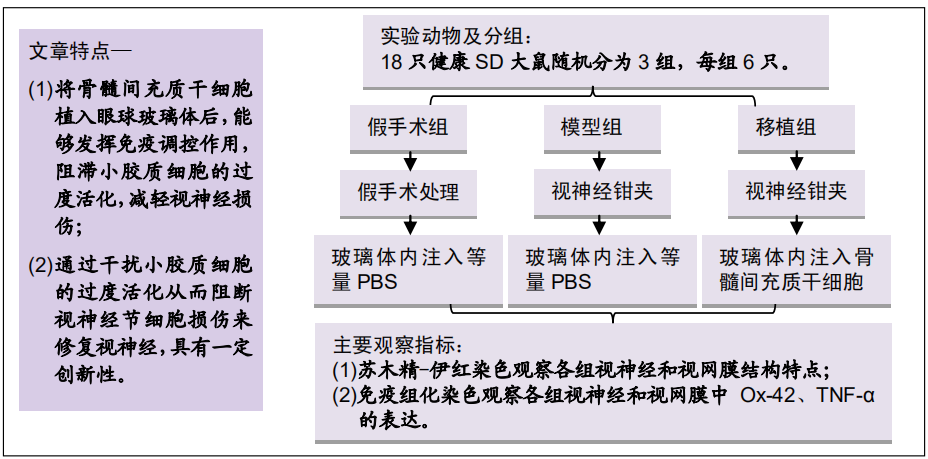
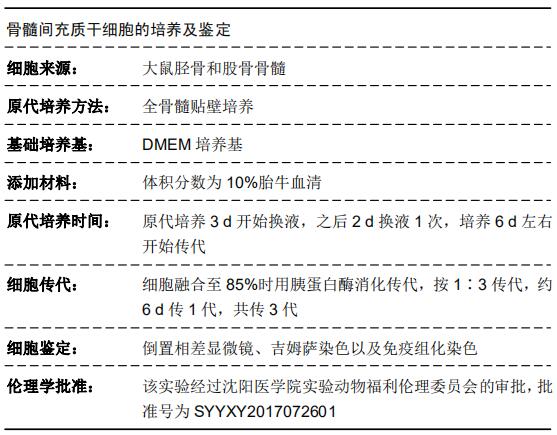
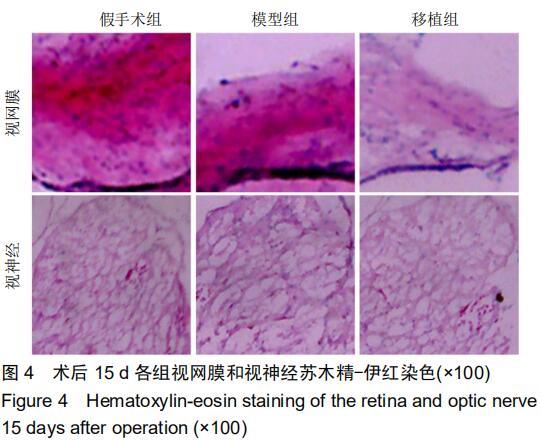
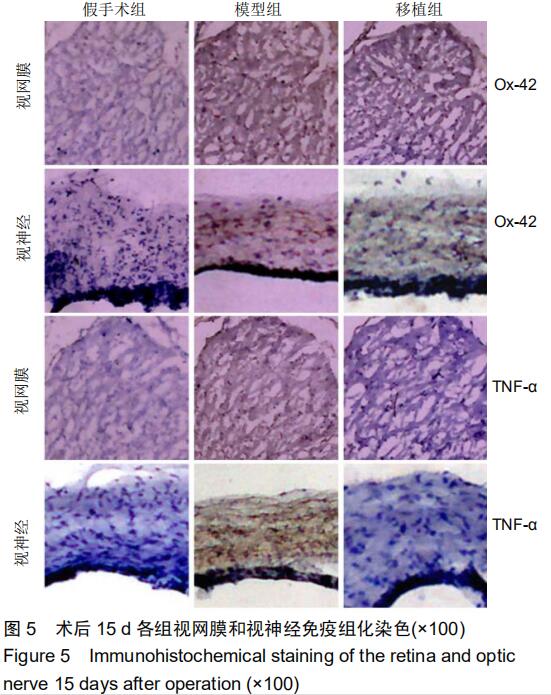
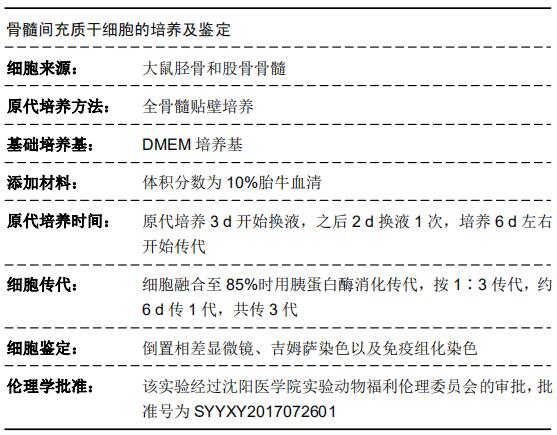
|
[1] 王凯.手术治疗脑外伤合并视神经损伤的临床分析[J].系统医学, 2019,4(7):81-83.
[2] 于莎莎,赵云,汤欣.视神经损伤药物治疗的研究进展[J].眼科新进展, 2019,39(3):291-295.
[3] 戴艳丽,王伟,张译心,等. 影响外伤性视神经病变视力好转的临床因素分析[J].眼科新进展,2013,33(3):243-247.
[4] 陈宾.MAPK/ERK信号通路在大鼠视神经损伤后小胶质细胞活化中的作用及机制研究[J].卒中与神经疾病,2018,25(4):427-430.
[5] 张智静,罗涛.小胶质细胞极性调节与神经损伤修复研究进展[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2019,14(1):26-32.
[6] 叶子,景瑾,张帅,等.小胶质细胞的分泌作用对神经损伤后修复的影响[J].现代医学与健康研究电子杂志,2018,2(8):195-196.
[7] 周亚莎,彭清华,文小娟,等.视网膜小胶质细胞的研究进展[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2016,36(1):85-88.
[8] 吴艺,郭小东,刘洁.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对视神经损伤大鼠视网膜细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国实验诊断学,2010,14(7):987-996.
[9] MIRON VE, BOYD A, ZHAO JW, et al. M2 microglia and macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16(9):1211-1218.
[10] 石晓燕,陈静.应用自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗视神经脊髓炎病人的护理[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2017,17(46):245.
[11] 王一玮,陈婷,马瑾,等.大鼠非动脉炎性前部缺血性视神经病变模型RGC及视神经损伤的特点[J].中华眼科杂志,2016, 52(12) :918-923.
[12] 陈柄全,彭漪,肖轶,等.人脐血间充质干细胞对小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞M2亚型的转化作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(25):3987-3992.
[13] LAMBERTSEN KL, CLAUSEN BH, BABCOCK AA, et al. Microglia protect neurons against ischemia by synthesis of tumor necrosis factor. J Neurosci. 2009;29(5):1319-1330.
[14] 欧阳明,刘静雯,刘珂,等.基因修饰诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化治疗视神经损伤[J].国际眼科杂志,2019,19(6):916-919.
[15] 孙晶晶,孔祥芬,赵平.视神经损伤后法舒地尔修复作用的实验研究[J].中华眼外伤职业眼病杂志,2016,38(12):881-885.
[16] 赵岩松,赵堪兴,王晓莉,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对视网膜病变新生大鼠视网膜细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国当代儿科杂志, 2012,14(12): 971-975.
[17] 廖宇,刘金华.胶质细胞与视神经损伤[J].医学综述,2008,14(7): 967-969.
[18] UEDA H, HALDER SK, MATSUNAGA H, et al. Neuroprotective impact of prothymosin alpha-derived hexapeptide against retinal ischemia-reperfusion. Neuroscience. 2016;318:206-218.
[19] 周小琳,李栋方,李平甘,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗对神经系统疾病免疫指标的影响及临床疗效[J].实用医学杂志, 2018,34(19): 3230-3233.
[20] TAKEURA N, NAKAJIMA H, WATANABE S, et al. Role of macrophages and activated microglia in neuropathic pain associated with chronic progressive spinal cord compression. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15656.
[21] FUJIKAWA R, HIGUCHI S, NAKATSUJI M, et al. EP4 Receptor-Associated Protein in Microglia Promotes Inflammation in the Brain. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(8):1982-1988.
[22] ANDRÉ C, GUZMAN-QUEVEDO O, REY C, et al. Inhibiting Microglia Expansion Prevents Diet-Induced Hypothalamic and Peripheral Inflammation. Diabetes. 2017;66(4):908-919.
[23] IMAM RA, RIZK AA. Efficacy of erythropoietin pretreated mesenchymal stem cells in murine burn wound healing: possible in vivo transdifferentiation into keratinocytes. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2019 Apr 5. doi: 10.5603/FM.a2019.0038. [Epub ahead of print]
[24] HUANG X, WANG W, LIU X, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells attenuate radicular pain by inhibiting microglial activation in a rat noncompressive disk herniation model. Cell Tissue Res. 2018; 374(1):99-110.
[25] LI J, DENG G, WANG H, et al. Interleukin-1β pre-treated bone marrow stromal cells alleviate neuropathic pain through CCL7-mediated inhibition of microglial activation in the spinal cord. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42260.
[26] JOSE S, TAN SW, OOI YY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells exert anti-proliferative effect on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia by reducing tumour necrosis factor-α levels. J Neuroinflammation. 2014;11:149.
[27] AGUILERA-CASTREJON A, PASANTES-MORALES H, MONTESINOS JJ, et al. Improved Proliferative Capacity of NP-Like Cells Derived from Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Neuronal Transdifferentiation by Small Molecules. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(2):415-427.
[28] YIN H, YIN H, ZHANG W, et al. Transcorneal electrical stimulation promotes survival of retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve transection in rats accompanied by reduced microglial activation and TNF-α expression. Brain Res. 2016;1650:10-20.
[29] TATSUMI E, YAMANAKA H, KOBAYASHI K, et al. RhoA/ROCK pathway mediates p38 MAPK activation and morphological changes downstream of P2Y12/13 receptors in spinal microglia in neuropathic pain. Glia. 2015;63(2):216-228.
[30] ZHOU YS, XU J, PENG J, et al. Research progress of stem cells on glaucomatous optic nerve injury. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016;9(8): 1226-1229.
[31] LIM HS, KIM YJ, KIM BY, et al. The Anti-neuroinflammatory Activity of Tectorigenin Pretreatment via Downregulated NF-κB and ERK/JNK Pathways in BV-2 Microglial and Microglia Inactivation in Mice With Lipopolysaccharide. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:462.
[32] GUO C, YANG L, WAN CX, et al. Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of Sophoraflavanone G from Sophora alopecuroides in LPS-activated BV2 microglia by MAPK, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine. 2016;23(13):1629-1637.
[33] KIM SM, YOKOYAMA T, NG D, et al. Retinoic acid-stimulated ERK1/2 pathway regulates meiotic initiation in cultured fetal germ cells. PLoS One. 2019;14(11):e0224628.
[34] ISHII A, FURUSHO M, BANSAL R. Sustained activation of ERK1/2 MAPK in oligodendrocytes and schwann cells enhances myelin growth and stimulates oligodendrocyte progenitor expansion. J Neurosci. 2013;33(1):175-186.
[35] WANG C, NIE X, ZHANG Y, et al. Reactive oxygen species mediate nitric oxide production through ERK/JNK MAPK signaling in HAPI microglia after PFOS exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015;288(2):143-151.
[36] CHUNG S, RHO S, KIM G, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells and chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote axon survival in a rat model of optic nerve crush injury. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(5):1170-1180.
[37] LOANE DJ, KUMAR A. Microglia in the TBI brain: The good, the bad, and the dysregulated. Exp Neurol. 2016;275 Pt 3:316-327.
[38] 王娜,陈乃耀.脐带间充质干细胞对小胶质细胞增殖及活化的影响[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2016,54(10):16-20.
[39] LAFRENAYE AD.Physical interactions between activated microglia and injured axons: do all contacts lead to phagocytosis? Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(4):538-540.
[40] 邱超,郑亚妮,许硕贵.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对周围神经损伤后施旺细胞的影响[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2018,14(1):28-30.
[41] RIAZI K, GALIC MA, KENTNER AC, et al. Microglia-dependent alteration of glutamatergic synaptic transmission and plasticity in the hippocampus during peripheral inflammation. J Neurosci. 2015;35(12):4942-4952.
|