| [1] 刘宝林.口腔种植学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:36.[2] 张士剑,包晓亮,蔺增,等.不同种植方式修复下颌后部游离缺失的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2011,31(1):12-15.[3] 李翠,郭新程,韦艺.应用三维有限元法对不同骨质牙种植修复体生物力学的研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,21(1):15-18.[4] 丁旭,丁毅,章加宇,等.下颌后牙种植固定桥不同桥体长度和连接体面积时受载的三维有限元分析[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2012,13(3): 142-145.[5] Koka P, Mohapatra A, Anandapandian PA, et al. The effect of implant design on the stress distribution in a three-unit implant- supported distal cantilever fixed partial denture: a three-dimensional finite-element analysis. Indian J Dent Res. 2012;23(2):129-134. [6] 陈庆生,陈笑风,单晔杰,等.松质骨和皮质骨厚度对种植体周围应力分布的影响[J]吉林大学学报(医学版),2016,42(2):204-209.[7] 沈梅洁,王格格,朱形好,等.骨小梁微结构对牙种植体三维有限元分析的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2016,51(9):542-545.[8] 李忠华,廖进民,陈海芳.下领骨的骨学测量及临床意义[J].四川解剖学杂志,2004,12(2):182-184.[9] 皮昕.口腔解剖生理学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.[10] Rieger MR, Adams WK, Kinzel GL. A finite element survey of eleven endosseous implants. J Prosthet Dent. 1990;63(4): 457-465. [11] 徐明志,王燕,刘洪臣.颊舌减径对固定修复后基牙牙周受力影响的三维有限元研究[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(3):249-251.[12] 张士剑.有限元法在种植修复中应用进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2010,3(11):697-694.[13] 马小娟,王超,庞琴.不同牙根形态对下颌第一磨牙即刻种植即刻负重影响的三维有限元分析[J].第三军医大学学报, 2017,39(1):28-33.[14] 牛文芝,袁媛,刘宗响.不同颈部螺纹设计种植体周围牙槽骨应力分布的三维有限元分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2017,33(5):262-265.[15] Toniollo MB, Macedo AP, Rodrigues RSC, et al. Three- dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution on different bony ridges with different lengths of morse taper implants and prosthesis dimensions. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23:1888-1892. [16] Almeida DAF, Pellizzer EP, Verri FR, et al. Influence of tapered and external hexagon connection on bone stress around tilted dental implants: three dimensional finite element method with statistical analysis. J Periodontol. 2014;85:261-269. [17] 王宏远,孙蕊,曹庆堂.冠高度连接角度基台种植体周围骨质应力分布的有限元分析[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2017,18(3):133-138.[18] Chang PK, Chen YC, Huang CC, et al. Distribution of micromotion in implants and alveolar bone with different thread profiles in immediate loading: a finite element study. Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27:96-101.[19] 雍苓,黄仕禄,刘洪,等.不同骨缺损类型牙种植体的三维有限元分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2016,31(2):148-153.[20] 李英,鲍萍萍,孙雯.下颌第一磨牙种植冠减径后的三维有限元分析[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2015,29(4):205-208.[21] Wang C, Li Q, McClean C, et al. Numerical simulation of dental bone remodeling induced by mplant‐supported fixed partial denture with or without cantilever extension. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2013;29(10):1134-1147. [22] Cheng YC, Lin DH, Jiang CP, et al. Application of uniform design to improve dental implant system. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;26 Suppl 1:S533-539. [23] 陆永健,唐震,龚璐璐,等.两种种植体支持式下颌半口固定义齿种植体应力三维有限元分析[J].第二军医大学学报, 2016,37(7):821-826.[24] Álvarez-Arenal Á, Segura-Mori L, Gonzalez-Gonzalez I, et al. Stress distribution in the transitional peri-implant bone in a single implant-supported prosthesis with platform-switching under different angulated loads. Odontology. 2017;105(1):68-75. [25] 赵宝红,张娇,蔺增,等.种植体长度与直径对骨界面应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2014,34(1):22-27.[26] Bahat O. Treatment planning and placement of implants in the posterior maxillae: report of 732 consecutive Nobelpharma implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1993;8(2):151-161. [27] 邹康元,李树荣,张佩芬.不同冠根比对种植单冠修复体临床效果的影响[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志:电子版,2012,6(4):366-370.[28] Demenko V, Linetskiy I, Nesvit K, et al. Importance of diameter-to-length ratio in selecting dental implants: a methodological finite element study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2014;17(4):443-449. [29] 金晓华,张剑.下颌后牙软组织水平种植体边缘骨吸收的影响因素分析[J].现代实用医学,2017,29(10):1352-1353.[30] Michailidis N, Karabinas G, Tsouknidas A, et al. A FEM based endosteal implant simulation to determine the effect of periimplant bone resorption on stress induced implant failure. Biomed Mater Eng. 2013;23(5):317-327. [31] 刘惠莉,张娴.后牙区种植义齿边缘骨吸收的相关因素分析[J].医药论坛杂志,2016,37(11):60-61.[32] 石倚天,姒蜜思.后牙区骨组织水平种植体与软组织水平种植体早期边缘骨吸收临床研究[J].浙江中西医结合杂志, 2014,24(9):765-767, 772.[33] Pjetursson BE, Thoma D, Jung R, et al. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of implant-supported fixed dental prostheses(FDPs) after a mean observation period of at least 5 yearsClin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(6):22-38.[34] 董凯,柳忠豪.种植体周围骨吸收影响因素的研究进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2011,16(3):192-196.[35] Esposito M, Lekholm U, Peter T, et al. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. Eur J Oral Sei. 1998;106(3):721-764. [36] Glantz PO, Rangert B, Svensson A, et al. On clinical loading of osseointegrated implants. A methodological and clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1993;4:99-105. [37] Nissan J, Ghelfan O, Gross M, et al. Analysis of load transfer and stress distribution by splinted and unsplinted implant-supported fixed cemented restorations. J Oral Rehabil. 2010;37:658-662. [38] 李振.末端游离缺失种植义齿修复的研究现状[J].口腔材料器械, 2009,18(3):153-155.[39] Toniollo MB, Macedo AP, Pupim D, et al. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Surface Stress Distribution on Regular and Short Morse Taper Implants Generated by Splinted and Nonsplinted Prostheses in the Rehabilitation of Various Bony Ridges. J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(3):e276-280. [40] Guichet DL, Yoshinobu D, Caputo AA. Effect of splinting and interproximal contact tightness on load transfer by implant restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2002;87(5):528-535. [41] Wang TM, Leu LJ, Wang JS, et al. Effects of prosthesis materials and prosthesis splinting on peri-implant bone stress around implants in poor-quality bone: a numeric analysis. Int J Oral Maxill Implants. 2002;17(2):231-237. [42] Iplikçio?lu H, Akça K. Comparative evaluation of the effect of diameter, length and number of implants supporting three-unit fixed partial prostheses on stress distribution in the bone. J Dent. 2002;30(1):41-46. [43] Akça K, Iplikçio?lu H. Evaluation of the effect of the residual bone angulation on implant-supported fixed prosthesis in mandibular posterior edentulism. Part II: 3-D finite element stress analysis. Implant Dent. 2001;10(4):238-245. |
.jpg)
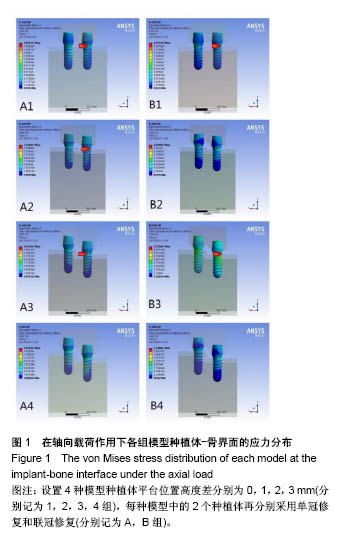
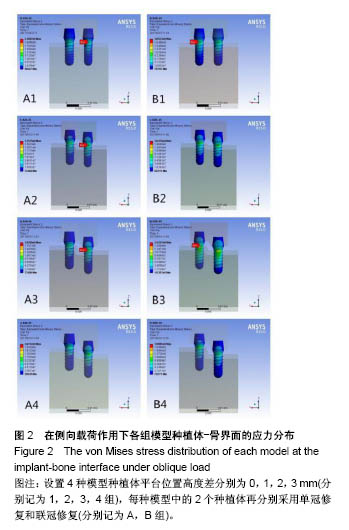
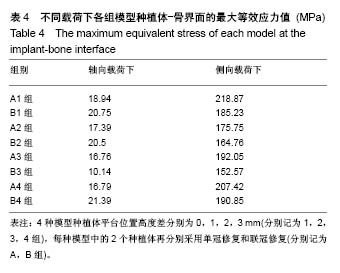
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)