| [1] Gorman AM,Healy SJ,Jäger R,et al.Stress managementat theER:regulators of ER stress-inducedapoptosis.Pharmacol Ther.2012;134(3):306-316.[2] Paschen W,Frandsen A. Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction acommon denominator for cell injury in acute and degenerativediseases of the brain.J Neurochem.2001;79(4) : 719-725.[3] Schroder M,Kaufman RJ. ER stress and the unfolded proteinresponse. Mutat Res.2005;569(1-2):29-63.[4] Zhang HY,Wang ZG,Lu XH,et al.Endoplasmic reticulumstress: relevance and therapeutics in central nervous systemdiseases.Mol Neurobiol.2015;51(3) : 1343-1352.[5] Breckenridge DG,Germain M,Mathai JP,et al.Regulation ofapoptosis by endoplasmic reticulum pathways. Oncogene.2003;22(53):8608-8618.[6] Volmer R,van der Ploeg K,Ron D.Membrane lipid saturation activates endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein responsetransducers through their transmembrane domains. Proc Natl AcadSci USA.2013;110(12) : 4628-4633.[7] Hetz C,Chevet E,Harding HP.Targeting the unfolded proteinresponse in disease.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2013;12(9):703-719.[8] Szegezdi E,Logue S,Gorman A,et al.Mediators of endoplasmicreticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep.2006;7 (9) :880-885.[9] Shen J,Chen X,Hendershot L,et al. ER stress regulation ofATF6 localization by dissociation of BiP /GRP78 binding andunmasking of Golgi localization signals.Dev Cell.2002;3(1):99-111.[10] Bertolotti A,Zhang Y,Hendershot LM,et al. Dynamicinteraction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfoldedproteinresponse. Nat Cell Biol.2000;2: 326-332.[11] 滕旭,齐永芬,唐朝枢.内质网应激与心脏疾病[J].生理科学进展,2009, 40(2):106-110.[12] Fu HY,Okada K,Liao Y,et al.Ablation of C/EBP homologousproteinatteuates ER-mediatedapoptosis and cardiacdysfunction induced by pressureoverload. Circulation. 2010;122(4):361-369.[13] Yoneda T,Imaizumi K,Oono K,et al. Activation of Caspase-12,an endoplastic reticulum (ER) resident caspase,throughtumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2-dependentmechanism in response to the ER stress. J Biol Chem.2001;276(17):13935-13940.[14] Tabas I,Ron D.Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis inducedby endoplasmic reticulum stress.Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(3):184-190.[15] 张凯强,张颖,顾何锋,等. 内质网应激与细胞凋亡研究进展[J]. 口腔医学,2013,33(6):415-417.[16] 张红菊, 赵忠新.大鼠脑缺血后内质网伴侣蛋白GRP78 和GRP94及胱冬酶12表达的改变[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志,2006, 3(4):164-166.[17] 刘洪亮,崔玉山. Caspase-12在内质网应激中的激活途径及与疾病关系研究进展[J]. 环境卫生学杂志,2011,1(4):42-43.[18] 杨琼,吴永全.内质网应激与心血管疾病[J]. 心脏杂志, 2015, 27(1):99-101.[19] 周婷,刘铁夫.内质网应激与肝脏疾病[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2012,12(30):5982-5984.[20] Taniguchi N, Carames B, Ronfani L, et al. Aging-related loss ofthe chromatin protein HMGB2 in articular cartilage is linked toreduced cellularity and osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2009;106(4):1181-1186.[21] Johnson EO, Charchandi A, Babis GC, et al. Apoptosis inosteoarthritis: morphology, mechanisms, and potential meansfor therapeutic intervention. J Surg Orthop Adv.2008;17(3):147-152.[22] Kawaguchi H. Mechanism of molecular backgrounds of osteoarthritis.Nihon Rinsho.2014;72(10):1729-1733.[23] Saito S, Murakoshi K, Kotake S, et al. Granzyme B inducesapoptosis of chondrocytes with natural killer cell-like cytotoxicityin rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol.2008;35(10): 1932-1943.[24] Becker SJ, Teunis T, Blauth J, et al. Medical services and associated costs vary widely among surgeons treating patients with hand osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(3):1111-1117.[25] Palmieri B, Lodi D, Capone S. Osteoarthritis and degenerativejoint disease: local treatment options update. Acta Biomed.2010;81(2):94-100.[26] Ryu JH, Shin Y, Huh YH, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpharegulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosisduringosteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(3):440-450.[27] Yang L, Carlson SG, McBurney D, et al. Multiple signalsinduce endoplasmic reticulum stress in both primary andimmortalized chondrocytes resulting in loss of differentiation,impaired cell growth, and apoptosis. J Biol Chem.2005;280(35): 31156-31165.[28] Oliver BL, Cronin CG, Zhang-Benoit Y, et al. Divergent stressresponses to IL-1beta, nitric oxide, and tunicamycin bychondrocytes. J Cell Physiol. 2005;204(1): 45-50.[29] Nugent AE, Speicher DM, Gradisar I, et al. Advancedosteoarthritis in humans is associated with altered collagen VIexpression and upregulation of ER-stress markers Grp78 andbag-1. J Histochem Cytochem. 2009; 57(10):923-931.[30] Yamabe S, Hirose J, Uehara Y, et al. Intracellular accumulationof advanced glycation end products induces apoptosis viaendoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrocytes. FEBS J.2013;280(7):1617-1629.[31] Palmieri B, Lodi D, Capone S. Osteoarthritis and degenerativejoint disease: local treatment options update. Acta Biomed.2010;81(2):94-100.[32] Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmicreticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2007;8(7): 519-529.[33] Tsang KY, Chan D, Cheslett D, et al. Surviving endoplasmicreticulum stress is coupled to altered chondrocyte differentiation and function. PLoS Biol. 2007; 5(3): e44.[34] van Meurs JB, Uitterlinden AG. Osteoarthritis year 2012 inreview: genetics and genomics. OsteoarthritisCartilage. 2012;20(12):1470-1476.[35] Thomas CM, Fuller CJ, Whittles CE, et al.Chondrocyte deathby apoptosis is associated with the initiation andseverity ofarticular cartilage degradation. Int J Rheum Dis.2011;14(2):191-198.[36] Li H, Zhang XY, Wu TJ, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stressregulates rat mandibular cartilage thinning undercompressivemechanical stress. J Biol Chem.2013; 288(25): 18172-18183.[37] Rasheed Z, Haqqi TM. Endoplasmic reticulum stress inducesthe expression of COX-2 through activation of eIF2alpha,p38-MAPK and NF-kappaB in advanced glycation endproducts stimulated human chondrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1823(12): 2179-2189.[38] Takada K, Hirose J, Senba K, et al. Enhanced apoptotic andreduced protective response in chondrocytes followingendoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritic cartilage.Int JExp Pathol.2011;92(4): 232-242.[39] 李载权,周爱儒,唐朝枢.内质网应激反应分子机理研究进展[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2004, 20(3): 283-288.[40] Feng J, Li S, Chen H. Tanshinone IIA ameliorates apoptosis of cardiomyocytes induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, NJ).2016, 241(18): 2042-2048.[41] Guo R, Wu Z, Jiang J,et al. New mechanism of lipotoxicity in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Deficiency of Endogenous H2S Production and ER stress. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017;162: 46-52.[42] Li B, Tian J, Sun Y,et al. Activation of NADPH oxidase mediates increased endoplasmic reticulum stress and left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in rabbits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852(5):805-815.[43] Lin Y,Zhang X,Wang L,et al.Polyamine depletion attenuates isoproterenol-induced hypertrophy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(5):1455-1465.[44] Lin Y, Zhang X, Xiao W,et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress is Involved in DFMO Attenuating Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016; 38(4):1553-1562.[45] Liu X, Kwak D, Lu Z,et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) protects against pressure overload-induced heart failure and lung remodeling. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex : 1979).2014;64(4): 738-744.[46] Meng C, Yuan CH, Zhang CC,et al. Ophiopogonin D protects cardiomyocytes against doxorubicin-induced injury through suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014;49(8):1117-123.[47] Sreedhar R, Giridharan VV, Arumugam S,et al. Role of MAPK-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in the heart during aging in senescence-accelerated prone mice. BioFactors (Oxford, England).2016;42(4): 368-375.[48] Tse G, Yan BP, Chan YW,et al. Reactive Oxygen Species, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction: The Link with Cardiac Arrhythmogenesis. Front Physiol. 2016;7:313.[49] Xu Z, Zhao Y, Zhong P,et al. EGFR inhibition attenuates diabetic nephropathy through decreasing ROS and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncotarget.2017;8(20): 32655-32667.[50] Zhang B, He P, Lu Y,et al. HSF1 Relieves Amyloid-beta-Induced Cardiomyocytes Apoptosis. Cell biochem biophys. 2015;72(2): 579-587.[51] Zhang GG, Cai HQ, Li YH,et al. Ghrelin protects heart against ERS-induced injury and apoptosis by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Peptides.2013;48:156-165.[52] Zhang Q, Lu L, Liang T,et al. MAPK pathway regulated the cardiomyocyte apoptosis in mice with post-infarction heart failure . Bratislavske lekarske listy, 2017;118(6): 339-346.[53] Zhang Z,Zhao L,Zhou Y,et al.Taurine ameliorated homocysteine-induced H9C2 cardiomyocyte apoptosis by modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Apoptosis. 2017; 22(5):647-661.[54] Ahn C,An BS,Jeung EB.Streptozotocin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis via disruption of calcium homeostasis in mouse pancreas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015; 412:302-308.[55] Ali BR.Is cystic fibrosis-related diabetes an apoptotic consequence of ER stress in pancreatic cells?. Med Hypotheses. 2009; 72(1):55-57.[56] Carrera Boada CA, Martinez-Moreno JM. Pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus type 2: beyond the duo "insulin resistance-secretion deficit" .Nutricion hospitalaria.2013; 28 Suppl 2:78-87.[57] Clemens DL, Schneider KJ, Arkfeld CK,et al. Alcoholic pancreatitis: New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2016; 7(1): 48-58.[58] Martinez-Useros J, Georgiev-Hristov T, Borrero-Palacios A,et al. Identification of Poor-outcome Biliopancreatic Carcinoma Patients With Two-marker Signature Based on ATF6alpha and p-p38 "STARD Compliant". Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(45):e1972.[59] Zhao L, Guo H, Chen H,et al. Effect of Liraglutide on endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 ;441(1):133-138. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
内质网:内质网是真核细胞重要的细胞器,它是由封闭膜系统以及互相沟通的膜腔而形成的网状结构。内质网膜是与细胞膜结构类似的单位膜,并且常与细胞核的外膜连在一起。内质网按其表面有无核糖体分为光面内质网和糙面内质网两类。
内质网应激:内质网内环境的稳定是实现内质网功能的基本条件,因此内质网具有极强的内稳态体系。但仍然有很多因素可导致内质网功能的内稳态失衡,形成内质网应激。例如缺血再灌注损伤、氧化应激、同型半胱氨酸等化学物质处理、细胞内蛋白质合成过快以至于超过蛋白折叠能力、内质网钙代谢紊乱、卵磷脂合成障碍等多种物理、化学或遗传因素等均可引发内质网应激。
文题释义:
内质网:内质网是真核细胞重要的细胞器,它是由封闭膜系统以及互相沟通的膜腔而形成的网状结构。内质网膜是与细胞膜结构类似的单位膜,并且常与细胞核的外膜连在一起。内质网按其表面有无核糖体分为光面内质网和糙面内质网两类。
内质网应激:内质网内环境的稳定是实现内质网功能的基本条件,因此内质网具有极强的内稳态体系。但仍然有很多因素可导致内质网功能的内稳态失衡,形成内质网应激。例如缺血再灌注损伤、氧化应激、同型半胱氨酸等化学物质处理、细胞内蛋白质合成过快以至于超过蛋白折叠能力、内质网钙代谢紊乱、卵磷脂合成障碍等多种物理、化学或遗传因素等均可引发内质网应激。.jpg) 文题释义:
内质网:内质网是真核细胞重要的细胞器,它是由封闭膜系统以及互相沟通的膜腔而形成的网状结构。内质网膜是与细胞膜结构类似的单位膜,并且常与细胞核的外膜连在一起。内质网按其表面有无核糖体分为光面内质网和糙面内质网两类。
内质网应激:内质网内环境的稳定是实现内质网功能的基本条件,因此内质网具有极强的内稳态体系。但仍然有很多因素可导致内质网功能的内稳态失衡,形成内质网应激。例如缺血再灌注损伤、氧化应激、同型半胱氨酸等化学物质处理、细胞内蛋白质合成过快以至于超过蛋白折叠能力、内质网钙代谢紊乱、卵磷脂合成障碍等多种物理、化学或遗传因素等均可引发内质网应激。
文题释义:
内质网:内质网是真核细胞重要的细胞器,它是由封闭膜系统以及互相沟通的膜腔而形成的网状结构。内质网膜是与细胞膜结构类似的单位膜,并且常与细胞核的外膜连在一起。内质网按其表面有无核糖体分为光面内质网和糙面内质网两类。
内质网应激:内质网内环境的稳定是实现内质网功能的基本条件,因此内质网具有极强的内稳态体系。但仍然有很多因素可导致内质网功能的内稳态失衡,形成内质网应激。例如缺血再灌注损伤、氧化应激、同型半胱氨酸等化学物质处理、细胞内蛋白质合成过快以至于超过蛋白折叠能力、内质网钙代谢紊乱、卵磷脂合成障碍等多种物理、化学或遗传因素等均可引发内质网应激。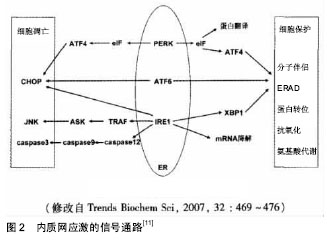

.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
内质网:内质网是真核细胞重要的细胞器,它是由封闭膜系统以及互相沟通的膜腔而形成的网状结构。内质网膜是与细胞膜结构类似的单位膜,并且常与细胞核的外膜连在一起。内质网按其表面有无核糖体分为光面内质网和糙面内质网两类。
内质网应激:内质网内环境的稳定是实现内质网功能的基本条件,因此内质网具有极强的内稳态体系。但仍然有很多因素可导致内质网功能的内稳态失衡,形成内质网应激。例如缺血再灌注损伤、氧化应激、同型半胱氨酸等化学物质处理、细胞内蛋白质合成过快以至于超过蛋白折叠能力、内质网钙代谢紊乱、卵磷脂合成障碍等多种物理、化学或遗传因素等均可引发内质网应激。
文题释义:
内质网:内质网是真核细胞重要的细胞器,它是由封闭膜系统以及互相沟通的膜腔而形成的网状结构。内质网膜是与细胞膜结构类似的单位膜,并且常与细胞核的外膜连在一起。内质网按其表面有无核糖体分为光面内质网和糙面内质网两类。
内质网应激:内质网内环境的稳定是实现内质网功能的基本条件,因此内质网具有极强的内稳态体系。但仍然有很多因素可导致内质网功能的内稳态失衡,形成内质网应激。例如缺血再灌注损伤、氧化应激、同型半胱氨酸等化学物质处理、细胞内蛋白质合成过快以至于超过蛋白折叠能力、内质网钙代谢紊乱、卵磷脂合成障碍等多种物理、化学或遗传因素等均可引发内质网应激。