中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (15): 2450-2460.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1176
• 组织构建循证医学 evidence-based medicine in tissue construction • 上一篇
肾移植后新发糖尿病危险因素的Meta分析
杨 进,张美霞,闫 沛,程 乔,李建珍
- (中国人民解放军空军军医大学第一附属医院护理处,陕西省西安市 710032)
Meta-analysis of risk factors for new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation
Yang Jin, Zhang Meixia, Yan Pei, Cheng Qiao, Li Jianzhen
- (Nursing Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Air Force Medical University of Chinese PLA, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
移植后新发糖尿病(new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation,NODAT):成功的实体器官移植后,有15%-40%的患者会发生移植后新发糖尿病。资料显示,分别有15%和27%糖耐量减低的肾移植患者在1年和6年后发展为肾移植后新发糖尿病。肾移植后新发糖尿病可使患者的心血管疾病和死亡风险增加两三倍,是心血管事件发生的独立危险因素。
队列研究:是将某一特定人群按是否暴露于某可疑因素或暴露程度分为不同的亚组,追踪观察两组或多组成员结局(如疾病)发生的情况,比较各组之间结局发生率的差异,从而判定这些因素与该结局之间有无因果关联及关联程度的一种观察性研究方法。
文题释义:
移植后新发糖尿病(new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation,NODAT):成功的实体器官移植后,有15%-40%的患者会发生移植后新发糖尿病。资料显示,分别有15%和27%糖耐量减低的肾移植患者在1年和6年后发展为肾移植后新发糖尿病。肾移植后新发糖尿病可使患者的心血管疾病和死亡风险增加两三倍,是心血管事件发生的独立危险因素。
队列研究:是将某一特定人群按是否暴露于某可疑因素或暴露程度分为不同的亚组,追踪观察两组或多组成员结局(如疾病)发生的情况,比较各组之间结局发生率的差异,从而判定这些因素与该结局之间有无因果关联及关联程度的一种观察性研究方法。
.jpg) 文题释义:
移植后新发糖尿病(new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation,NODAT):成功的实体器官移植后,有15%-40%的患者会发生移植后新发糖尿病。资料显示,分别有15%和27%糖耐量减低的肾移植患者在1年和6年后发展为肾移植后新发糖尿病。肾移植后新发糖尿病可使患者的心血管疾病和死亡风险增加两三倍,是心血管事件发生的独立危险因素。
队列研究:是将某一特定人群按是否暴露于某可疑因素或暴露程度分为不同的亚组,追踪观察两组或多组成员结局(如疾病)发生的情况,比较各组之间结局发生率的差异,从而判定这些因素与该结局之间有无因果关联及关联程度的一种观察性研究方法。
文题释义:
移植后新发糖尿病(new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation,NODAT):成功的实体器官移植后,有15%-40%的患者会发生移植后新发糖尿病。资料显示,分别有15%和27%糖耐量减低的肾移植患者在1年和6年后发展为肾移植后新发糖尿病。肾移植后新发糖尿病可使患者的心血管疾病和死亡风险增加两三倍,是心血管事件发生的独立危险因素。
队列研究:是将某一特定人群按是否暴露于某可疑因素或暴露程度分为不同的亚组,追踪观察两组或多组成员结局(如疾病)发生的情况,比较各组之间结局发生率的差异,从而判定这些因素与该结局之间有无因果关联及关联程度的一种观察性研究方法。摘要
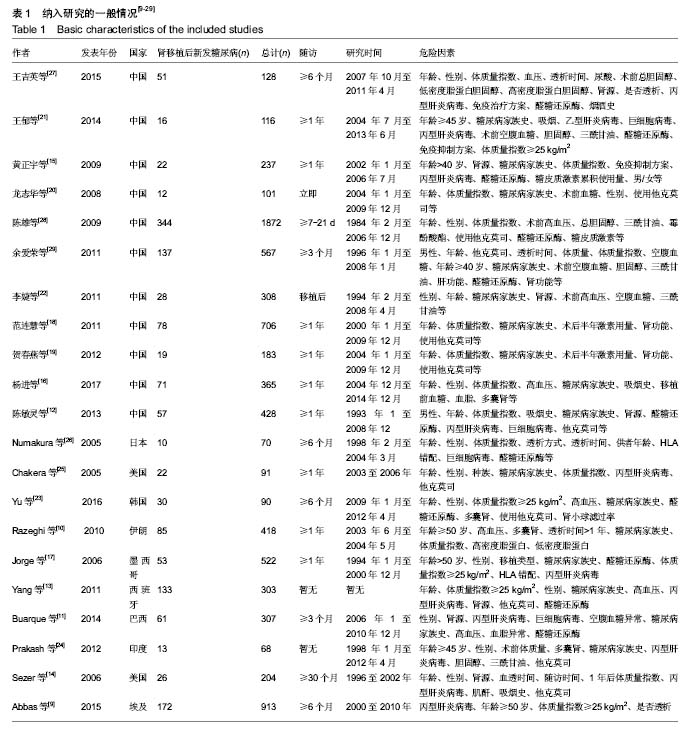
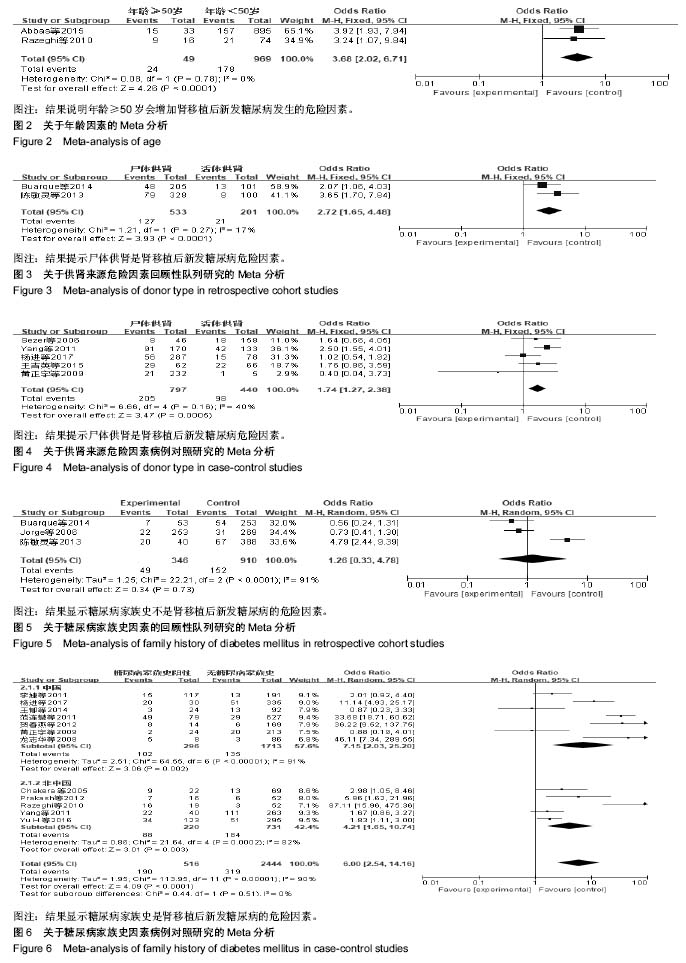
背景:研究显示年龄、性别、体质量指数、丙肝感染、免疫抑制药物和糖尿病家族史等是肾移植后新发糖尿病相关的危险因素,但危险因素对肾移植后新发糖尿病的影响尚存争议。
目的:荟萃分析近10年来影响肾移植后新发糖尿病可能相关的危险因素,为肾移植后新发糖尿病的预防和控制提供参考依据。
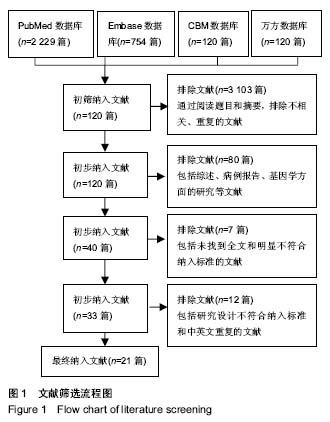
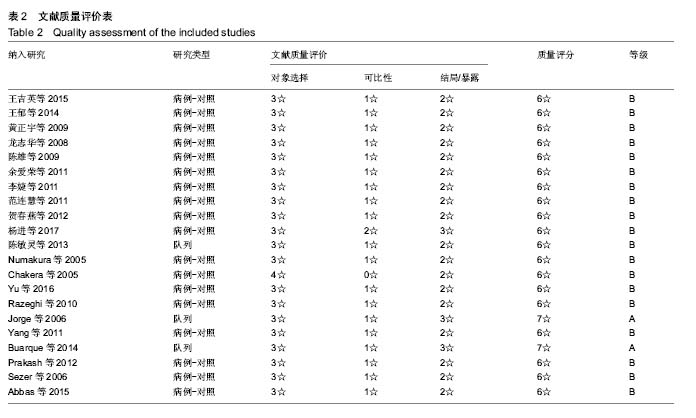
方法:检索国内外与肾移植后新发糖尿病危险因素相关研究的文献,检索的数据库包括PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library、中国生物医学文献数据库(CBMdisc),检索时间限定为2005年1月到2018年5月,语种限定为中文和英文。由2名评价员按照纳入和排除标准筛选文献并提取资料,参考Newcastle-Ottawa Scale质量评价标准进行质量评价,用RevMan5.3软件进行荟萃分析,提取影响肾移植后新发糖尿病的危险因素。
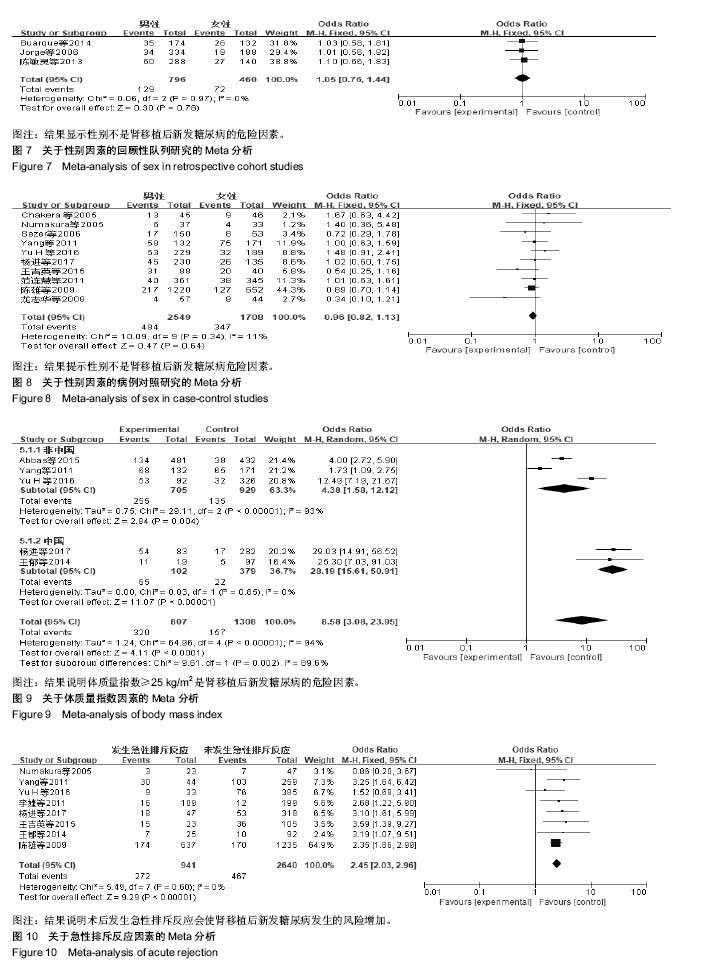
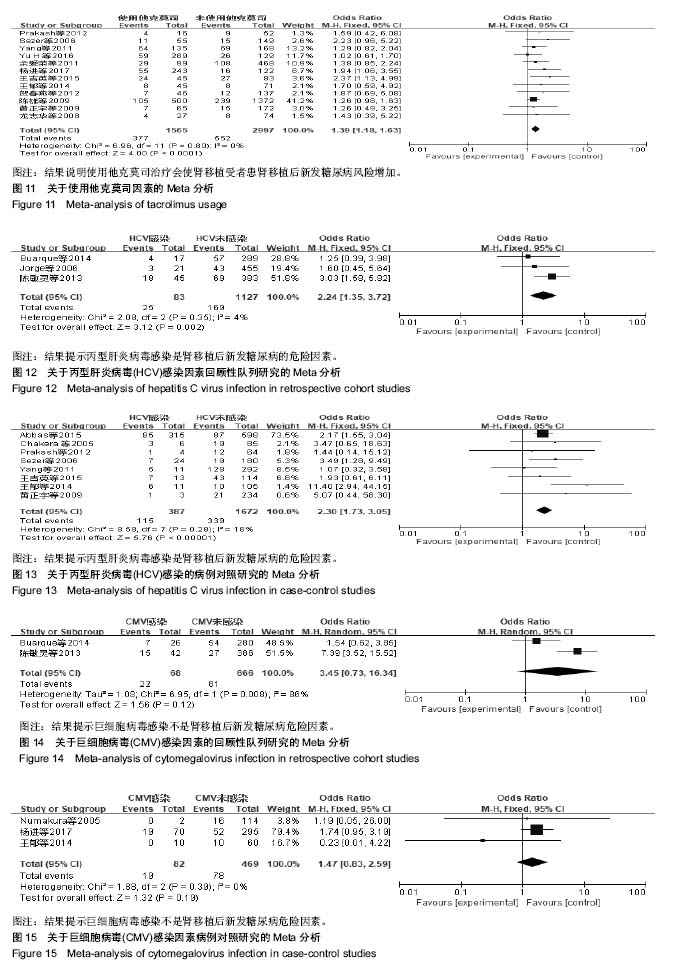
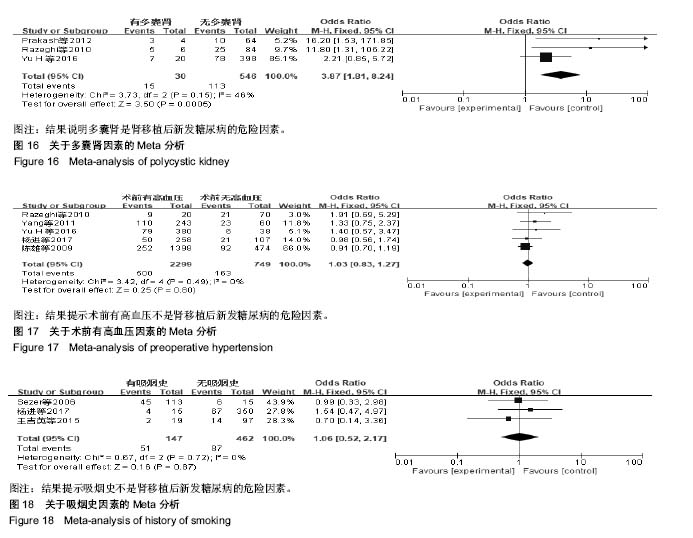
结果与结论:①21个研究被纳入,纳入研究的总病例数为8 206例,其中1 489例发生肾移植后新发糖尿病,总发病率为18.15%;②经过荟萃分析,共有7个因素对肾移植后新发糖尿病发病的影响有统计学意义,其中不可干预的危险因素依次为年龄≥50岁、供肾来源;可干预的危险因素依次为:体质量指数≥25 kg/m2、急性排斥反应、使用他克莫司、丙型肝炎病毒感染、多囊肾;③不能确定是否为肾移植后新发糖尿病危险因素:糖尿病家族史;④结果提示,年龄> 50岁、供肾来源、体质量指数≥25 kg/m2、急性排斥反应、使用他克莫司、丙型肝炎病毒感染、多囊肾7个因素是肾移植后新发糖尿病的危险因素,而糖尿病家族史尚不能确定是否为肾移植后新发糖尿病的危险因素。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3578-1252(杨进)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
移植后新发糖尿病(new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation,NODAT):成功的实体器官移植后,有15%-40%的患者会发生移植后新发糖尿病。资料显示,分别有15%和27%糖耐量减低的肾移植患者在1年和6年后发展为肾移植后新发糖尿病。肾移植后新发糖尿病可使患者的心血管疾病和死亡风险增加两三倍,是心血管事件发生的独立危险因素。
队列研究:是将某一特定人群按是否暴露于某可疑因素或暴露程度分为不同的亚组,追踪观察两组或多组成员结局(如疾病)发生的情况,比较各组之间结局发生率的差异,从而判定这些因素与该结局之间有无因果关联及关联程度的一种观察性研究方法。
文题释义:
移植后新发糖尿病(new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation,NODAT):成功的实体器官移植后,有15%-40%的患者会发生移植后新发糖尿病。资料显示,分别有15%和27%糖耐量减低的肾移植患者在1年和6年后发展为肾移植后新发糖尿病。肾移植后新发糖尿病可使患者的心血管疾病和死亡风险增加两三倍,是心血管事件发生的独立危险因素。
队列研究:是将某一特定人群按是否暴露于某可疑因素或暴露程度分为不同的亚组,追踪观察两组或多组成员结局(如疾病)发生的情况,比较各组之间结局发生率的差异,从而判定这些因素与该结局之间有无因果关联及关联程度的一种观察性研究方法。