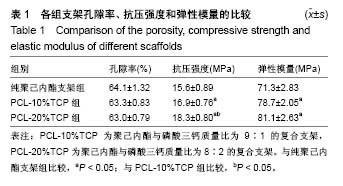
| [1] Oryan A, Alidadi S, Moshiri A, et al. Bone regenerative medicine: classic options, novel strategies, and future directions.2014:9,18.[2] Campana V, Milano G, Pagano E, et al. Bone substitutes in orthopaedic surgery: from basic science to clinical practice. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2014;25(10):2445-2461.[3] Polo-Corrales L, Latorre-Esteves M, Ramirez-Vick J E. Scaffold design for bone regeneration. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014; 14(1): 15-56.[4] Giannoudis PV, Chris Arts JJ,Schmidmaier G,et al. What should be the characteristics of the ideal bone graft substitute? Injury. 2011; 42:S1-S2.[5] Lee JW, Kim JY, Cho DW. Solid Free-form Fabrication Technology and Its Application to Bone Tissue Engineering.Int J Stem Cells. 2010;3(2): 85-95.[6] Tabata Y. Biomaterial technology for tissue engineering applications. J R Soc Interface.2009;6 Suppl 3:S311-S324.[7] Hutmacher DW.Scaffold design and fabrication technologies for engineering tissues--state of the art and future perspectives.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2001;12(1):107-124.[8] Lee J, Choi B, Wu B, et al. Customized biomimetic scaffolds created by indirect three-dimensional printing for tissue engineering. Biofabrication.2013;5(4):45003.[9] Frame M, Huntley JS. Rapid Prototyping in Orthopaedic Surgery: A User's Guide. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:1-7.[10] Li Y,Wu Z,Li X,et al.A polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate composite scaffold as an autograft-free spinal fusion cage in a sheep model.Biomaterials.2014;35(22):5647-5659.[11] Rai B,Lin JL,Lim ZX, et al. Differences between in vitro viability and differentiation and in vivo bone-forming efficacy of human mesenchymal stem cells cultured on PCL–TCP scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2010;31(31):7960-7970.[12] Pati F,Song TH, Rijal G,et al.Ornamenting 3D printed scaffolds with cell-laid extracellular matrix for bone tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2015;37:230-241.[13] Ba LN,Min YK,Lee BT.Hybrid hydroxyapatite nanoparticles-loaded PCL/GE blend fibers for bone tissue engineering. 2013:24, 520-538.[14] Becker J,Lu L,Runge MB,et al.Nanocomposite bone scaffolds based on biodegradable polymers and hydroxyapatite.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(8):2549-2557.[15] Thadavirul N,Pavasant P,Supaphol P.Improvement of dual-leached polycaprolactone porous scaffolds by incorporating with hydroxyapatite for bone tissue regeneration.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2014;25(17):1986-2008.[16] Lohfeld S,Cahill S,Barron V,et al.Fabrication, mechanical and in vivo performance of polycaprolactone/tricalcium phosphate composite scaffolds.Acta Biomater. 2012;8(9): 3446-3456.[17] Yeo A,Cheok C,Teoh SH,et al.Lateral ridge augmentation using a PCL-TCP scaffold in a clinically relevant but challenging micropig model.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23(12):1322-1332.[18] Khojasteh A,Behnia H,Hosseini FS,et al.The effect of PCL-TCP scaffold loaded with mesenchymal stem cells on vertical bone augmentation in dog mandible: a preliminary report.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(5): 848-854.[19] Bose S,Roy M,Bandyopadhyay A.Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds.Trends Biotechnol.2012;30(10):546-554.[20] Calori GM,Mazza E,Colombo M,et al.The use of bone-graft substitutes in large bone defects: Any specific needs? Injury. 2011;42:S56-S63.[21] Saiz E,Zimmermann EA,Lee JS,et al.Perspectives on the role of nanotechnology in bone tissue engineering.Dent Mater. 2013; 29(1):103-115.[22] Baykan E,Koc A,Eser EA,et al.Evaluation of a biomimetic poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/beta-tricalcium phosphate multispiral scaffold for bone tissue engineering: in vitro and in vivo studies. Biointerphases.2014;9(2):29011.[23] Yang K,Zhang J,Ma X,et al.β-Tricalcium phosphate/poly(glycerol sebacate) scaffolds with robust mechanical property for bone tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2015;56:37-47.[24] Idaszek J,Bruinink A,Swieszkowski W.Ternary composite scaffolds with tailorable degradation rate and highly improved colonization by human bone marrow stromal cells.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015; 103(7):2394-2404.[25] Sharaf B,Faris CB,Abukawa H,et al. Three-dimensionally printed polycaprolactone and β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: an in vitro study.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70(3):647-656.[26] Doyle H,Lohfeld S,Mchugh P.Predicting the elastic properties of selective laser sintered PCL/beta-TCP bone scaffold materials using computational modelling.Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(3): 661-677.[27] Xu N, Ye X, Wei D, et al. 3D artificial bones for bone repair prepared by computed tomography-guided fused deposition modeling for bone repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(17):14952-14963. [28] Shor L,Guceri S,Wen X,et al. Fabrication of three-dimensional polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite tissue scaffolds and osteoblast-scaffold interactions in vitro. Biomaterials. 2007;28(35): 5291-5297.[29] Beguma Z,Chhedat P.Rapid prototyping--when virtual meets reality. Int J Comput Dent.2014;17(4):297-306.[30] Kim J,Mcbride S,Tellis B,et al.Rapid-prototyped PLGA/beta-TCP/ hydroxyapatite nanocomposite scaffolds in a rabbit femoral defect model. Biofabrication.2012;4(2):25003.[31] Park S, Kim G, Jeon YC, et al.3D polycaprolactone scaffolds with controlled pore structure using a rapid prototyping system.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2009;20(1):229-234.[32] Hutmacher DW.Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials.2000;21(24):2529-2543.[33] Briggs T, Matos J, Collins G, et al. Evaluating protein incorporation and release in electrospun composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(10): 3117-3127. [34] Shim JH, Huh JB, Park JY, et al. Fabrication of blended polycaprolactone/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/beta-tricalcium phosphate thin membrane using solid freeform fabrication technology for guided bone regeneration.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013; 19(3-4):317-328.[35] Doyle H, Lohfeld S, Mchugh P. Evaluating the effect of increasing ceramic content on the mechanical properties, material microstructure and degradation of selective laser sintered polycaprolactone/ β-tricalcium phosphate materials.Med Eng Phys. 2015;37(8):767-776.[36] Nyberg E,Rindone A,Dorafshar A,et al. Comparison of 3D-Printed Poly-?-Caprolactone Scaffolds Functionalized with Tricalcium Phosphate, Hydroxyapatite, Bio-Oss, or Decellularized Bone Matrix. Tissue Eng Part A.2017;23(11-12):503-514.[37] Park S, Lee H, Kim K, et al. In Vivo Evaluation of 3D-Printed Polycaprolactone Scaffold Implantation Combined with β-TCP Powder for Alveolar Bone Augmentation in a Beagle Defect Model. Materials, 2018,11(2):238.[38] Kim J,Ahn G,Kim C,et al.Synergistic Effects of Beta Tri-Calcium Phosphate and Porcine-Derived Decellularized Bone Extracellular Matrix in 3D-Printed Polycaprolactone Scaffold on Bone Regeneration.Macromolecular Bioscience.2018;18(6):1800025.[39] Bae J,Lee J,Shim J,et al.Development and Assessment of a 3D-Printed Scaffold with rhBMP-2 for an Implant Surgical Guide Stent and Bone Graft Material: A Pilot Animal Study. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(12):1434.[40] Konopnicki S,Sharaf B,Resnick C,et al. Tissue-engineered bone with 3-dimensionally printed β-tricalcium phosphate and polycaprolactone scaffolds and early implantation: an in vivo pilot study in a porcine mandible model.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 73(5):1011-1016.[41] Yao Q,Cosme JG, Xu T,et al.Three dimensional electrospun PCL/PLA blend nanofibrous scaffolds with significantly improved stem cells osteogenic differentiation and cranial bone formation. Biomaterials. 2017;115:115-127. |
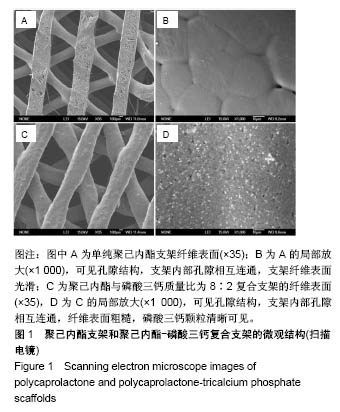
.jpg)
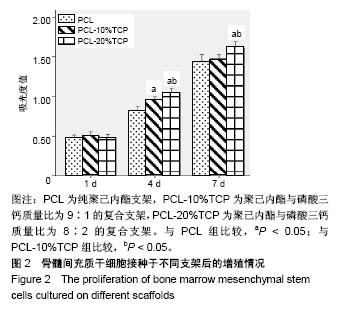
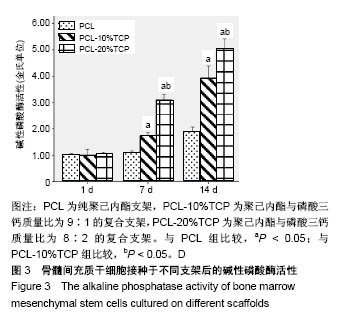
.jpg)