| [1] 丁宇.脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].当代医药论丛, 2014,12(3): 295-296.[2] Mcdonald JW, Sadowsky C. Spinal-cord injury. Lancet. 2002; 359(9304):417-425. [3] 李柯柯,宗少晖.脊髓损伤中的免疫炎性细胞因子[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,18(53):8646-8646.[4] Hagg T, Oudega M. Degenerative and spontaneous regenerative processes after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(3-4):264-280. [5] Dougherty KD, Dreyfus CF, Black IB. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia/macrophages after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2000;7(6):574-585. [6] Kaplin AI, Deshpande DM, Scott E, et al. IL-6 induces regionally selective spinal cord injury in patients with the neuroinflammatory disorder transverse myelitis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(10):2731-41. [7] 郑晶晶,姚安会,刘芳芳,等.小鼠脊髓损伤早期不同炎症因子的表达变化[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2012,28(4):391-394.[8] Lan WB, Lin JH, Chen XW, et al. Overexpressing neuroglobin improves functional recovery by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2014;1562:100-108. [9] Zhou HL, Zhang XJ, Zhang MY, et al. Transplantation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells promotes functional recovery in a rat model of traumatic spinal cord injury. Neurochem Res. 2016;475(2):1-11. [10] Nakata N, Kato H, Kogure K. Protective effects of basic fibroblast growth factor against hippocampal neuronal damage following cerebral ischemia in the gerbil. Brain Res. 1993;605(2):354-356. [11] Fahmy GH, Moftah MZ. FGF-2 in astroglial cells during vertebrate spinal cord recovery. Front Cell Neurosci. 2010;4(1):129. [12] Brown A, Ricci MJ, Weaver LC. NGF message and protein distribution in the injured rat spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 2004; 188(1):115-127. [13] Filli L, Engmann AK, Zörner B, et al. Bridging the gap: a reticulo-propriospinal detour bypassing an incomplete spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2014;34(40):13399-13410. [14] Yuan Y, Su Z, Pu Y, et al. Ethyl pyruvate promotes spinal cord repair by ameliorating the glial microenvironment. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;166(2):749-763. [15] 宫德星,吕奎荣.急性脊髓损伤的MRI诊断[J].齐鲁医学杂志, 2008,23(6):516-517.[16] 王方永,李建军.脊髓损伤神经学分类国际标准(ASIA 2011版)最新修订及标准解读[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2012,18(8):797-800.[17] Chhabra HS, Sarda K, Arora M, et al. Autologous bone marrow cell transplantation in acute spinal cord injury-an Indian pilot study. Spinal Cord. 2015;54(1):57-64. [18] Tuna M, Polat S, Erman T, et al. Effect of anti-rat interleukin-6 antibody after spinal cord injury in the rat: inducible nitric oxide synthase expression, sodium- and potassium-activated, magnesium-dependent adenosine-5-triphosphatase and superoxide dismutase activation, and ultrastructural changes. J Neurosurg. 2001;95(1):64-73. [19] Park DY, Mayle RE, Smith RL, et al. Combined transplantation of human neuronal and mesenchymal stem cells following spinal cord injury. Global Spine J. 2013;3(1):1-6. [20] De Moraes JK, Wagner VP, Fonseca FP, et al. Uncovering the role of brain‐derived neurotrophic factor/tyrosine kinase receptor B signaling in head and neck malignancies. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018;47(3):221-227. [21] Yang JW, Liang Z, Deng SD, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes growth of neurons and neural stem cells possibly by triggering the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT/ glycogen synthase kinase-3β/β-catenin pathway. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(7):828-836. [22] ang B, Qin J, Nie Y, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor propeptide inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in C6 glioma cells. Neuroreport. 2017;28(12):726-730. [23] Habtemariam S.The brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuronal plasticity and neuroregeneration: new pharmacological concepts for old and new drugs.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(6):983-984.[24] Martiñón S, García-Vences E, Toscano-Tejeida D, et al. Long-term production of BDNF and NT-3 induced by A91-immunization after spinal cord injury. BMC Neurosci. 2016;17(1):42. [25] Alonso Vanegas MA, Fawcett JP, Causing CG, et al. Characterization of dopaminergic midbrain neurons in a DBH: BDNF transgenic mouse. J Comp Neurol. 2015;413(3): 449-462. [26] Sharma HS, Nyberg F, Westman J, et al. Brain derived neurotrophic factor and insulin like growth factor-1 attenuate upregu-lation of nitric oxide synthase and cell injury following trauma to the spinal cord: an immunohistochemical study in the rat. Amino Acids. 1998;14(1):121-129. [27] Garraway SM, Anderson AJ, Mendell LM. BDNF-induced facilitation of afferent-evoked responses in lamina II neurons is reduced after neonatal spinal cord contusion injury. J Neurophysiol. 2005;94(3):1798-804. [28] Zhao YZ, Lin M, Lin Q, et al. Intranasal delivery of bFGF with nanoliposomes enhances in vivo, neuroprotection and neural injury recovery in a rodent stroke model. J Control Release. 2016;224:165-175. [29] Rabchevsky AG, Fugaccia I, Turner AF, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) enhances functional recovery following severe spinal cord injury to the rat. Exp Neurol. 2000;164(2): 280-291. [30] Chen B, He J, Yang H, et al. Repair of spinal cord injury by implantation of bFGF-incorporated HEMA-MOETACL hydrogel in rats. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9017. [31] 蔡俊赢,董效禹,赖嘉新,等.bFGF通过抑制Nogo-A信号减少脊髓损伤后胶质瘢痕的形成[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2017, 33(7):681-686.[32] Aoyagi A, Nishikawa K, Saito H, et al. Characterization of basic fibroblast growth factor-mediated acceleration of axonal branching in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1994;661(1-2):117-126. [33] Kojima A, Tator CH. Intrathecal administration of epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor 2 promotes ependymal proliferation and functional recovery after spinal cord injury in adult rats. J Neurotrauma. 2002;19(2):223-38. [34] Li Y, Xia B, Li R, Yin D, et al. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factors, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4 in the nucleus accumbens during heroin dependency and withdrawal. Neuroreport. 2017;28(11):654-660.[35] Tseng PT, Chen YW, Tu KY, et al. State-dependent increase in the levels of neurotrophin-3 and neurotrophin-4/5 in patients with bipolar disorder: a meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Res. 2016;79:86-92.[36] Loch AA, Zanetti MV, de Sousa RT, et al. Elevated neurotrophin-3 and neurotrophin 4/5 levels in unmedicated bipolar depression and the effects of lithium. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015;56:243-246. [37] Szczepankiewicz A, Rachel M, Sobkowiak P, et al. Serum neurotrophin-3 and neurotrophin-4 levels are associated with asthma severity in children. Eur Respir J. 2012;39(4): 1035-1037. [38] Hechler D, Boato F, Nitsch R, et al. Differential regulation of axon outgrowth and reinnervation by neurotrophin-3 and neurotrophin-4 in the hippocampal formation. Exp Brain Res. 2010;205(2):215-221. [39] Nassenstein C, Braun A, Erpenbeck VJ, et al. The neurotrophins nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4 are survival and activation factors for eosinophils in patients with allergic bronchial asthma. J Exp Med. 2003;198(3):455-467.[40] Guo Y, Ma Y, Pan YL,et al.Jisuikang, a Chinese herbal formula, increases neurotrophic factor expression and promotes the recovery of neurological function after spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(9):1519-1528.[41] Yang Z, Duan H, Mo L, et al. The effect of the dosage of NT-3/chitosan carriers on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(18):4846-4854. [42] Schnell L, Schneider R, Kolbeck R, et al. Neurotrophin-3 enhances sprouting of corticospinal tract duringdevelopment and after adult spinal cord lesion. Nature. 1994;367(6459): 170-173. [43] Harvey AR, Lovett SJ, Majda BT, et al. Neurotrophic factors for spinal cord repair: Which, where, how and when to apply, and for what period of time? Brain Res. 2015;1619:36-71. [44] Tobias CA, Shumsky JM, Tuszynski MH, et al. Delayed grafting of BDNF and NT-3 producing fibroblasts into the injured spinal cord stimulates sprouting, partially rescues axotomized red nucleus neurons from loss and atrophy, and provides limited regeneration. Exp Neurol. 2003;184(1): 97-113. [45] Junger H, Varon S. Neurotrophin-4 (NT-4) and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) promote the survival of corticospinal motor neurons of neonatal rats in vitro. Brain Res.1997;762(1-2):56-60. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓损伤:按病理机制可分为原发性与继发性损伤。前者指脊髓遭受外力冲击下直接导致的脊髓机械性损伤,属永久性损伤;后者指在原发性损伤基础上引发瀑布式级联反应而导致的组织进行性、自毁性破坏过程,属可逆性损伤。
脊髓损伤微环境改变:脊髓损伤后,早期病理变化为结构破坏、局部组织水肿、神经元损伤及脊髓组织缺血损害等,继而产生一系列病理生理改变。一方面脊髓损伤后刺激机体产生各类免疫炎症因子,诱导炎症级联反应、加重其损伤的程度,加快神经细胞死亡及脱髓鞘,最后神经胶质增生及瘢痕形成;另一方面,脊髓损伤后也会刺激机体生成一系列神经营养因子,保护受损神经系统、促进其分化和再生,加快神经功能恢复。
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:按病理机制可分为原发性与继发性损伤。前者指脊髓遭受外力冲击下直接导致的脊髓机械性损伤,属永久性损伤;后者指在原发性损伤基础上引发瀑布式级联反应而导致的组织进行性、自毁性破坏过程,属可逆性损伤。
脊髓损伤微环境改变:脊髓损伤后,早期病理变化为结构破坏、局部组织水肿、神经元损伤及脊髓组织缺血损害等,继而产生一系列病理生理改变。一方面脊髓损伤后刺激机体产生各类免疫炎症因子,诱导炎症级联反应、加重其损伤的程度,加快神经细胞死亡及脱髓鞘,最后神经胶质增生及瘢痕形成;另一方面,脊髓损伤后也会刺激机体生成一系列神经营养因子,保护受损神经系统、促进其分化和再生,加快神经功能恢复。.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓损伤:按病理机制可分为原发性与继发性损伤。前者指脊髓遭受外力冲击下直接导致的脊髓机械性损伤,属永久性损伤;后者指在原发性损伤基础上引发瀑布式级联反应而导致的组织进行性、自毁性破坏过程,属可逆性损伤。
脊髓损伤微环境改变:脊髓损伤后,早期病理变化为结构破坏、局部组织水肿、神经元损伤及脊髓组织缺血损害等,继而产生一系列病理生理改变。一方面脊髓损伤后刺激机体产生各类免疫炎症因子,诱导炎症级联反应、加重其损伤的程度,加快神经细胞死亡及脱髓鞘,最后神经胶质增生及瘢痕形成;另一方面,脊髓损伤后也会刺激机体生成一系列神经营养因子,保护受损神经系统、促进其分化和再生,加快神经功能恢复。
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:按病理机制可分为原发性与继发性损伤。前者指脊髓遭受外力冲击下直接导致的脊髓机械性损伤,属永久性损伤;后者指在原发性损伤基础上引发瀑布式级联反应而导致的组织进行性、自毁性破坏过程,属可逆性损伤。
脊髓损伤微环境改变:脊髓损伤后,早期病理变化为结构破坏、局部组织水肿、神经元损伤及脊髓组织缺血损害等,继而产生一系列病理生理改变。一方面脊髓损伤后刺激机体产生各类免疫炎症因子,诱导炎症级联反应、加重其损伤的程度,加快神经细胞死亡及脱髓鞘,最后神经胶质增生及瘢痕形成;另一方面,脊髓损伤后也会刺激机体生成一系列神经营养因子,保护受损神经系统、促进其分化和再生,加快神经功能恢复。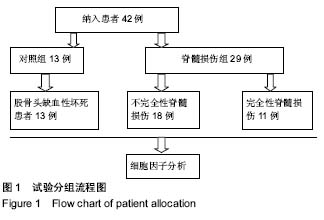
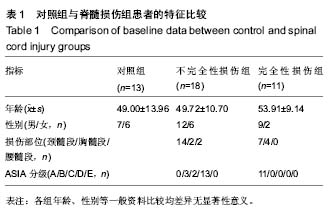
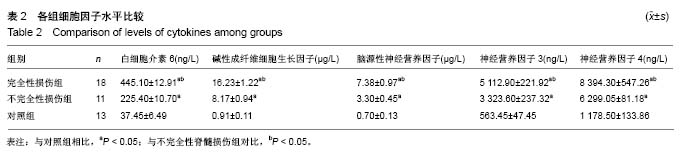
.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓损伤:按病理机制可分为原发性与继发性损伤。前者指脊髓遭受外力冲击下直接导致的脊髓机械性损伤,属永久性损伤;后者指在原发性损伤基础上引发瀑布式级联反应而导致的组织进行性、自毁性破坏过程,属可逆性损伤。
脊髓损伤微环境改变:脊髓损伤后,早期病理变化为结构破坏、局部组织水肿、神经元损伤及脊髓组织缺血损害等,继而产生一系列病理生理改变。一方面脊髓损伤后刺激机体产生各类免疫炎症因子,诱导炎症级联反应、加重其损伤的程度,加快神经细胞死亡及脱髓鞘,最后神经胶质增生及瘢痕形成;另一方面,脊髓损伤后也会刺激机体生成一系列神经营养因子,保护受损神经系统、促进其分化和再生,加快神经功能恢复。
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:按病理机制可分为原发性与继发性损伤。前者指脊髓遭受外力冲击下直接导致的脊髓机械性损伤,属永久性损伤;后者指在原发性损伤基础上引发瀑布式级联反应而导致的组织进行性、自毁性破坏过程,属可逆性损伤。
脊髓损伤微环境改变:脊髓损伤后,早期病理变化为结构破坏、局部组织水肿、神经元损伤及脊髓组织缺血损害等,继而产生一系列病理生理改变。一方面脊髓损伤后刺激机体产生各类免疫炎症因子,诱导炎症级联反应、加重其损伤的程度,加快神经细胞死亡及脱髓鞘,最后神经胶质增生及瘢痕形成;另一方面,脊髓损伤后也会刺激机体生成一系列神经营养因子,保护受损神经系统、促进其分化和再生,加快神经功能恢复。