| [1] Wei C, Zhang F, Chen L, et al. Factors associated with post-stroke depression and fatigue: lesion location and coping styles. J Neurol.2016;263(2):269-276.[2] Howells DW, Porritt MJ, Rewell SS, et al. Different strokes for different folks: the rich diversity of animal models of focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30(8): 1412-1431.[3] Sehara Y, Inaba T, Urabe T, et al. Survivin Overexpression via Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Rh10 Ameliorates Ischemic Damage after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2018 Sep 25. [4] Yan Y, Fan W, Liu L, et al. The effects of Xingnao Jieyu capsules on post-stroke depression are similar to those of fluoxetine. Neural Regen Res.2013;(19):1765-1772.[5] Yan Y, Li T, Liu L, et al. Effect of tonifying liver and kidney-essence herbs on expression of Nogo-A and p75(NTR) in cerebral ischemic stroke rats model. J Tradit Chin Med. 2012;32(4):664-668.[6] 范文涛,闫咏梅,别玉龙,等.脑卒中后抑郁症患者肠道菌群的多样性分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2016,36(10):1305-1311.[7] 范文涛,闫咏梅,别玉龙,等.大鼠卒中后肠道菌群紊乱与抑郁的关系[J].中国脑血管病杂志, 2016(12):644-649.[8] 张慧,闫咏梅,谢福恒,等. 醒脑解郁胶囊干预卒中后抑郁及与NEI网络关系的临床研究[J]. 现代中医药, 2016;36(4):46-48.[9] Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.[10] Qi X, Hosoi T, Okuma Y, et al. Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate protects against cerebral ischemic injury. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66(4):899-908.[11] 常晓波,王舒,樊小农,等.脑梗死大鼠模型神经功能缺损评分的动态变化分析[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2015,30(11):4053-4056.[12] Willner P, Towell A, Sampson D, et al. Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology (Berl).1987;93(3):358-364.[13] Gaur V, Kumar A. Behavioral, biochemical and cellular correlates in the protective effect of sertraline against transient global ischemia induced behavioral despair: possible involvement of nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate study pathway. Brain Res Bull.2010;82(1-2): 57-64.[14] Yan B, Wang DY, Xing DM, et al. The antidepressant effect of ethanol extract of radix puerariae in mice exposed to cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.2004;78(2): 319-325.[15] Zhang G, Chen L, Yang L, et al. Combined use of spatial restraint stress and middle cerebral artery occlusion is a novel model of post-stroke depression in mice. Sci Rep.2015; 5:16751.[16] Luo L, Deng S, Yi J, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction Ameliorates Poststroke Depression via Promoting Neurotrophic Pathway Mediated Neuroprotection and Neurogenesis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017; 2017:4072658.[17] de Oliveira GS, Cereser KM, Fernandes BS, et al. Decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor in medicated and drug-free bipolar patients. J Psychiatr Res. 2009;43(14):1171-1174.[18] Pinnock SB, Herbert J. Brain-derived neurotropic factor and neurogenesis in the adult rat dentate gyrus: interactions with corticosterone. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(10):2493-2500.[19] Boyko M, Kutz R, Gruenbaum BF, et al. The influence of aging on poststroke depression using a rat model via middle cerebral artery occlusion. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci.2013; 13(4):847-859.[20] Ji XW, Wu CL, Wang XC, et al. Monoamine neurotransmitters and fibroblast growth factor-2 in the brains of rats with post-stroke depression. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(1):159-164.[21] Yan HC,Cao X,Das M, et al. Behavioral animal models of depression. Neurosci Bull. 2010;26(4):327-337.[22] Abelaira HM, Reus GZ, Quevedo J. Animal models as tools to study the pathophysiology of depression. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2013;35 Suppl 2:S112-S120.[23] Nestler EJ, Hyman SE. Animal models of neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(10):1161-1169.[24] Astrom M, Adolfsson R, Asplund K. Major depression in stroke patients. A 3-year longitudinal study. Stroke. 1993; 24(7): 976-982.[25] Ren L, Qian X, Zhai L, et al. Loss of Ahi1 impairs neurotransmitter release and causes depressive behaviors in mice. PLoS One.2014;9(4):e93640. [26] Lin R, Li X, Liu W, et al. Electro-acupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment via improvement of brain-derived neurotropic factor-mediated hippocampal synaptic plasticity in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(3):2373-2379. |
.jpg)
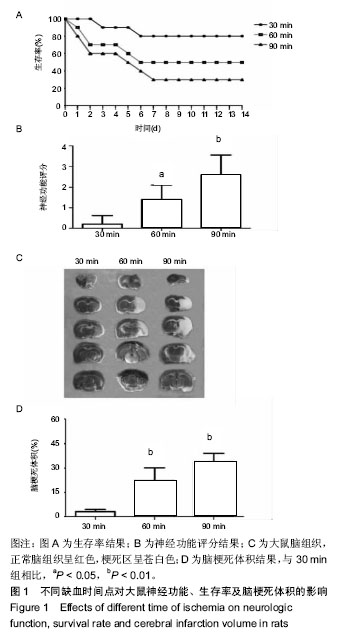
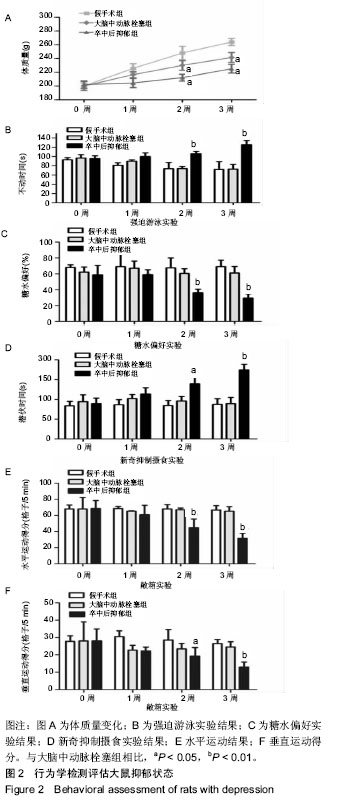
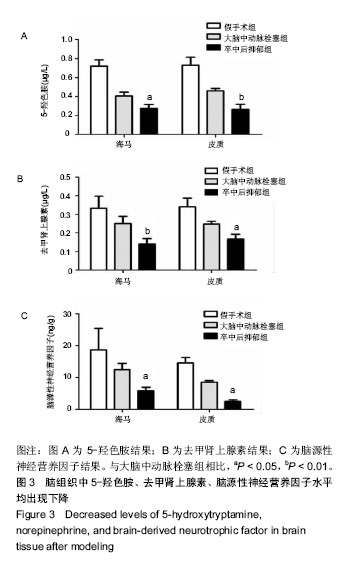
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
卒中后抑郁:是脑卒中常见的并发症之一,是与脑卒中事件相关的,临床表现抑郁心境的情感障碍性疾病。严重影响患者及家属的生活质量,阻碍神经功能的恢复,主要表现为情绪低落、兴趣丧失、睡眠障碍、食欲减退、悲观厌世、妄想、甚至产生自杀倾向等。#br#
慢性温和不可预知应激(chronic unpredictable mild stress,CUMS)模型:是一种经典抑郁症动物模型,其常与孤养模型相结合,制作轻度不可预见的应激抑郁模型,其理论依据与人类抑郁症中慢性、低水平的应激源导致抑郁症的发生并加速抑郁症发展的机制更为接近,利用孤养模拟人类失去社会和家庭支持的孤独状态,轻度不可预见应激模拟抑郁症发病的压力源,造成孤养动物的抑郁状态。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
卒中后抑郁:是脑卒中常见的并发症之一,是与脑卒中事件相关的,临床表现抑郁心境的情感障碍性疾病。严重影响患者及家属的生活质量,阻碍神经功能的恢复,主要表现为情绪低落、兴趣丧失、睡眠障碍、食欲减退、悲观厌世、妄想、甚至产生自杀倾向等。#br#
慢性温和不可预知应激(chronic unpredictable mild stress,CUMS)模型:是一种经典抑郁症动物模型,其常与孤养模型相结合,制作轻度不可预见的应激抑郁模型,其理论依据与人类抑郁症中慢性、低水平的应激源导致抑郁症的发生并加速抑郁症发展的机制更为接近,利用孤养模拟人类失去社会和家庭支持的孤独状态,轻度不可预见应激模拟抑郁症发病的压力源,造成孤养动物的抑郁状态。