中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (10): 1599-1604.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1575
• 材料力学及表面改性 material mechanics and surface modification • 上一篇 下一篇
经导管主动脉瓣流固耦合分析
朱宏伟,袁 泉,刘杏铭,丛 华
- 山东大学机械工程国家级实验教学示范中心,高效洁净机械制造教育部重点实验室,山东省济南市 250061
Fluid structure interaction analysis of transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Zhu Hongwei, Yuan Quan, Liu Xingming, Cong Hua
- National Demonstration Center for Experimental Mechanical Engineering Education of Shandong University, Key Laboratory of High-Efficiency and Clean Mechanical Manufacture of Ministry of Education, Jinan 250061, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
经导管主动脉瓣置换:主动脉瓣发生病变后无法正常工作,通过心尖、股动脉或肺主动脉送入介入导管,将人工心脏瓣膜输送至主动脉瓣区打开,从而完成人工瓣膜置入,恢复瓣膜功能。手术无需开胸,因而创伤小、术后恢复快。由有经验的心血管内科医师实施。
经导管主动脉瓣流固耦合分析:通过三维建模建立经导管主动脉瓣有限元分析的几何模型,研究主动脉瓣与血液的流固耦合理论,通过进行有限元分析,研究主动脉瓣变形特点和应力分布。变形特点通过实验对比分析其工作性能,应力分布目前实验无法获取。采用有限元软件进行分析,是目前经导管主动脉瓣研究中成本较低和时效较快的方案,可获得更为优化的经导管主动脉瓣结构。
背景:心脏瓣膜病的治疗手段主要为心脏瓣膜置换术。与开胸手术比较,以经导管主动脉瓣置换术为代表的介入式换瓣手术具有创口小、恢复快的特点。目前国内经导管主动脉瓣置换术的应用范围仍较小,研究主要在患者术后的生理条件变化,少有对经导管主动脉瓣模型本身的分析。
目的:探究经导管主动脉瓣变形特点和应力分布,验证其工作性能。
方法:建立包括主动脉瓣、血管壁、血液和支架的经导管主动脉瓣有限元几何模型和数学模型,采用浸没边界法进行流固耦合分析,计算有效开口面积指数进行实验对比,验证模型的工作性能。
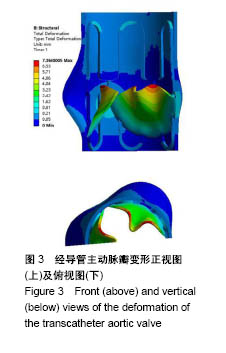
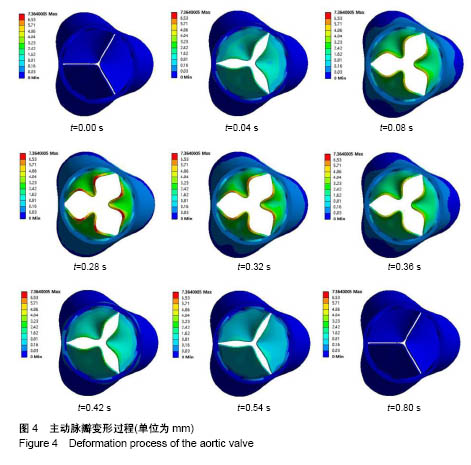
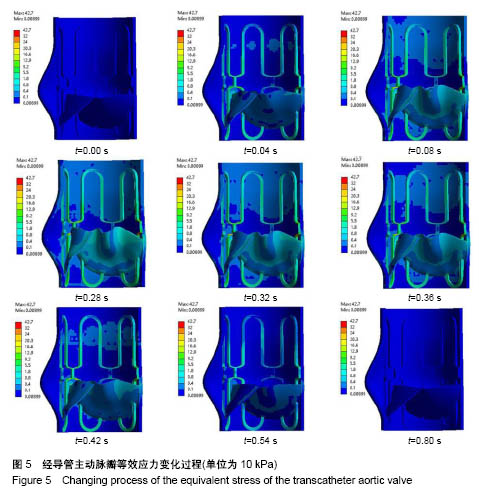
结果与结论:①经导管主动脉瓣在血液冲击过程中,瓣叶变形最大且存在卷曲,最大变形处发生在瓣叶自由边1/4处和3/4处;②经导管主动脉瓣模型等效应力最大处在支架上,但其变形较小,瓣叶应力集中位置在自由边卷曲明显处和缝合边与支架接触的缝合点上,是容易发生瓣叶破坏的位置;③经脉动流实验验证,模型变形过程和有效开口面积均与实验结果接近,所建模型合理有效。
ORCID: 0000-0003-0278-4112(朱宏伟)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)