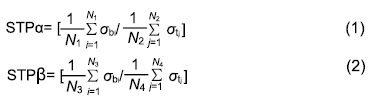中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1574-1579.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1887
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
基于正交试验接骨螺钉参数的生物相容性评价
龙登燕1,纪爱敏1,赵仲航1,方润心1,陈长胜1,2
- 1河海大学机电工程学院,江苏省常州市 213022;2常州奥斯迈医疗器械有限公司,江苏省常州市 213000
Orthopedic screw parameters in the orthogonal test: biocompatibility evaluation
Long Dengyan1, Ji Aimin1, Zhao Zhonghang1, Fang Runxin1, Chen Changsheng1,2
- 1College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hohai University, Changzhou 213022, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Changzhou Orthmed Medical Instrument Co., Ltd., Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
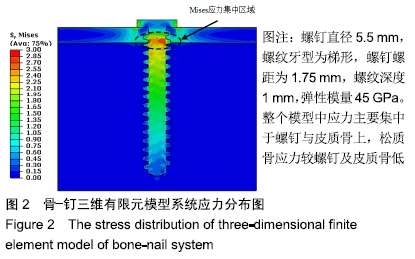
应力遮挡:金属接骨螺钉作为内固定器械常用于临床骨折治疗。由于金属接骨螺钉的弹性模量比骨的弹性模量要高很多,接骨螺钉植入骨折骨后承担了大部分载荷,骨钉附近的骨组织在骨钉的保护下承受的载荷较少,这样的现象称为应力遮挡。
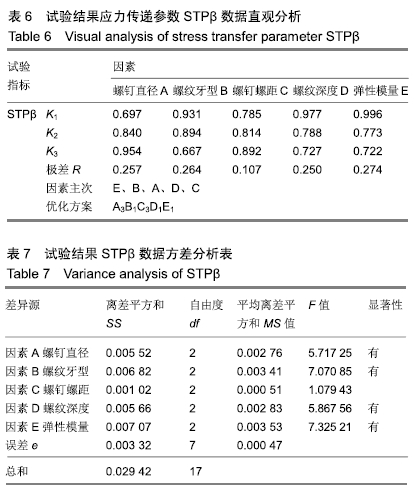
应力传递参数STP:一个用于评估应力遮挡程度的无量纲常数,定义为接骨螺钉附近骨组织的应力值与接骨螺钉螺纹的应力值之比。此参数表明接骨螺钉与附近骨组织之间的应力传递情况,数值越大、越接近1表明两者之间的应力差异越小,应力分布更均匀;数值越小,结果反之。
背景:当前骨科螺钉参数研究多集中于力学性能方面,缺少对其生物相容性的评估。
目的:探究接骨螺钉材料属性及几何参数对生物相容性的影响规律,探求各因素及水平的最佳组合,为接骨螺钉的设计提供理论参考。
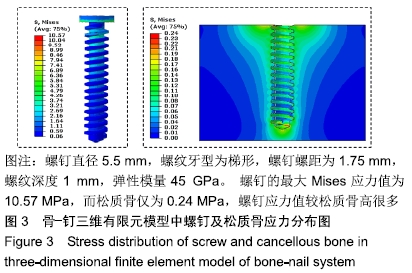
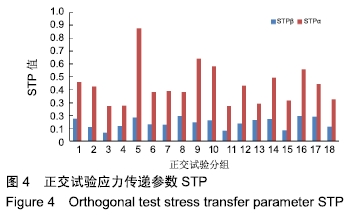
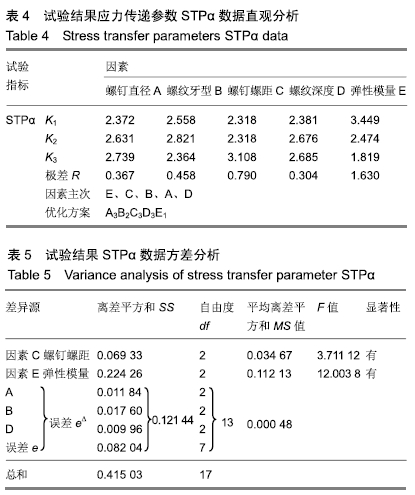
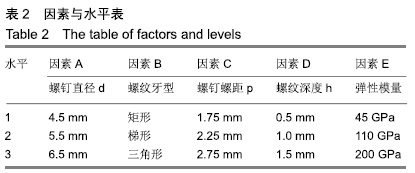
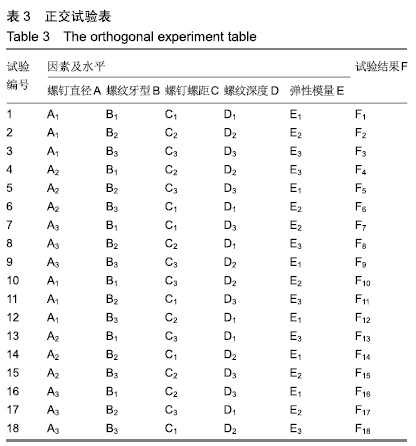
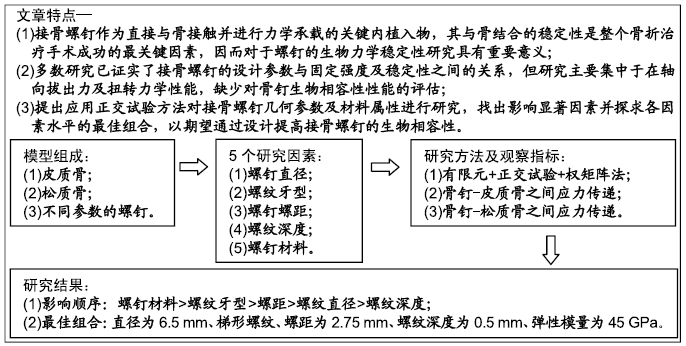
方法:针对接骨螺钉5个因素的3个水平进行正交试验方案设计,因素A为螺钉直径(4.5,5.5,6.5 mm),因素B为螺纹牙型(矩形、梯形、三角形),因素C为螺钉螺距(1.75,2.25,2.75 mm),因素D为螺纹深度(0.5,1.0,1.5 mm),因素E为弹性模量(45,110,200 GPa),分别对18组不同螺钉参数下的骨-钉三维模型进行生物力学有限元分析,得出各组试验方案下的应力分布情况及2个试验指标值:皮质骨-螺钉之间的应力传递参数STPα,松质骨-螺钉之间的应力传递参数STPβ。利用权矩阵分析方法对正交试验数据进行分析进而得出影响规律及最佳组合。
结果与结论:不同因素的不同水平对于生物相容性影响程度不同,其中螺钉材料属性为最主要影响因素,其次是螺纹牙型、螺距和螺纹直径并且三者影响程度相近,而螺纹深度影响最小。正交试验所得最佳组合方案为大径为6.5 mm、梯形螺纹、螺距为2.75 mm、螺纹深度为0.5 mm、弹性模量为45 GPa的接骨螺钉。
ORCID: 0000-0001-9645-6077(龙登燕)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: