| [1]Tervonen HE,Chen TYT,Lin E,et al.Risk of emergency hospitalisation and survival outcomes following adjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer in New South Wales, Australia. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2019;21:e13125.[2]Giudici F,Petracci E,Nanni O,et al.Elevated levels of eEF1A2 protein expression in triple negative breast cancer relate with poor prognosis.PLoS One.2019;14(6):e0218030.[3]江泽飞,邵志敏,徐兵河,等.人表皮生长因子受体2阳性乳腺癌临床诊疗专家共识2016[J].中华医学杂志, 2016,96(14):1091-1096.[4]姜朋丽,付彤,武盼盼,等.不同T分期乳腺癌患者分子分型与腋窝淋巴结转移的关系及其临床意义[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2016,42(1):144-148.[5]Choi HS,Jang HS,Kang KM,et al.Symptom palliation of hypofractionated radiotherapy for patients with incurable inflammatory breast cancer. Radiat Oncol.2019;14(1):110.[6]Rattanaburee T,Thongpanchang T,Wongma K,et al.Anticancer activity of synthetic (±)-kusunokinin and its derivative (±)-bursehernin on human cancer cell lines. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;117:109115.[7]梁跃,陈小松,吴佳毅,等.绝经前乳腺癌卵巢功能抑制辅助治疗的影响因素[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2016,38(5):357-362.[8]周儒兵,李伟,周双容.多西他赛注射剂联合吡柔比星注射剂治疗乳腺癌的临床研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2017,33(13):1194-1197.[9]闫海山,张冰雁.曲妥珠单抗联合新辅助化疗用于HER2过度表达乳腺癌的临床观察[J].中国药房,2016,27(29):4127-4130.[10]Yang L,Yan F,Ma J,et al.Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction-Mediated Co-Delivery of Cxcl12 (Sdf-1alpha) and Bmp2 Genes for Myocardial Repair.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019; 15(6):1299-1312.[11]Xu J,Wang Y,Li Z,et al.Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction (UTMD) Combined with Liposome Increases the Effectiveness of Suppressing Proliferation,Migration,Invasion,and Epithelial- Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) via Targeting Metadherin (MTDH) by ShRNA.Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2640-2648.[12]Sun W,Li Z,Zhou X,et al.Efficient exosome delivery in refractory tissues assisted by ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction. Drug Deliv.2019;26(1):45-50.[13]Sun T,Gao F,Li X,et al.A combination of ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction with transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes recovery of acute liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther.2018;9(1):356.[14]Bastarrachea RA,Chen J,Kent JW Jr,et al.Engineering brown fat into skeletal muscle using ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction gene delivery in obese Zucker rats: Proof of concept design. Iubmb Life.2017;69(9):745-755.[15]Chen S,Grayburn PA.Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction for cardiac gene delivery. Methods MolBiol.2017;1521:205-218.[16]Xiang X,Tang Y,Leng Q,et al.Targeted gene delivery to the synovial pannus in antigen-induced arthritis by ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction in vivo.Ultrasonics.2016;65:304-314.[17]Nesbitt H,Sheng Y,Kamila S,et al.Gemcitabine loaded microbubbles for targeted chemo-sonodynamic therapy of pancreatic cancer.J Control Release.2018;279:8-16.[18]Cui J,Deng Q,Zhou Q,et al.Enhancement of angiogenesis by ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction combined with nuclear localization signaling peptides in canine myocardial infarction. Biomed Res Int.2017;2017:9390565.[19]Unga J, Omata D, Kudo N, et al.Development and evaluation of stability and ultrasound response of DSPC-DPSG-based freeze-dried microbubbles. J Liposome Res. 2018,10:1-7.[20]Segers T,Lassus A,Bussat P,et al.Improved coalescence stability of monodisperse phospholipid-coated microbubbles formed by flow-focusing at elevated temperatures.Lab Chip. 2018;19(1): 158-167.[21]Sun S,Xu Y,Fu P,et al.Ultrasound-targeted photodynamic and gene dual therapy for effectively inhibiting triple negative breast cancer by cationic porphyrin lipid microbubbles loaded with HIF1α-siRNA. Nanoscale.2018;10(42):19945-19956.[22]黄丹凤,陈琬萍,陈志奎,等.比较嵌段共聚物微泡与脂质微泡造影剂的体外稳定性及体内超声造影效果[J].中国介入影像与治疗学, 2014, 11(4):234-237.[23]林敏,黄丹凤,陈志奎,等.自制高分子微泡超声造影机械指数与频率和峰值强度的相关性[J].中国医学影像技术,2014,30(6):805-808.[24]林艺凯,苏婕,黄嵘森,等.微泡剂量与注射速度对高分子微泡兔肾脏超声造影参数的影响[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2014,11(11):744-747.[25]Horsley H,Owen J,Browning R,et al.Ultrasound-activated microbubbles as a novel intracellular drug delivery system for urinary tract infection.J Control Release.2019;301:166-175.[26]Fan CH,Wang TW,Hsieh YK,et al.Enhancing boron uptake in brain glioma by a boron-polymer/microbubble complex with focused ultrasound.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2019;11(12):11144-11156.[27]Yuan M,Li R,Zhang Y,et al.Enhancement patterns of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma on contrast-enhanced ultrasound: correlation with clinicopathologic findings and prognosis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019;45(1):26-34.[28]Zhang Y,Zhang M,Fan X,et al.Effect of STAT3 decoy oligodeoxynucleotides mediated by ultrasound- targeted microbubbles combined with ultrasound on the growth of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Oncol Lett.2019;17(2):2151-2158.[29]He K,Ran H,Su Z,et al.Perfluorohexane-encapsulated fullerene nanospheres for dual-modality US/CT imaging and synergistic high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:519-529. [30]Mašková E,Naiserová M,Kubová K,et al.Highly Soluble drugs directly granulated by water dispersions of insoluble eudragit® polymers as a part of hypromellose K100M matrix systems. Biomed Res Int.2019;2019:8043415.[31]Srikanth M,Asmatulu R,Cluff K,et al.Material characterization and bioanalysis of hybrid scaffolds of carbon nanomaterial and polymer nanofibers.ACS Omega.2019;4(3):5044-5051.[32]Marie A,Keeling A,Hyde TP,et al. Deformation and retentive force following in vitro cyclic fatigue of cobalt-chrome and aryl ketone polymer (AKP) clasps.Dent Mater.2019. pii: S0109-5641(18)31198-9.[33]Bartold K,Pietrzyk-Le A,Lisowski W,et al. Promoting bioanalytical concepts in genetics: A TATA box molecularly imprinted polymer as a small isolated fragment of the DNA damage repairing system. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2019;100:1-10.[34]Gomes TF,Gualberto FCM,Perasoli FB,et al.Intra-articular leflunomide-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) implants to treat synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis.Pharmazie.2019;74(4):212-220.[35]乔伟,杨莉,钱胜利,等.携带凝血酶原复合物的阴离子脂膜微泡造影剂联合超声治疗对兔肾创伤性出血模型的止血效果[J].中国医学影像技术,2017,33(4):494-498.[36]王晓妤,穆玉明,麦培培,等.制备RGDS/rt-PA双负载靶向微泡并初步评价其靶向性溶栓效果[J].中国医学影像技术,2018,34(8):1126-1130.[37]陈颖.VEGFRⅡ介导靶向微泡显像剂的制备及体外肿瘤靶向性实验研究[J].中国药师,2017,20(1):73-76.[38]徐秀霞,宋竹清,徐健蓉,等.RGD靶向微泡造影剂的制备及其黏附效能[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2015,23(2):87-90.[39]卢晓婷,齐杰.赫赛汀治疗乳腺癌的心脏毒性反应及其影响因素[J].中国药物与临床,2016,16(10):1463-1466.[40]袁超,郭书坤,杨其峰.长链非编码RNAH19对人乳腺癌细胞BT-474赫赛汀抵抗影响机制探讨[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2017,24(24): 1712-1717. |

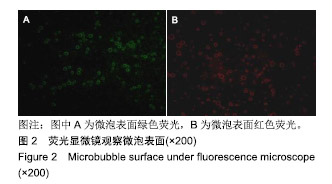
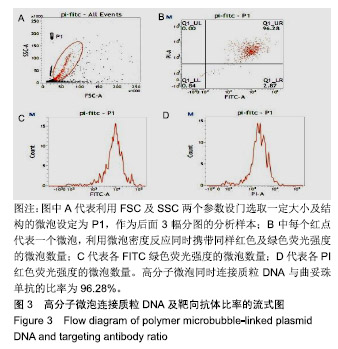
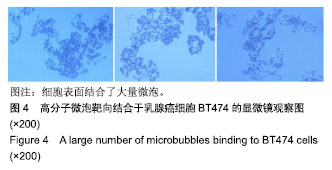
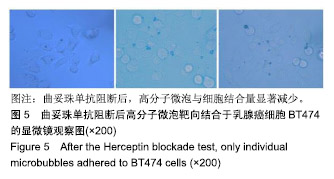
.jpg)
