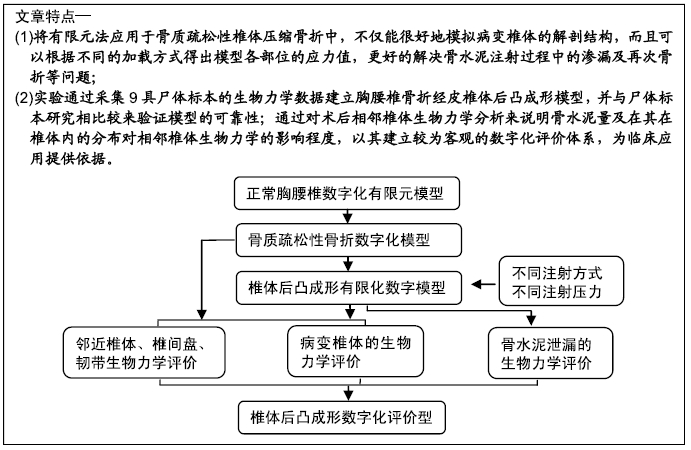
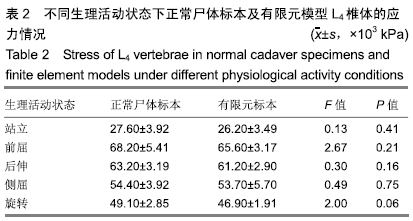
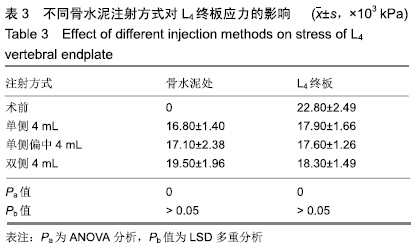
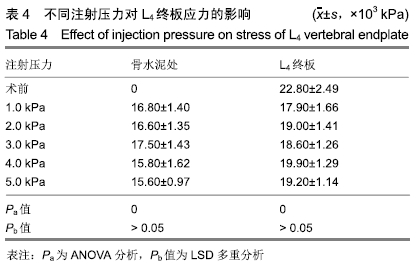
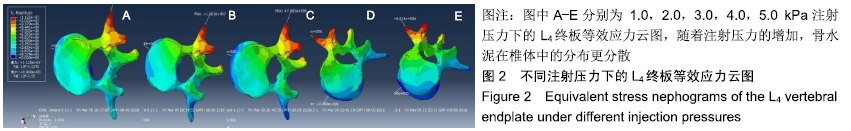
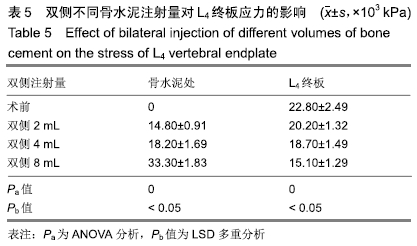
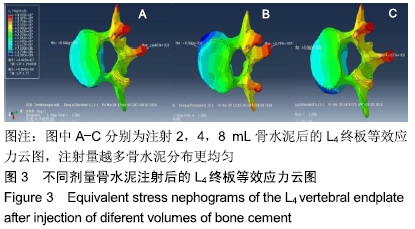
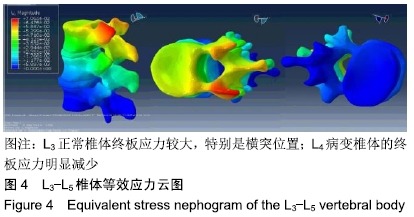
[1] 许正伟,贺宝荣,郝定均,等.胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥渗漏的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(17): 1142.
[2] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al.Finite element stress analysis of anintervertebral disc. Biomechanics. 1974;7(3):277-285.
[3] 彭小东,张晓刚,赵文韬,等.有限元分析在过伸复位治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折生物力学研究中的应用进展[J].中医正骨, 2018,30(7):25-26.
[4] 李静.基于MRI图像的人体腰椎节段三维有限元模型重建及分析[D].天津:天津理工大学,2013.
[5] 卢昌怀,刘志军,张宏波,等.骨水泥量及分布对椎体成形术后相邻椎体生物力学影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(1):29-33.
[6] 杨掌权,蔡建平.椎体成形术在人体生物力学方面的研究进展[J].黑龙江医药,2009,22(2):143-145.
[7] 阮狄克.再谈椎体成形术的适应证、禁忌证及并发症[J].中国骨伤,2008,21(6):403-404.
[8] LAREDO JD, HAMZE B.Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty and their prevention.Skeletal Radiol.2004; 33(9):493-505.
[9] TEO CHOON MENG J.Patient specific finite volume modeling for intraosseous PMMA cement flow simulation in vertebral cancellous bone.NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE, 2007. http://scholarbank.nus.edu.sg/handle/10635/13092.
[10] GALIBERT P, DERAMOND H, ROSAT P, et al.Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty.Neurochirurgie.1987;33:166-168.
[11] ZEISER T, BASHOOR-ZADEH M, DARABI A, et al. Pore-scale analysis of Newtonian flow in the explicit geometry of vertebral trabecular bones using lattice Boltzmann simulation. Proc Inst Mech Eng H.2008;222:185-194.
[12] CHEVALIER Y, PAHR D, CHARLEBOIS M, et al.Cement distribution, volume, and compliance in vertebroplasty: some answers from an anatomybased nonlinear finite element study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33:1722-1730.
[13] HULME PA, BOYD SK, HEINI PF, et al.Differences in endplate deformation of the adjacent and augmented vertebra following cement augmentation.Eur Spine J.2009;18:614-623.
[14] HEINI PF, WÄLCHLI B, BERLEMANN U.Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty with PMMA: operative technique and early results. A prospective study for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures.Eur Spine J. 2000;9:445-450.
[15] 叶春万,朱敏,樊道斌,等.经椎弓根打压植骨与骨水泥椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎压缩骨折的生物力学比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(7):610-613.
[16] SUN H, LI C.Comparison of unilateral and bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res.2016;11:156.
[17] 刘祥飞,何金国,蒋钰钢,等.单侧与双侧入路椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的有限元分析及临床应用[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(3):218-223.
[18] COTTEN A, DEWATRE F, CORTET B, et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up.Radiology.1996;200: 525-530.
[19] LIEBSCHNER MA, ROSENBERG WS, KEAVENY TM.Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26: 1547-1554.
[20] LI X, YANG H, TANG T, et al.Comparison of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: twelve-month follow-up in a prospective nonrandomized comparative study.J Spinal Disord Techn.2012;25:142-149.
[21] LIN EP, EKHOLM S, HIWATASHI A, et al.Vertebroplasty: cement leakage into the disc increases the risk of new fracture of adjacent vertebral body.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:175-180.
[22] RHO YJ, CHOE WJ, CHUN YI.Risk factors predicting the new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty.Eur Spine J. 2012;21:905-911.
[23] TENG MMH, CHENG H, HO DMT, et al.Intraspinal leakage of bone cement after vertebroplasty: a report of 3 cases.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2006;27:224-229.
[24] LAI PL, TAI CL, CHEN LH, et al.Cement leakage causes potential thermal injury in vertebroplasty. BMC Musculoskel Disord.2011;12:116.
[25] 陆声,徐永清,张美超,等.骨质疏松椎体增强后对相邻椎体生物力学影响的有限元研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(9):864-867.
[26] 雷丙俊,牛国旗.三维有限元法在椎体成形术力学研究中的应用进展[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2011,36(5):539-541.
[27] BOHNER M, GASSER B, BAROUD G, et al.Theoretical and experimental model to describe the injection of a polymethylmethacrylate cement into a porous structure. Biomaterials.2003;24(16):2721-2730.
[28] 康乐. 防腐标本椎体成形术中生理盐水灌洗对骨水泥注射压力、分布、外渗的实验研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2014.
[29] KAUFMANN TJ, TROUT AT, KALLMES DF.The effects of cement volume on clinical outcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2006;27:1933-1937.
[30] PHILLIPS FM, TODD WF, LIEBERMAN I, et al.An in vivo comparison of the potential for extravertebral cement leak after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27:2173-2178.
[31] BELKOFF SM, MATHIS JM, JASPER LE,et al.The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26: 1537-1541.
[32] ALKALAY RN, VON STECHOW D, TORRES K, et al.The effect of cement augmentation on the geometry and structural response of recovered osteopenic vertebrae: an anterior-wedge fracture model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33:1627-1636.
[33] 李家琼,王冬梅,孙璟川,等骨水泥对椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松压缩性骨折的生物力学影响[J].医用生物力学, 2018,33(1):6-12.
[34] 王伟.经皮椎体成形术与经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术的生物力学有限元对比研究[D].西宁:青海大学,2018.
|