中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (36): 5841-5845.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1909
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
有限元法分析儿童发育不良髋关节“人”字型固定后的应力特征
蔡振存,朴成哲,周宏宇,孙 明,高振淮
- 沈阳医学院附属中心医院骨关节科,辽宁省沈阳市 110024
Stress characteristics after fixation in herringbone position in children with developmental dislocation of the hip by finite element analysis
Cai Zhencun, Piao Chengzhe, Zhou Hongyu, Sun Ming, Gao Zhenhuai
- Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, the Central Hospital of Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110024, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
儿童发育性髋关节发育不良的治疗依据:遵循Harris定律,即决定髋关节发育的先决条件是股骨头髋臼同心,头臼同心可以促进髋臼软骨向正常恢复。
有限元分析法:是近年来研究人体生物力的有效方法,其基本原理是把连续的物体离散为一组有限个、按一定方式相互联结在一起的单元组合体,然后求其相互之间力的关系及特征。
摘要
背景:目前对于儿童发育性髋关节发育不良患者复位后固定的体位有很大争议,虽然大家公认髋关节的外展角度大有助于复位后关节稳定,但外展角度越大,生物力越异常,股骨头髋臼间压力越大,进而容易引起股骨头坏死。当前“人”字型固定是临床常用的固定体位,但其生物力到底如何分布尚不明确。
目的:利用有限元分析方法,研究发育性髋关节发育不良患儿在“人”字型固定后髋关节的生物力分布情况,探讨临床合理的固定体位。
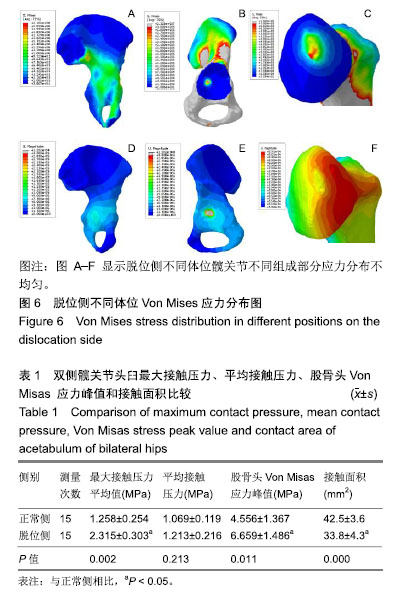
方法:选取1例来沈阳医学院附属中心医院就诊的单侧发育性髋关节发育不良患儿骨盆和股骨近端原始 CT 数据,导入Mimics 15.0软件,经区域增长、编辑笼罩、光滑、包裹等处理重建双侧髋关节三维有限元模型,并在 Hypermesh 12.0软件中进行网格划分、定义材料属性、设定边界条件、加载负荷,模拟“人”字型固定时髋关节体位及受力情况进行三维有限元计算分析。得到骨盆、髋臼和股骨近端的Von Mises应力分布云图和力学位移云图,评价力学云图特点并计算出股骨头与髋臼间的平均接触压力,最大接触压力和接触面积。
结果与结论:①“人”字型固定时脱位侧的股骨头髋臼间平均接触压力、最大接触压力及股骨头所受Von Misas应力峰值都高于未脱位侧,头臼接触面积小于未脱位侧,头臼接触面积、最大接触压力和股骨头所受Von Misas应力峰值比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②结果证实,对发育性髋关节发育不良患儿而言,静态的“人”字型固定时脱位侧髋关节生物力分布异常,股骨头臼间存在较高压力,容易股骨头坏死。试验方案已经于2018年通过沈阳医学院附属中心医院医学道德伦理委员会批准(批准号:20180987)。
ORCID: 0000-0003-2778-4151(蔡振存)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)