| [1] Fi re A , Xu S, Montgomery MK, et al .Potent and specific genetic interference by doublest randed RNA in Caenorhabdit is elegans. Nature. 1998;391(6669):806.[2] Tuschl T, Borkhardt A. Small interfering RNAs: a revolutionary tool for the analysis of gene function and gene therapy. Mol Interv. 2002;1:58.[3] Stahmann N, Woods A, Spengler K, et al . Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by vascular endothelial growth factor mediates endothelial angiogenesis independently of nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(14):10638-10652.[4] Lefloch R, Pouyssegur J, Lenormand P. Single and combined silencing of ERK1 and ERK2 reveals their positive contribution to growth signaling depending on their expression levels. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(1):511-527.[5] Lemgo GN, Sabbadini S, Pandolfini T, et al .Biosafety considerations of RNAi-mediated virus resistance in fruit-tree cultivars and in rootstock. Transgenic Res. 2013;22(6): 1073-1088.[6] Leboulle G, Niggebrügge C, Roessler R, et al. Characterisation of the RNA interference response against the long-wavelength receptor of the honeybee. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;43(10):959-969.[7] National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center. Spinal cord injury.Facts and figures at a glance. J Spinal Cord Med. 2005;28:379-380.[8] Liu P, Yao Y, Liu MY, et al. Spinal Trauma in Mainland China from 2001 to 2007: An Pidemiological Study Based on a Nationwide Database. Spine. 2011;12:28.[9] Shamim MS, Ali SF, Enam SA. Non-operative management is superior to surgical stabilization in spine injury patients with complete neurological deficits: A perspective study from a developing world country, Pakistan. Surg Neurol Int. 2011;2:166.[10] Hannon GJ. RNA interference.Nature, 2002,418(6894): 244-251.[11] MacRae IJ, Ma E, Zhou M, et al. In vitro reconstitution of the human RISC-loading complex.Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:512.[12] Schwarz DS, Hutvagner G, Du T, et al. Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex.Cell. 2003;115:199.[13] Rand TA, Petersen S, Du FH, et al. Argonaute2 cleaves the anti-guide strand of siRNA during RISC activation.Cell. 2005;123:621.[14] Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, et al.Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391(6669):806-811.[15] Tabara H, Grishok A, Mello CC. RNAi in C. elegans: Soaking in the Genome Sequence. Science. 1998;282(16): 430-431.[16] Suarez E, Syed F, Alonso-Rasgado T, et al.Up-Regulation of Tension-Related Proteins in Keloids: Knockdown of Hsp27, α2β1-Integrin, and PAI-2 Shows Convincing Reduction of Extracellular Matrix Production. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013 ; 131(2):158e-173e.[17] Carreras Puigvert J, von Stechow L, Siddappa R, et al. Systems biology approach identifies the kinase csnk1a1 as a regulator of the DNA damage response in embryonic stem cells. Sci Signal. 2013; 6(259):225-234.[18] Attia RR, Sharma P, Janssen RC, et al. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta). J Biol Chem. 2011;286(27):23799-23807.[19] Bühler M, Spies N, Bartel DP, et al. TRAMP-mediated RNA surveillance prevents spurious entry of RNAs into the Schizosaccharomyces pombe siRNA pathway. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008;15(10):1015-1023.[20] Matzke M ,Matzke AJ ,Kooter JM .RNA:guiding gene silencing.Science. 2001;293(5532):1080-1083.[21] Sijen T, Fleenor J , Simmer F, et al.On the role of RNA amplification in dsRNA-triggered gene silencing.Cell. 2001;107(4):465-476.[22] Petri S, Meister G. siRNA design principles and off-target effects. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;986:59-71.[23] Izquierdo M.Short interfering RNAs as a tool for cancer gene therapy .Cancer Gene Therapy. 2005;12(3):217-222.[24] Brennecke J, Aravin AA, Stark A,et al. Discrete small RNA generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell. 2007;128(6): 1089-1103.[25] Sakurai K, Amarzguioui M,Kim DH, et al. A role for human Dicer in pre RISC loading of siRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;39(4):1510-1525.[26] Girardi E, Chane-Woon-Ming B, Messmer M. Identification of RNase L-dependent, 3'-end-modified, viral small RNAs in Sindbis virus-infected mammalian cells. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014;5(2):141-181.[27] Ui-Tei K, Naito Y, Saigo K. Guidelines for the selection of effective short-interfering RNA sequences for functional genomics. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;361:201-216.[28] Jagla B, Aulner N, Kelly PD, et al. Sequence characteristics of functional siRNAs. RNA. 2005;11(6):864-872.[29] Shabalina SA, Spiridonov AN, Ogurtsov AY.Computational models with thermodynamic and composition features improve siRNA design. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006;12(7):65.[30] Reynolds A, Leake D, Boese Q, et al. Rational siRNA design for RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22(3):326-330.[31] Forbes DC, Peppas NA. Oral delivery of small RNA and DNA. J Control Release. 2012;3:234-253.[32] Dalby B, Cates S, Harris A, et al. Advanced transfection with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent: primary neurons, siRNA, and high-throughput applications. Methods. 2004;33:95-103.[33] Palliser D, Chowdhury D, Wang QY, et al. An siRNAbased microbicide protects mice from lethal herpes simplex virus 2 infection.Nature. 2006; 439:89-94. [34] Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BRG, et al. How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227-264.[35] Shah S, Jain PK, Kala A, et al. Light-activated RNA interference using double-stranded siRNA precursors modified using a remarkable regiospecificity of diazo-based photolabile groups.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(13):4508-4517.[36] Di Giovanni S, De Biase A, Yakovlev A, et al. In vivo and in vitro characterization of novel neuronal plasticity factors identified following spinal cord injury. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(3):2084-2091.[37] Toyooka T, Nawashiro H, Shinomiya N, et al. Down-regulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin by RNA interference improves acute urinary dysfunction associated with spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28(4):607-618.[38] Zhou H, Li X, Wu Q. shRNA against PTEN promotes neurite outgrowth of cortical neurons and functional recovery in spinal cord contusion rats. Regen Med. 2014;15:1-19.[39] Irie N, Sakai N, Ueyama T, et al .Subtype- and species-specific knockdown of PKC using short interfering RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;298(5):738-743.[40] Dorn G, Patel S, Wotherspoon G, et al. siRNA relieves chronic neuropathic pain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:e49.[41] Toyooka T, Nawashiro H, Shinomiya N, et al .Down-regulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin by RNA interference improves acute urinary dysfunction associated with spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28: 607-618.[42] Edalat H, Hajebrahimi Z, Pirhajati V, et al. Transplanting P75-Suppressed Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Promotes Functional Behavior in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Iran Biomed J. 2013;17(3):140-145. [43] Goel A. Stem cell therapy in spinal cord injury: Hollow promise or promising science? J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2016;7: 121-126. [44] Gazdic M, Volarevic V, Arsenijevic A, et al. Stem Cells and Labeling for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:6. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
RNA干扰:真核生物中普遍存在的一种自然现象,是由双链RNA诱导同源靶基因的mRNA 发生特异性降解,从而导致基因沉默的过程,由于这种现象发生在转录后水平,故又称之为转录后基因沉默。
RNA诱导沉默复合体:是由siRNA与Argonaute蛋白和Dicer酶复合形成的复合物。在RNA干扰中,利用siRNA的反义链切割靶mRNA,达到基因沉默的效果。
文题释义:
RNA干扰:真核生物中普遍存在的一种自然现象,是由双链RNA诱导同源靶基因的mRNA 发生特异性降解,从而导致基因沉默的过程,由于这种现象发生在转录后水平,故又称之为转录后基因沉默。
RNA诱导沉默复合体:是由siRNA与Argonaute蛋白和Dicer酶复合形成的复合物。在RNA干扰中,利用siRNA的反义链切割靶mRNA,达到基因沉默的效果。.jpg) 文题释义:
RNA干扰:真核生物中普遍存在的一种自然现象,是由双链RNA诱导同源靶基因的mRNA 发生特异性降解,从而导致基因沉默的过程,由于这种现象发生在转录后水平,故又称之为转录后基因沉默。
RNA诱导沉默复合体:是由siRNA与Argonaute蛋白和Dicer酶复合形成的复合物。在RNA干扰中,利用siRNA的反义链切割靶mRNA,达到基因沉默的效果。
文题释义:
RNA干扰:真核生物中普遍存在的一种自然现象,是由双链RNA诱导同源靶基因的mRNA 发生特异性降解,从而导致基因沉默的过程,由于这种现象发生在转录后水平,故又称之为转录后基因沉默。
RNA诱导沉默复合体:是由siRNA与Argonaute蛋白和Dicer酶复合形成的复合物。在RNA干扰中,利用siRNA的反义链切割靶mRNA,达到基因沉默的效果。
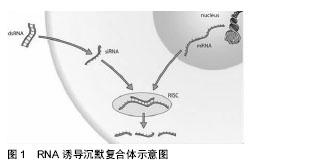
.jpg) 文题释义:
RNA干扰:真核生物中普遍存在的一种自然现象,是由双链RNA诱导同源靶基因的mRNA 发生特异性降解,从而导致基因沉默的过程,由于这种现象发生在转录后水平,故又称之为转录后基因沉默。
RNA诱导沉默复合体:是由siRNA与Argonaute蛋白和Dicer酶复合形成的复合物。在RNA干扰中,利用siRNA的反义链切割靶mRNA,达到基因沉默的效果。
文题释义:
RNA干扰:真核生物中普遍存在的一种自然现象,是由双链RNA诱导同源靶基因的mRNA 发生特异性降解,从而导致基因沉默的过程,由于这种现象发生在转录后水平,故又称之为转录后基因沉默。
RNA诱导沉默复合体:是由siRNA与Argonaute蛋白和Dicer酶复合形成的复合物。在RNA干扰中,利用siRNA的反义链切割靶mRNA,达到基因沉默的效果。