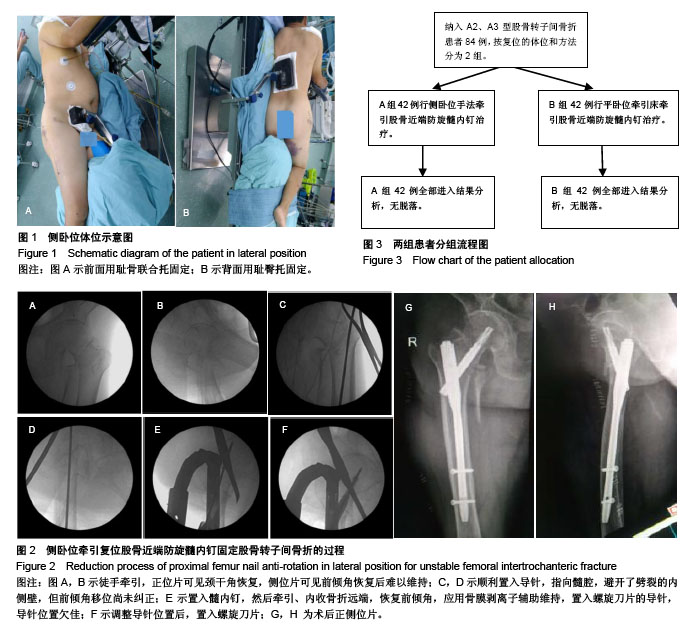
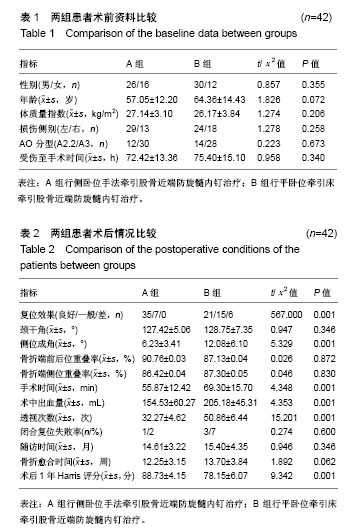
| [1] Sambandam SN, Chandrasekharan J, Mounasamy V, et al. Intertrochanteric fractures: a review of fixation methods. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016;26(4):1-15.[2] 纪泉, 薛庆云, 文良元,等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的安全性和疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2010, 25(4):302-304.[3] Kumar S, Chadha GN. Dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric fractures without using traction table. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 2016;82(2):346-350.[4] Gooi SG, Khoo EH, Benny E, et al. Dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of femur : a comparison of outcome with and without using traction table. Malays Orthop J. 2011; 1: 2126.[5] Haidukewych GJ. Intertrochanteric fractures: ten tips to improve results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(3):503-509.[6] Diaz VJ, Canizares AC, Martín IA, et al. Predictive variables of open reduction in intertrochanteric fracture nailing: a report of 210 cases. Injury. 2016;47 Suppl 3:S51.[7] 殷婷,王珺琛. 有限切开辅助复位治疗难复性股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2016, 10(10):1409-1413.[8] 佟大可,丁文彬,王光超,等. 难复性股骨转子间骨折的临床分型与治疗[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(2):109-114.[9] 张剑锋,杨伟臻,李文琴,等. 侧卧位手法牵引复位技术在股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗不稳定型股骨转子间骨折中的应用[J]. 中国医学创新, 2017,14(4):64-68.[10] Fogagnolo F,Kfuri M Jr,Paccola CA.Intramedullary fixation of pertrochanteric hip fractures with the short AO-ASIF proximal femoral nail. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124(1):31-37.[11] 曾昭玦,陈永雄. 防旋型股骨近端髓内钉内固定治疗不稳定型股骨转子间骨折78例[J]. 广东医学院学报,2012,30(5):519-520.[12] 冯传汉,张汉良. 临床骨科学[M]. 2版. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2004:1064.[13] Yam M, Chawla A, Kwek E. Rewriting the tip apex distance for the proximal femoral nail anti-rotation.Injury.2017:1843-1847.[14] Frisch NB, Nahm NJ, Khalil JG, et al. Short versus long cephalomedullary nails for pertrochanteric hip fracture. Orthopedics. 2017;40(2):83-88.[15] Schmutz B, Kmiec JS, Wullschleger ME, et al. 3D Computer graphical anatomy study of the femur: a basis for a new nail design. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(3):1-11.[16] Socci AR, Casemyr NE, Leslie MP, et al. Implant options for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip: rationale, evidence, and recommendations. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(1): 128.[17] Sun D, Park BS, Jang GI, et al. The fixation method according to the fracture type of the greater trochanter in unstable intertrochanteric fractures undergoing arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(1):62-67.[18] Tan WL, Low SL, Shen L, et al. Osteoporotic hip fractures: 10-year review in a Singaporean hospital. J Orthop Surg. 2015; 23(2):150.[19] Chehade MJ, Carbone T, Awward D, et al. The influence of fracture stability on early patient mortality and reoperation after pertrochanteric and intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(12):538-543.[20] 李悦芃,田京. 不稳定性股骨转子间骨折的手术治疗进展[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2011,14(2):210-213.[21] Cummings SR, Melton III JR. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet. 2002;359(9319):1761-1767. [22] Chun YS, Oh H, Cho YJ, et al. Technique and early results of percutaneous reduction of sagittally unstable intertrochateric fractures. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(3):217-224.[23] 殷婷,王珺琛.有限切开辅助复位治疗难复性股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2016, 10(10):1409-1413.[24] 佟大可, 丁文彬, 王光超,等. 难复性股骨转子间骨折的临床分型与治疗[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2017, 19(2):109-114.[25] 赵鹏飞,宋祥义,薛建华,等.不同体位下股骨重建钉治疗肥胖患者股骨转子间骨折的疗效评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(2): 119-124.[26] Said GZ, Farouk O, Said HG. An irreducible variant of intertrochanteric fractures: a technique for open reduction. Injury. 2005;36(7):871-874.[27] 张树, 张继源, 杨杜明, 等. 矢状位不稳定转子间骨折的形态特征和复位技术[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2017, 49(2): 236-241.[28] Cho JW, Kim HJ, Kim J, et al. Provisional pin fixation can maintain reduction in A3 intertrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(7):945-955.[29] Kim Y, Dheep K, Lee J, et al. Hook leverage technique for reduction of intertrochanteric fracture. Injury. 2014;45(6): 1006-1010.[30] Cho WT, Cho JW, Yoon YC, et al. Provisional pin fixation: An efficient alternative to manual maintenance of reduction in nailing of intertrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(1):55-63.[31] Gadegone WM, Shivashankar B, Lokhande V, et al. Augmentation of proximal femoral nail in unstable trochanteric fractures. Sicot J. 2017;3:12.[32] Kulkarni SG, Babhulkar SS, Kulkarni SM, et al. Augmentation of intramedullary nailing in unstable intertrochanteric fractures using cerclage wire and lag screws: a comparative study. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 2:S18.[33] 张晟,杨俊,胡岩君,等. 髓内钉治疗复杂不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的经验总结[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015, 17(11) :958-961.[34] 郭元利,胡宝山,芮钢,等. 侧卧位置入PFN内固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的可行性研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(12): 1108-1109.[35] 黄晋,杨松杰,罗勤瑜,等. 侧卧位与平卧位下股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗肥胖患者股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014,16(4):364-366.[36] Stephen DJ, Kreder HJ, Schemitsch EH, et al. Femoral intramedullary nailing: comparison of fracture-table and manual traction. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(9):1514-1521.[37] Sahin E, Songur M, Kalem M,et al.Traction table versus manual traction in the intramedullary nailing of unstable intertrochanteric fractures: A prospective randomized trial. Injury. 2016;47(7):1547-1554.[38] 孙秀钦. 侧卧位与平卧位下股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的临床效果分析[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2015,7(27): 150-151.[39] 杨明,张晓萌,张培训,等. 经皮导入导针结合纯侧位透视简化股骨近端防旋髓内钉操作[J]. 北京大学学报:医学版,2015,47(2): 258-262.[40] 周家钤,李兵,李海丰,等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的复位技巧[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(4):299-303.[41] Turgut A, Kalenderer O, Gunayd?n B, et al. Fixation of intertrochanteric femur fractures using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) in the lateral decubitus position without a traction table. Acta Orthopaedica Et Traumatologica Turcica. 2014; 48(5):513.[42] 付尧. 股骨干骨折牵引床辅助闭合复位与切开复位髓内钉固定的临床分析[D].苏州大学,2013.[43] 罗勤瑜,胡奕山,陈春雷,等. 两种体位行PFNA治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的对比研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2012, 20(8):681-684. |
.jpg)
.jpg)