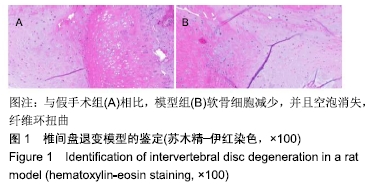
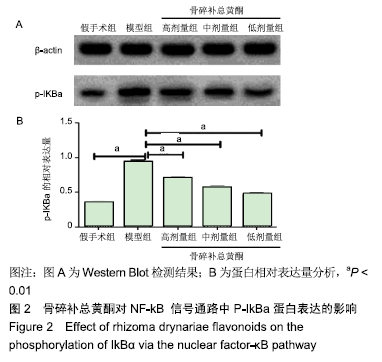
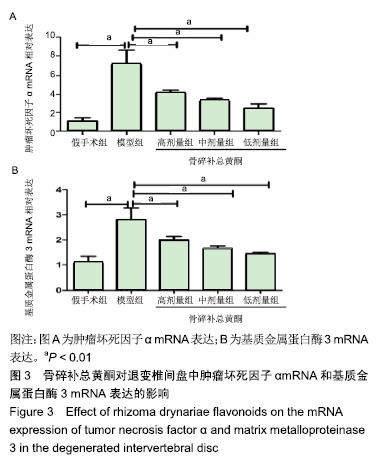
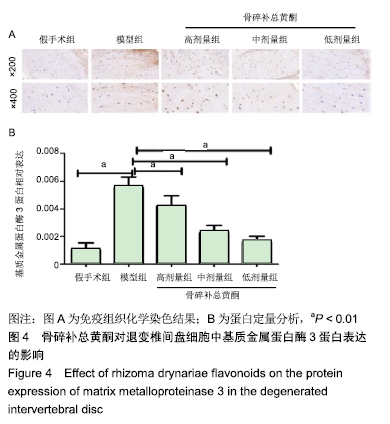
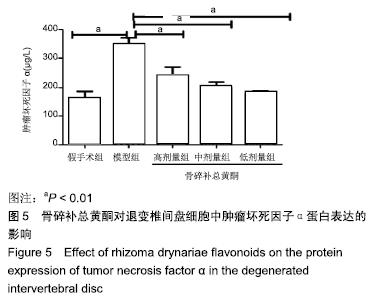
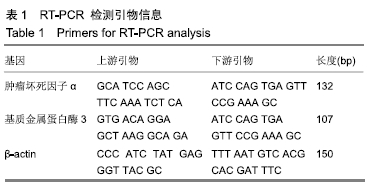
[1] 余城墙,张宇,谢程欣,等.椎间盘退变分子生物学机制及再生治疗的优势与未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(30):4889-4896.
[2] 王挽涛,祁全,赵大航.椎间盘退变的再生修复治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(13):1210-1214.
[3] URBAN JP, ROBERTS S. Degeneration of the intervertebral disc.Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5(3):120-130.
[4] 檀龙颜,马洪娜.骨碎补药理作用的研究进展[J].中国民族民间医药,2017,26(11):66-70.
[5] XIE J, LI B, ZHANG P, et al. Osteogenic protein-1 attenuates the inflammatory cytokine-induced NP cell senescence through regulating the ROS/NF-κB pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;99:431-437.
[6] WU X, LIU Y, GUO X, et al. Prolactin inhibits the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration through inactivation of the NF-κB pathway in rats.Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):98.
[7] LUO L, GAO Y, YANG C, et al. Halofuginone attenuates intervertebral discs degeneration by suppressing collagen I production and inactivating TGFβ and NF-кB pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;101:745-753.
[8] ZHU C, JIANG W, CHENG Q, et al.Hemeoxygenase-1 Suppresses IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis Through the NF-κB Pathway in Human Degenerative Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2):644-653.
[9] WANG S, LIU C, SUN Z, et al. IL-1β increases asporin expression via the NF-κB p65 pathway in nucleus pulposus cells during intervertebral disc degeneration.Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):4112.
[10] 李明,李君,付昆.骨碎补总黄酮对膝骨关节炎模型兔HIF-1α和VEGF表达的影响[J].中国药房,2018,29(18):2484-2488
[11] 王拥军,施杞,沈培芝,等.动静力失衡性大鼠颈椎间盘退变模型的动态观察[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2001,21(3):199-202.
[12] 李建国,谢兴文,李晶,等.骨碎补总黄酮防治原发性骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].生命的化学,2019,39(2):229-233
[13] 申意伟,徐西林,张晓峰,等.骨碎补中柚皮苷治疗股骨头坏死研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(7):128-131.
[14] 李冬霞,陈颖颖,罗静,等.骨碎补总黄酮干预骨关节炎机制的研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2019,8(3):66-69.
[15] 玉超杰,楚野,梁斌.腰椎间盘突出发病机制的研究进展[J].中国临床新医学,2017,10(8):824-828
[16] 潘亚伟,王海彬,周健和,等.颈椎间盘退变患者椎间盘组织炎症因子表达水平与临床特征的关系[J].广东医学,2019,40(6): 826-829.
[17] 刁志君,姜宏,刘锦涛,等.炎症因子在椎间盘退变中的作用[J].中医正骨,2018,30(7):32-35.
[18] 周德华,李志军,张元智.促进椎间盘退变的细胞因子的相关研究[J].中国伤残医学,2014,22(4):297-297.
[19] MAVROGONATOU E, ANGELOPOULOU MT, KLETSAS D. The catabolic effect of TNFα on bovine nucleus pulposus intervertebral disc cells and the restraining role of glucosamine sulfate in the TNFα-mediated up-regulation of MMP-3.J Orthop Res. 2014;32(12):1701-1707.
[20] YIN J, REN K, HUANG Y, et al. Exploration about changes of IL-10, NF-κB and MMP-3 in a rat model of cervical spondylosis.Molecular Immunology.2018;93:184-188.
[21] ZHANG XH, XU XX, XU T. Ginsenoside Ro suppresses interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis and inflammation in rat chondrocytes by inhibiting NF-kappaB.Chin J Nat Med.2015; 13 (4):283-289.
[22] TU J, LI W, ZHANG Y, et al. Simvastatin Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation by Suppressing the NF-kB and MAPK Pathways in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Inflammation.2017;40(3):725-734.
[23] YAO Z, NIE L, ZHAO Y, et al.Salubrinal Suppresses IL-17-Induced Upregulation of MMP-13 and Extracellular Matrix Degradation Through the NF-kB Pathway in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Inflammation.2016;39(6):1997-2007.
[24] WANG J, PAN H, LI X, et al. Hypoxia suppresses serum deprivation-induced degradation of the nucleus pulposus cell extracellular matrix through the JNK and NF-κB pathways.J Orthop Res. 2017;35(9):2059-2066.
[25] JOHNSON ZI, SCHOEPFLIN ZR, CHOI H, et al.Disc in flames: Roles of TNF-α and IL-1β in intervertebral disc degeneration.Eur Cell Mater.2015;30:104-116.
[26] 张金虎.骨碎补总黄酮联合硫酸氨基葡萄糖对膝骨关节炎患者症状、骨代谢和炎症因子的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2018, 24(7):884-887.
[27] 殷方明,肖涟波,张昀,等.骨碎补柚皮苷对炎症及骨作用的相关研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(2):182-186.
[28] 左渝陵,陈果.骨碎补对牙龈卟啉单胞菌胰酶样蛋白酶和糖苷酶活性的抑制作用[J].中华中医药学刊,2008,26(10):2195-2196.
|