中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (32): 5169-5174.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0399
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
激素性股骨头缺血性坏死动物模型的建立及综合评估
佟 鹏1,王 洋2,梁 瀛3
- 葫芦岛市中心医院,1放射科,2核医学科,3导管室,辽宁省葫芦岛市 125000
Establishment and comprehensive evaluation of animal models of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head
Tong Peng1, Wang Yang2, Liang Ying3
- 1Department of Radiology, 2Nuclear Medicine, 3Catheter Room, Huludao Central Hospital, Huludao 125000, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
激素性股骨头缺血性坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变,激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
血液流变学:是一门新兴的生物力学及生物流变学分支,是研究血液宏观流动性质、人和动物体内血液流动和细胞变形以及血液与血管、心脏之间相互作用,血细胞流动性质及生物化学成分的一门科学,近20年来才发展成为一门独立的新兴边缘学科。
文题释义:
激素性股骨头缺血性坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变,激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
血液流变学:是一门新兴的生物力学及生物流变学分支,是研究血液宏观流动性质、人和动物体内血液流动和细胞变形以及血液与血管、心脏之间相互作用,血细胞流动性质及生物化学成分的一门科学,近20年来才发展成为一门独立的新兴边缘学科。
.jpg) 文题释义:
激素性股骨头缺血性坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变,激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
血液流变学:是一门新兴的生物力学及生物流变学分支,是研究血液宏观流动性质、人和动物体内血液流动和细胞变形以及血液与血管、心脏之间相互作用,血细胞流动性质及生物化学成分的一门科学,近20年来才发展成为一门独立的新兴边缘学科。
文题释义:
激素性股骨头缺血性坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变,激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
血液流变学:是一门新兴的生物力学及生物流变学分支,是研究血液宏观流动性质、人和动物体内血液流动和细胞变形以及血液与血管、心脏之间相互作用,血细胞流动性质及生物化学成分的一门科学,近20年来才发展成为一门独立的新兴边缘学科。摘要
背景:建立简便可行、失败率低的激素性股骨头缺血性坏死动物模型,是研究激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的主要途径。
目的:建立激素性股骨头缺血性坏死动物模型,并进行病理学、影像学、骨/血清生化、血流变学评价。
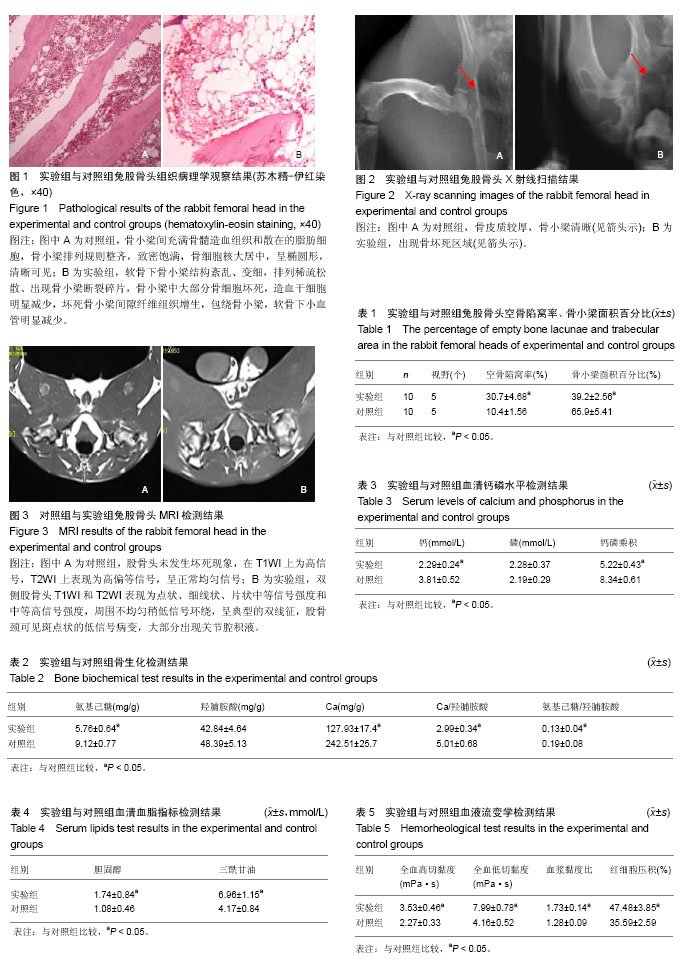
方法:将20只大耳白兔随机分2组,实验组经耳缘静脉注射马血清10 mL/kg,14 d后再注射1次,再次注射14 d后,臀肌注射醋酸泼尼松龙8 mg/kg,1次/d,连续注射6 d,建立激素性股骨头缺血性坏死模型;对照组注射等量生理盐水。造模后8周,进行股骨头X射线、MRI检查;造模后10周,进行骨生化、血清生化、血液流变学及股骨头组织学观察。
结果与结论:①X射线:对照组骨皮质较厚,骨小梁清晰;实验组关节间隙变窄,骨皮质显著变薄,骨密度明显降低,骨小梁重度紊乱;②MRI检测:对照组未见股骨头坏死现象,实验组表现典型的双线征;③骨生化:实验组氨基己糖、钙/羟脯胺酸、氨基己糖/羟脯胺酸、钙含量低于对照组(P < 0.05);④血清生化:实验组钙磷乘积、胆固醇、钙水平低于对照组(P < 0.05),三酰甘油水平高于对照组(P < 0.05);⑤血液流变学:实验组全血高切黏度及低切黏度、血浆黏度比及红细胞压积高于对照组(P < 0.05);⑥组织学观察:实验组骨小梁中大部分骨细胞坏死,未坏死的骨细胞肿胀,细胞核严重变形、边聚,还有细胞核碎化、溶解、空鼓等现象,多核破骨细胞明显增多,造血干细胞明显减少;对照组未见上述现象;⑦结果表明,采用马血清联合大剂量和醋酸泼尼松龙可得到较理想的激素性兔股骨头缺血性坏死动物模型,X射线、MRI检查及骨/血清生化、血流变学评价可作为激素性股骨头缺血性坏死辅助诊断手段。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-2134-7663(佟鹏)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
激素性股骨头缺血性坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变,激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
血液流变学:是一门新兴的生物力学及生物流变学分支,是研究血液宏观流动性质、人和动物体内血液流动和细胞变形以及血液与血管、心脏之间相互作用,血细胞流动性质及生物化学成分的一门科学,近20年来才发展成为一门独立的新兴边缘学科。
文题释义:
激素性股骨头缺血性坏死:股骨头坏死又称股骨头无菌性坏死,或股骨头缺血性坏死,是由于多种原因导致的股骨头局部血运不良,从而引起骨细胞进一步缺血、坏死、骨小梁断裂、股骨头塌陷的一种病变,激素性股骨头坏死就是因为长时间使用激素而引起的一种股骨头坏死。
血液流变学:是一门新兴的生物力学及生物流变学分支,是研究血液宏观流动性质、人和动物体内血液流动和细胞变形以及血液与血管、心脏之间相互作用,血细胞流动性质及生物化学成分的一门科学,近20年来才发展成为一门独立的新兴边缘学科。