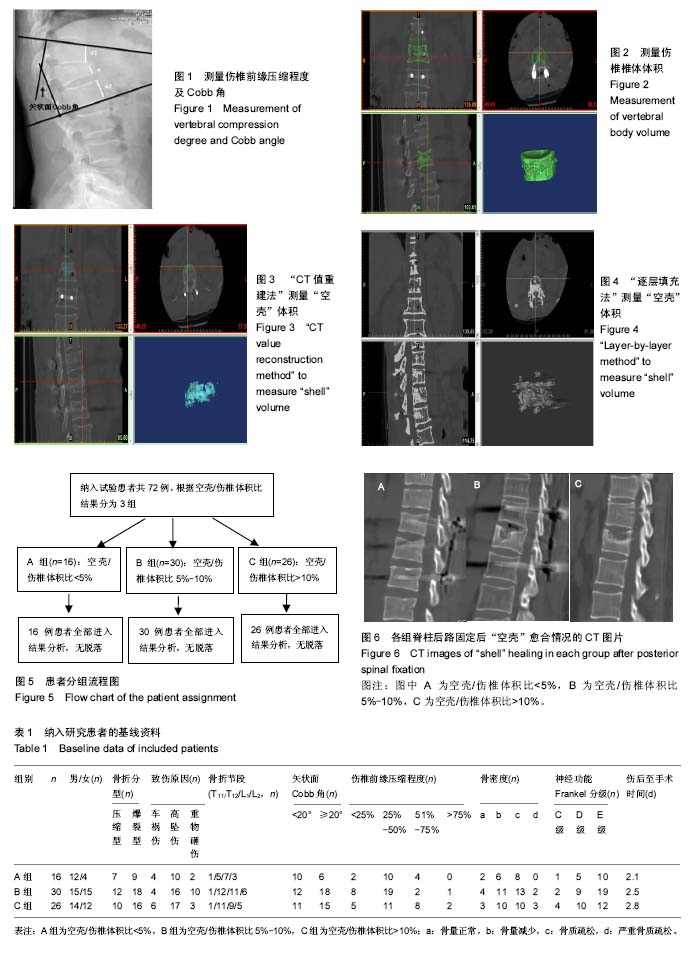
| [1] 王小刚,杨彬,王亚寒,等.附加伤椎钉治疗单节段胸腰椎骨折的疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(10):942-945.[2] 赵杰,田海军.胸腰椎骨折诊治中存在的争议问题[J].中华创伤杂志,2017, 33(7):581-584.[3] 印飞,孙振中,殷渠东,等.短节段椎弓根钉固定联合重组人BMP-2和同种异体骨植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2017,9: 1080-1085.[4] 叶晶华,王剑锋,顾豪杰,等.对不同年龄段胸腰椎骨折复位后“空壳”现象的处理[J].吉林医学, 2016,37(4):808-810.[5] 胡海刚,谭伦,林旭,等.胸腰椎骨折复位术后椎体“空壳现象”的相关因素分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(3):242-247.[6] 胡海刚,林旭,谭伦,等.胸腰椎骨折后路复位术后椎体“空壳”现象的影像学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017, 31(8): 976-981.[7] 印飞,张绍东,吴小涛,等.短节段椎弓根螺钉复位固定伤椎内植骨治疗Denis B型胸腰椎骨折的影像学观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013,23(4): 341-346.[8] 敖俊,辛志军,陈方,等.两种植骨法对胸腰椎爆裂骨折复位后骨缺损空隙残存率及压缩刚度的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013(8):974-979.[9] Chirat R, Moulton DE, Goriely A. Mechanical basis of morphogenesis and convergent evolution of spiny seashells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(15):6015-6020.[10] Denis F. Spinal instability as defined by the three-column spine concept in acute spinal trauma. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1984;189(189):65.[11] Ditunno JF, Young W, Donovan WH, et al. The international standards booklet for neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord.1994;32(2): 70-80.[12] 谭伦,吴超,罗晓中,等.以椎板边缘对腰椎椎弓根螺钉进钉点的个体化定位[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(3):207-210. [13] 杜桂迎,余卫,林强,等.WHO双能 X 线吸收仪骨质疏松症诊断标准及其相关问题[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(3): 330-338. [14] Wewers ME, Lowe NK. A critical review of visual analogue scales in the measurement of clinical phenomena. Public Health Nurs.1990; 13(4):227-236.[15] 钱冰,郝定均,郑永宏,等.两种术式治疗不稳定型Kümmell病的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2017,2:185-190.[16] Phillips FM, Ho E, Campbellhupp M, et al. Early radiographic and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine.2003; 28(19):2265-2267.[17] 刘建泉,于远洋,孔祥录,等.经椎弓根椎体内植骨治疗胸腰椎骨折的影像学观察[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2014,1:45-48.[18] 姜猛.胸腰椎骨折去除内固定后“蛋壳样椎体”与椎体矫正度丢失关系的有限元分析[D].河北医科大学, 2014.[19] Hulme PA, Boyd SK, Ferguson SJ, et al. Regional variation in vertebral bone morphology and its contribution to vertebral fracture strength. Bone.2007; 41(6):946-957.[20] 刘团江,郝定均,王晓东,等.胸腰段骨折椎弓根钉复位固定术后骨缺损的CT研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(10):35-37.[21] 王鹏,王静成,冯新民,等.胸腰椎骨折术后伤椎上终板骨缺损的生物力学有限元分析[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2017, 27(7):72-79.[22] 张君哲,朱康.经椎弓根椎体内植骨对胸腰椎骨折复位术后防止矫正度丢失的作用研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2017,16(6):575-577.[23] 叶森,郝杰,胡侦明,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折伴后凸畸形的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017(11),1462-1467. [24] 阮文枫,冯帆,赵星,等.经伤椎椎弓根椎体内植骨与后外侧植骨在治疗胸腰段骨折疗效的系统评价[J].中华实验外科杂志,2016, 33(11):2589-2592.[25] 林玉江,杨利民,杨健.经皮穿刺加压植入骨棒骨粉椎体成形治疗胸腰椎体压缩性骨折:恢复伤椎结构完整性和稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(23):3670-3675.[26] Aono H, Tobimatsu H, Ariga K, et al. Surgical outcomes of temporary short-segment instrumentation without augmentation for thoracolumbar burst fractures. Injury. 2016;47(6):1337-1344.[27] Kao FC, Hsieh MK, Yu CW, et al. Additional vertebral augmentation with posterior instrumentation for unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures. Injury.2017 ;48(8):1806-1812[28] Katsumi K, Hirano T, Watanabe K, et al. Surgical treatment for osteoporotic thoracolumbar vertebral collapse using vertebroplasty with posterior spinal fusion: a prospective multicenter study. Int Orthop.2016;40(11):1-7. [29] 王振昊,彭磊,刘建莉,等.自体骨联合同种异体骨与同种异体骨在治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折中的疗效差异[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016, 24(14):1278-1282.[30] 刘达,罗杨,郑伟,等.相邻节段骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定联合伤椎植骨置钉治疗重度骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2016, 26(7): 662-664. |
.jpg)
.jpg)