存在于芸香科植物中的一种二氢黄酮类化合物,能促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化,抑制破骨细胞的活性和生成。
牙周膜干细胞:是存在于牙周膜中的一种未分化的间充质细胞,具有高增殖能力和多能性,能定向分化为成骨细胞,其成骨分化能力受细胞因子、激素、药物等诸多因素的调节。
背景:柚皮素具有抗菌、抗炎、抗纤维化、抗氧化等多种生理活性,被广泛应用于医药和食品领域。近来有研究证明,柚皮素能有效促进间充质干细胞成骨分化,但柚皮素是否有调节牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化能力尚不清楚。
目的:探究不同浓度柚皮素对人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化能力的影响。
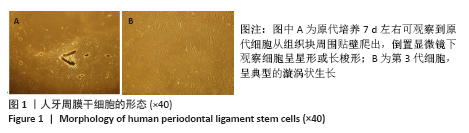
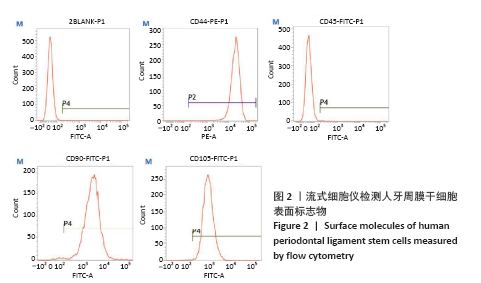
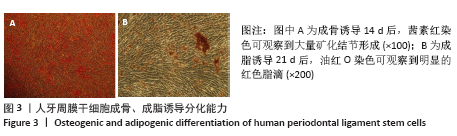
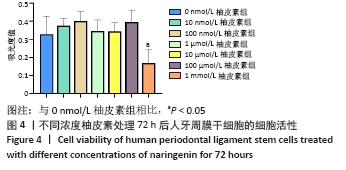
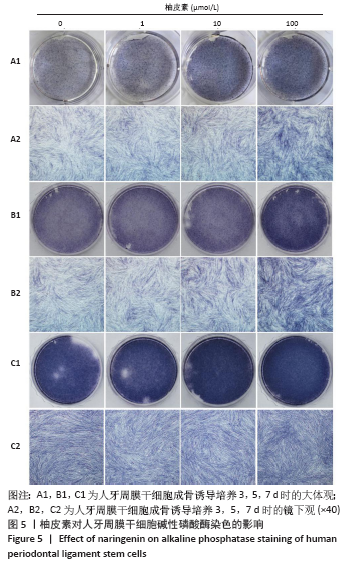
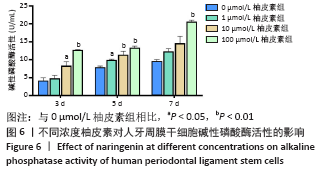
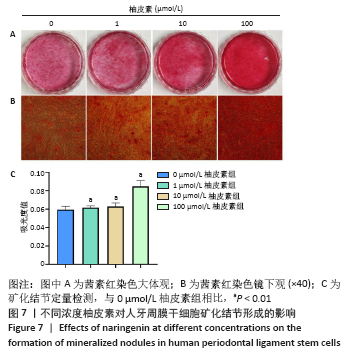
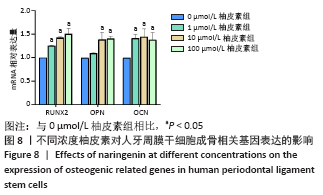
方法:原代分离培养人牙周膜干细胞,分别用含浓度为10,100 nmol/L、1,10,100 μmol/L和1 mmol/L柚皮素的α-MEM培养基处理72 h后,CCK-8法检测柚皮素对人牙周膜干细胞的细胞毒性。取第3代人牙周膜干细胞,分别用含0,1,10,100 μmol/L柚皮素的成骨诱导液培养,诱导3,5,7 d后分别进行碱性磷酸酶染色和碱性磷酸酶活性检测,诱导7 d后Real-time PCR检测成骨相关因子Runx2、骨桥蛋白和骨钙素的表达,诱导14 d后进行茜素红染色和矿化结节的定量分析。
结果与结论:10 nmol/L-100 μmol/L柚皮素对人牙周膜干细胞没有细胞毒性,1 mmol/L柚皮素对人牙周膜干细胞有明显的细胞毒性;1-100 μmol/L柚皮素显著促进碱性磷酸酶活性和矿物质沉积,上调Runx2、骨桥蛋白和骨钙素的基因表达。结果表明,柚皮素能显著促进人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化,100 μmol/L时促成骨分化能力最强。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1935-5824(罗小玲);https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2211-655X(徐晓梅)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: