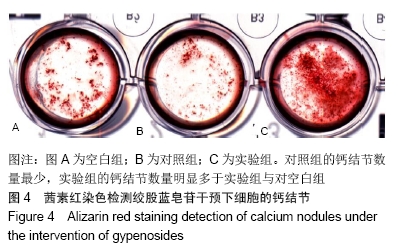
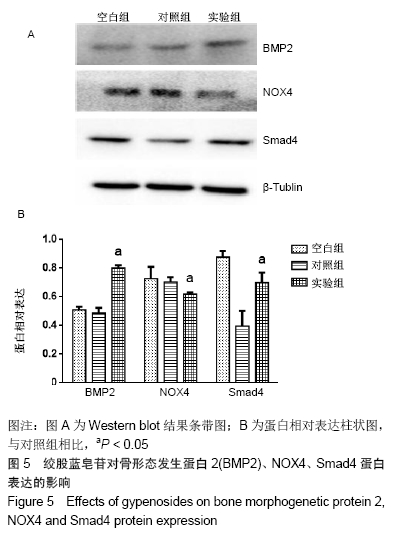
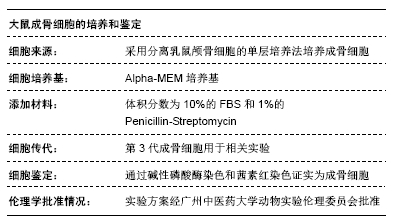
[1] COMPSTON JE, MCCLUNG MR, LESLIE WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019;393(10169):364-376.
[2] WAUQUIER F, LEOTOING L, COXAM V, et al. Oxidative stress in bone remodelling and disease.Trends Mol Med. 2009;15(10):468-477.
[3] SÁNCHEZ-RODRÍGUEZ MA, RUIZ-RAMOS M, CORREA-MUÑOZ E, et al. Oxidative stress as a risk factor for osteoporosis in elderly Mexicans as characterized by antioxidant enzymes.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2007;8:124.
[4] LUSHCHAK VI. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification.Chemico-Biological Interaction.2014;224: 164-175.
[5] GARG AD, DUDEK AM, FERREIRA GB, et al. ROS-induced autophagy in cancer cells assists in evasion from determinants of immunogenic cell death.Autophagy.2013;9(9):1292-1307.
[6] BRANDES RP, WEISSMANN N, SCHRÖDER K. Nox family NADPH oxidases: Molecular mechanisms of activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;76:208-226.
[7] LASSÈGUE B, GRIENDLING KK. NADPH oxidases: functions and pathologies in the vasculature. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2010; 30(4):653-661.
[8] ZHU S, EHNERT S, ROUß M, et al. From the Clinical Problem to the Basic Research-Co-Culture Models of Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts. Int J Mol Sci.2018;19(8):2284.
[9] SHI Y, LIU XY, JIANG YP, et al. Monotropein attenuates oxidative stress via Akt/mTOR-mediated autophagy in osteoblast cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121:109566.
[10] PAN H, ZHANG H, ABRAHAM P, et al. BmpR1A is a major type 1 BMP receptor for BMP-Smad signaling during skull development. Dev Biol. 2017;429(1):260–270.
[11] CHEN G,DENG C,LI YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation.Int J Biol Sci.2012;8(2):272–288.
[12] 鲍凤霞,陶泠雪,章海燕.绞股蓝有效成分的药理作用研究进展[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2018,37(1) :11-17.
[13] LEE HS, LIM SM, JUNG JI, et al. Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Extract Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in C57BL/6N Mice by Upregulating SIRT1. Nutrients.2019;11(10):2475.
[14] WEI X, LI L, LIU J, et al. Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Gynostemma for Bioimaging and Antioxidant in Zebrafish. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2019;11(10):9832-9840.
[15] PARK HJ, ZHAO TT, KIM SH, et al. Ethanol extract from Gynostemma pentaphyllum ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal cell death in transgenic mice expressing mutant A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neural Regen Res.2020;15(2):361-368.
[16] HAN J, GAO W, SU D, et al. Gypenoside inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by regulating NF-κB, AKT, and MAPK signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem.2018;119(9):7310-7318.
[17] 乔久涛,关德宏,王冬艳,刘艾芸.左归丸对成骨细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(7):1052-1056.
[18] ENSRUD KE, KATS AM, BOYD CM, et al. Association of Disease Definition, Comorbidity Burden, and Prognosis With Hip Fracture Probability Among Late-Life Women. JAMA Intern Med. 2019 Jun 17. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.0682.
[19] HE XF, ZHANG L, ZHANG CH, et al. Berberine alleviates oxidative stress in rats with osteoporosis through receptor activator of NF-kB/ receptor activator of NF-kB ligand/osteoprotegerin (RANK/RANKL/ OPG) pathway. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2017;17(4):295-301.
[20] BONACCORSI G, PIVA I, GRECO P, et al. Oxidative stress as a possible pathogenic cofactor of post-menopausal osteoporosis: Existing evidence in support of the axis oestrogen deficiency-redox imbalance-bone loss. Indian J Med Res. 2018;147(4):341-351.
[21] MANDAL CC, GANAPATHY S, GORIN Y, et al. Reactive oxygen species derived from Nox4 mediate BMP2 gene transcription and osteoblast differentiation. Biochem J. 2011;433(2):393-402.
[22] PARK E, KIM J, YEO S, et al. Anti-Osteoporotic Effects of Combined Extract of Lycii Radicis Cortex and Achyranthes japonica in Osteoblast and Osteoclast Cells and Ovariectomized Mice. Nutrients. 2019;11(11): 2716.
[23] DONG SQ, ZHANG QP, ZHU JX, et al. Gypenosides reverses depressive behavior via inhibiting hippocampal neuroinflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;106:1153-1160.
[24] ALHASANI RH, BISWAS L, TOHARI AM, et al. Gypenosides protect retinal pigment epithelium cells from oxidative stress. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018;112:76-85.
[25] WANG QF, CHIANG CW, WU CC, et al. Gypenosides induce apoptosis in human hepatoma Huh-7 cells through a calcium/reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Planta Med.2007; 73(6):535-544.
[26] 李文雄,张晶宇,杨锋.中药调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J].中医正骨, 2016, 28(7):68-71.
[27] 张乃丹,蒋益萍,薛黎明,等. 仙茅酚苷类成分促进成骨细胞骨形成和抑制破骨细胞骨吸收[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2016, 37(5): 562-568.
[28] 雷群,林东,黄文秀,吴东,陈江.钙离子对人成骨细胞迁移与成骨分化的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(6):602-608.
[29] FLORCZYK U, JAZWA A, MALESZEWSKA M, et al. Nrf2 regulates angiogenesis: effect on endothelial cells, bone marrow-derived proangiogenic cells and hind limb ischemia. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;20(11):1693-1708.
[30] MUÑOZ M, LÓPEZ-OLIVA ME, RODRÍGUEZ C, et al. Differential contribution of Nox1, Nox2 and Nox4 to kidney vascular oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in obesity. Redox Biol. 2020;28: 101330.
[31] LI H, ZHANG S, NIE B, et al. KR-12-a5 Reverses Adverse Effects of Lipopolysaccharides on HBMSC Osteogenic Differentiation by Influencing BMP/Smad and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. Front Pharmacol.2019;10:639.
[32] CHENG Q,TANG W,SHEU TJ,et al.Circulating TGF-β1 levels are negatively correlated with sclerostin levels in early postmenopausal women. Clin Chim Acta.2016;455:87-92.
[33] WANG J, WANG M, CHEN F, et al. Nano-Hydroxyapatite Coating Promotes Porous Calcium Phosphate Ceramic-Induced Osteogenesis Via BMP/Smad Signaling Pathway. Int J Nanomedicine.2019;14: 7987-8000.
[34] YANG J, SHI P, TU M, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins: relationship between molecular structure and their osteogenic activity. Food Sci Human Wellness.2014;3(3-4):127-135.
[35] WAN M, CAO X. BMP signaling in skeletal development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(3):651-657.
[36] ZHANG H, CHEN X, ZONG B, et al. Gypenosides improve diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Cell Mol Med.2018;22(9):4437-4448.
|