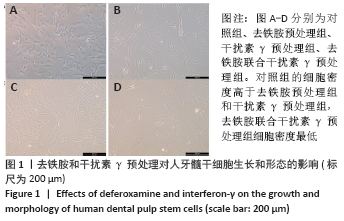
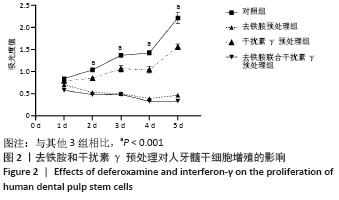
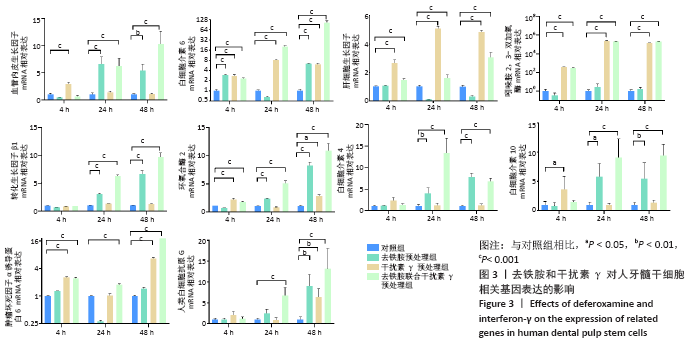
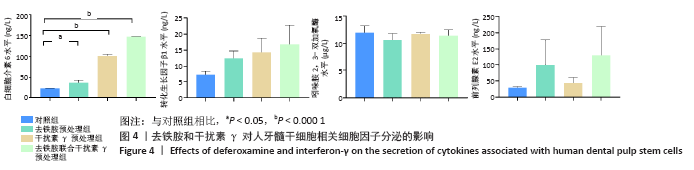
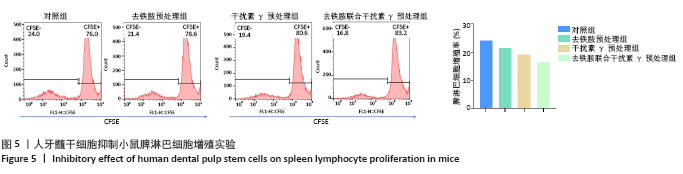
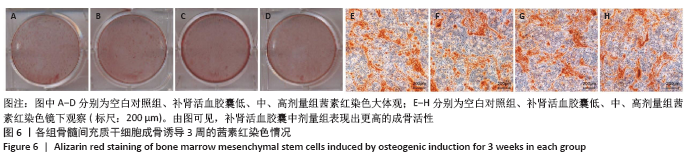
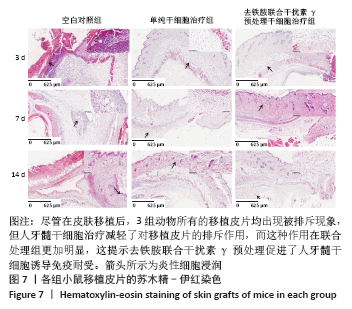
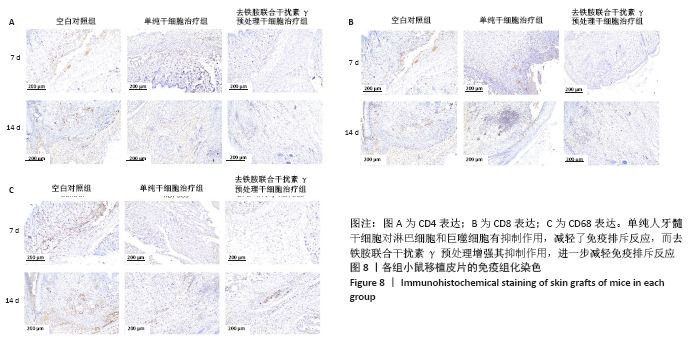
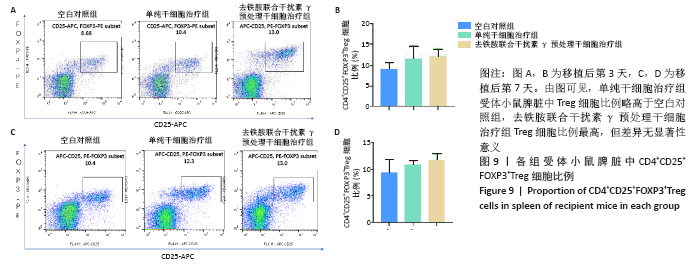
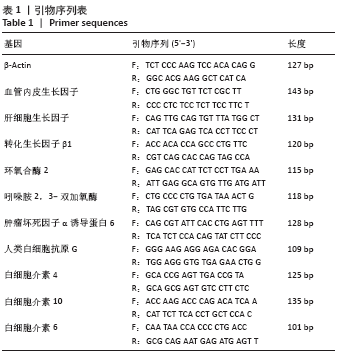
[1] KITTLESON MM, KOBASHIGAWA JA. Cardiac Transplantation: Current Outcomes and Contemporary Controversies. JACC Heart Fail. 2017;5(12): 857-868.
[2] STEHLIK J, KOBASHIGAWA J, HUNT SA, et al. Honoring 50 Years of Clinical Heart Transplantation in Circulation: In-Depth State-of-the-Art Review. Circulation. 2018;137(1):71-87.
[3] YANG H, APRECIO RM, ZHOU X, et al. Therapeutic effect of TSG-6 engineered iPSC-derived MSCs on experimental periodontitis in rats: a pilot study. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100285.
[4] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97(25):13625-13630.
[5] JI L, BAO L, GU Z, et al. Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and dental pulp stem cells. Immunol Res. 2019;67(4-5):432-442.
[6] DUIJVESTEIN M, WILDENBERG ME, WELLING MM, et al. Pretreatment with interferon-γ enhances the therapeutic activity of mesenchymal stromal cells in animal models of colitis. Stem Cells. 2011;29(10):1549-1558.
[7] OSES C, OLIVARES B, EZQUER M, et al. Preconditioning of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells with deferoxamine increases the production of pro-angiogenic, neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory factors: Potential application in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0178011.
[8] 孙卫民,王惠琴.细胞因子研究方法学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1998:165-175.
[9] 赵洁. TGF-β对骨髓间充质干细胞免疫抑制作用的影响及机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2019.
[10] HOLDEN P, NAIR LS. Deferoxamine: An Angiogenic and Antioxidant Molecule for Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25(6):461-470.
[11] BEEREPOOT LV, SHIMA DT, KUROKI M, et al. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production by iron chelators. Cancer Res. 1996; 56(16):3747-3751.
[12] SHEN X, WAN C, RAMASWAMY G, et al. Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors increase neoangiogenesis and callus formation following femur fracture in mice. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(10):1298-1305.
[13] IKEDA Y, TAJIMA S, YOSHIDA S, et al. Deferoxamine promotes angiogenesis via the activation of vascular endothelial cell function. Atherosclerosis. 2011;215(2):339-347.
[14] CHEKANOV VS, NIKOLAYCHIK V, MATERNOWSKI MA, et al. Deferoxamine enhances neovascularization and recovery of ischemic skeletal muscle in an experimental sheep model. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75(1):184-189.
[15] HOFFBRAND AV, GANESHAGURU K, HOOTON JW, et al. Effect of iron deficiency and desferrioxamine on DNA synthesis in human cells. Br J Haematol. 1976;33(4):517-526.
[16] LEDERMAN HM, COHEN A, LEE JW, et al. Deferoxamine: a reversible S-phase inhibitor of human lymphocyte proliferation. Blood. 1984;64(3):748-753.
[17] HU K, OLSEN BR. The roles of vascular endothelial growth factor in bone repair and regeneration. Bone. 2016;91:30-38.
[18] PRICOLA KL, KUHN NZ, HALEEM-SMITH H, et al. Interleukin-6 maintains bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell stemness by an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(3):577-588.
[19] HOOGDUIJN MJ, POPP F, VERBEEK R, et al. The immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their use for immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010;10(12):1496-1500.
[20] DE MIGUEL MP, FUENTES-JULIAN S, BLAZQUEZ-MARTINEZ A, et al. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells: advances and applications. Curr Mol Med. 2012;12(5):574-591.
[21] YOU S, THIEBLEMONT N, ALYANAKIAN MA, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta and T-cell-mediated immunoregulation in the control of autoimmune diabetes. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:185-202.
[22] KEHRL JH. Transforming growth factor-beta: an important mediator of immunoregulation. Int J Cell Cloning. 1991;9(5):438-450.
[23] HUANG YH, ZOZULYA AL, WEIDENFELLER C, et al. T cell suppression by naturally occurring HLA-G-expressing regulatory CD4+ T cells is IL-10-dependent and reversible. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86(2):273-281.
[24] GREENHOUGH A, SMARTT HJ, MOORE AE, et al. The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(3):377-386.
[25] WILLIAMS CS, MANN M, DUBOIS RN. The role of cyclooxygenases in inflammation, cancer, and development. Oncogene. 1999;18(55):7908-7916.
[26] SUBBARAMAIAH K, DANNENBERG AJ. Cyclooxygenase 2: a molecular target for cancer prevention and treatment. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24(2):96-102.
[27] NAKANISHI M, ROSENBERG DW. Multifaceted roles of PGE2 in inflammation and cancer. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35(2):123-137.
[28] MOLNARFI N, BENKHOUCHA M, FUNAKOSHI H, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor: A regulator of inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(4):293-303.
[29] SU J, CHEN X, HUANG Y, et al. Phylogenetic distinction of iNOS and IDO function in mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression in mammalian species. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(3):388-396.
[30] DAY AJ, MILNER CM. TSG-6: A multifunctional protein with anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective properties. Matrix Biol. 2019;78-79:60-83.
[31] ALEXANDER DZ, PEARSON TC, HENDRIX R, et al. Analysis of effector mechanisms in murine cardiac allograft rejection. Transpl Immunol. 1996; 4(1):46-48.
[32] YAMAMOTO N, EINAGA-NAITO K, KURIYAMA M, et al. Cellular basis of skin allograft rejection in mice: specific lysis of allogeneic skin components by non-T cells. Transplantation. 1998;65(6):818-825.
[33] GERSHON RK. A disquisition on suppressor T cells. Transplant Rev. 1975;26: 170-185. |