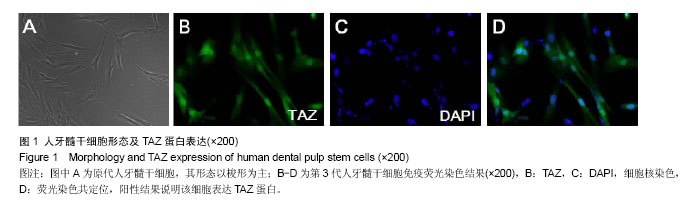
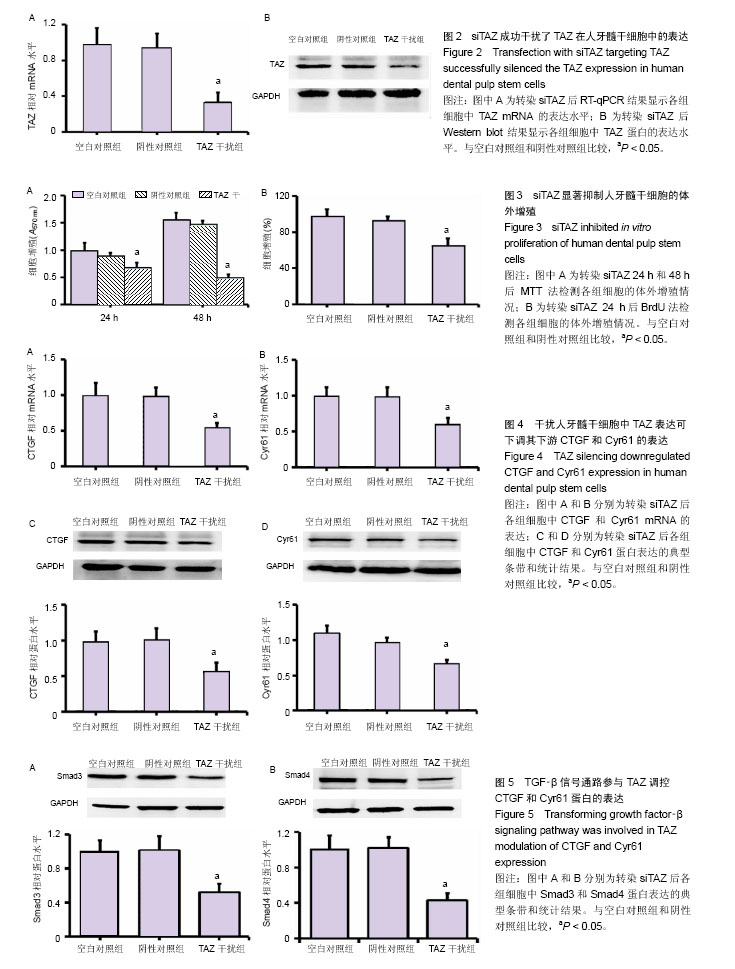
| [1] Downing TL, Soto J, Morez C, et al. Biophysical regulation of epigenetic state and cell reprogramming. Nat Mater. 2013; 12(12):1154-1162.[2] Karaöz E, Demircan PC, Sa?lam O, et al. Human dental pulp stem cells demonstrate better neural and epithelial stem cell properties than bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Histochem Cell Biol. 2011;136(4):455-473. [3] Liu P, Cai J, Dong D, et al. Effects of SOX2 on Proliferation, Migration and Adhesion of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0141346. [4] Liu L, Wu L, Wei X, et al. Induced overexpression of Oct4A in human dental pulp cells enhances pluripotency and multilineage differentiation capability. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(8):962-972. [5] Jayaraman P, Govindasamy V, Gnanasegaran N, et al. Expression patterns of immune genes in long-term cultured dental stem cells. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(1):109-116.[6] Han SM, Han SH, Coh YR, et al. Enhanced proliferation and differentiation of Oct4- and Sox2-overexpressing human adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Mol Med. 2014;46:e101. [7] Liu L, Wei X, Ling J, et al. Expression pattern of Oct-4, Sox2, and c-Myc in the primary culture of human dental pulp derived cells. J Endod. 2011;37(4):466-472. [8] Jeong H, Bae S, An SY, et al. TAZ as a novel enhancer of MyoD-mediated myogenic differentiation. FASEB J. 2010; 24(9):3310-3320.[9] Luo Z, Li D, Kohli MR, et al. Effect of Biodentine™ on the proliferation, migration and adhesion of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent. 2014;42(4):490-497.[10] Tate MC, García AJ, Keselowsky BG, et al. Specific beta1 integrins mediate adhesion, migration, and differentiation of neural progenitors derived from the embryonic striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004;27(1):22-31.[11] Kanai F, Marignani PA, Sarbassova D, et al. TAZ: a novel transcriptional co-activator regulated by interactions with 14-3-3 and PDZ domain proteins. EMBO J. 2000;19(24): 6778-6791.[12] Tian S, Tian X, Liu Y, et al. Effects of TAZ on human dental pulp stem cell proliferation and migration. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(6):4326-4332.[13] Pan D.The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev Cell. 2010;19(4):491-505.[14] Hong JH, Yaffe MB. TAZ: a beta-catenin-like molecule that regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(2):176-179.[15] Hong JH, Hwang ES, McManus MT, et al. TAZ, a transcriptional modulator of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Science. 20052;309(5737):1074-1078.[16] Murakami M, Nakagawa M, Olson EN, et al. A WW domain protein TAZ is a critical coactivator for TBX5, a transcription factor implicated in Holt-Oram syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(50):18034-18039. [17] Park KS, Whitsett JA, Di Palma T, et al. TAZ interacts with TTF-1 and regulates expression of surfactant protein-C. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(17):17384-17390.[18] Suh JS, Kim KS, Lee JY, et al. A cell-permeable fusion protein for the mineralization of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2012;91(1):90-96. [19] Iohara K, Zheng L, Wake H, et al. A novel stem cell source for vasculogenesis in ischemia: subfraction of side population cells from dental pulp. Stem Cells. 2008;26(9):2408-2418. [20] Nakamura S, Yamada Y, Katagiri W, et al. Stem cell proliferation pathways comparison between human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp stem cells by gene expression profile from promising dental pulp. J Endod. 2009;35(11):1536-1542. [21] La Noce M, Paino F, Spina A, et al. Dental pulp stem cells: state of the art and suggestions for a true translation of research into therapy. J Dent. 2014;42(7):761-768.[22] Liu J, Yu F, Sun Y, et al. Concise reviews: Characteristics and potential applications of human dental tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2015;33(3):627-638.[23] Tirino V, Paino F, d'Aquino R, et al. Methods for the identification, characterization and banking of human DPSCs: current strategies and perspectives. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(3): 608-615. [24] Conde MC, Nedel F, Campos VF, et al. Odontoblast RNA stability in different temperature-based protocols for tooth storage. Int Endod J. 2012;45(3):266-272.[25] Hong W, Guan KL.The YAP and TAZ transcription co-activators: key downstream effectors of the mammalian Hippo pathway. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012;23(7):785-793.[26] Wang K, Degerny C, Xu M, et al. YAP, TAZ, and Yorkie: a conserved family of signal-responsive transcriptional coregulators in animal development and human disease. Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;87(1):77-91.[27] Zeng Q, Hong W. The emerging role of the hippo pathway in cell contact inhibition, organ size control, and cancer development in mammals. Cancer Cell. 2008;13(3):188-192. [28] Lei QY, Zhang H, Zhao B, et al. TAZ promotes cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is inhibited by the hippo pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(7): 2426-2436. [29] Chan SW, Lim CJ, Guo K, et al. A role for TAZ in migration, invasion, and tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68(8):2592-2598.[30] Wang Q, Xu Z, An Q, et al. TAZ promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition via the upregulation of connective tissue growth factor expression in neuroblastoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(2):982-988.[31] Dhar A, Ray A.The CCN family proteins in carcinogenesis. Exp Oncol. 2010;32(1):2-9. [32] Leivonen SK, Kähäri VM. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in cancer invasion and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(10):2119-2124.[33] Kim KM, Choi YJ, Hwang JH, et al. Shear stress induced by an interstitial level of slow flow increases the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through TAZ activation. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92427.[34] Xie JJ, Xu LY, Wu JY, et al. Involvement of CYR61 and CTGF in the fascin-mediated proliferation and invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas cells. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(2):939-951.[35] Labbé E, Lock L, Letamendia A, et al. Transcriptional cooperation between the transforming growth factor-beta and Wnt pathways in mammary and intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2007;67(1):75-84. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)