| [1] Geng CK,Cao HH,Ying X,et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells transplantation combining with hyperbaric oxygen therapy on rehabilitation of rat spinal cord injury. Asian Pac J Trop Med.2015; 8(6):468-473.[2] Haapanen H,Herajärvi J,Arvola O,et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning protects the spinal cord against ischemic insult: An experimental study in a porcine model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151(3): 777-785.[3] Kieffer E,Chiche L,Cormier E, et al.Recurrent spinal cord ischemia after endovascular stent grafting for chronic traumatic aneurysm of the aortic isthmus.J Vasc Surg.2007; 45(4): 831-833.[4] Svensson LG, Von Ritter CM, Groeneveld HT, et al. Cross-clamping of the thoracic aorta: influence of aortic shunts, laminectomy, papaverine, calcium channel blocker, allopurinol, and superoxide dismutase on spinal cord blood flow and paraplegia in baboons. Ann Surg.1986; 204(1): 38-47.[5] Lang-Lazdunski L, Matsushita K, Hirt L, et al. Spinal cord ischemia. Development of a model in the mouse. Stroke. 2000; 31: 208-213.[6] Smith PD, Puskas F, Meng X, et al. The evolution of chemokine release supports a bimodal mechanism of spinal cord ischemia and reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2012; 126(11 Suppl 1): S110-S117.[7] Allen AR. Surgery of experimental lesion of spinal cord equivalent to crush injury of fracture dislocation of spinal column: preliminary report. JAMA. 1911; 57: 878 -880.[8] Panthee N,Ono M. Spinal cord injury following thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic repairs. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2015; 23(2): 235-246.[9] Katsargyris A,Oikonomou K,Kouvelos G,et al.Spinal cord ischemia after endovascular repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms with fenestrated and branched stent grafts. J Vasc Surg. 2015;62(6):1450-1456.[10] Kato M,Motoki M, Isaji T, et al.Spinal cord injury after endovascular treatment for thoracoabdominal aneurysm or dissection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2015; 48(4): 571-577.[11] Etz DC, Luehr M, Aspern KV, et al. Spinal cord ischemia in open and endovascular thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair: new concepts. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2014; 55 (2 Suppl 1): 159-168. [12] Hetz C, Russelakis-Carneiro M, Walchli S, et al. The disulfide isomerase Grp58 is a protective factor against prion neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 2005; 25(11): 2793- 2802.[13] Garbi N, Tanaka S, Momburg F, et al. Impaired assembly of the major histocompatibility complex class I peptide-loading complex in mice deficient in the oxidoreductase ERp57. Nat Immunol. 2006; 7(1): 93-102. [14] Bennett CF,Balcarek JM,Varrichio A,et al. Molecular cloning and complete amino-acid sequence of form-I phosphoinositide specific phospholipase C.Nature. 1988; 334(6179): 268-270.[15] Matsushita T,Lankford KL, Arroyo EJ, et al. Diffuse and persistent blood-spinal cord barrier disruption after contusive spinal cord injury rapidly recovers following intravenous infusion of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Neurol. 2015; 267: 152-164.[16] Yang MC,Zhang HZ,Wang Z,et al.The molecular mechanism and effect of cannabinoid-2 receptor agonist on the lood-spinal cord barrier permeability induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Res.2016; 1636: 81-92.[17] Zhang C,Ma J,Fan L, Zou Y, et al.Neuroprotective effects of safranal in a rat model of traumatic injury to the spinal cord by anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory and edema-attenuating. Tissue Cell.2015; 47(3): 291-300. [18] Matsushita Y, Shima K, Nawashiro H, et al. Real-time monitoring of glutamate following fluid percussion brain injury with hypoxia in the rat. J Neurotrauma. 2000; 17(2): 143-153.[19] Segal JL, Gonzales E, Yousefi S, et al. Circulating levels of IL-2R, ICAM-1, and IL-6 in spinal cord injuries. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1997; 78(1): 44 -47.[20] Salzman SK, Acosta R, Beck G, et al. Spinal endothelin content is elevated after moderate local trauma in the rat to levels associated with locomotor dysfunction after intrathecal injection. J Neurotrauma.1996;13(2): 93-101.[21] Zhang S, Wu D, Wang J, et al. Stress protein expression in early phase spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(24): 2225-2235.[22] Gao Q, Liang Y, Yang X, et al. Differential protein expression in spinal cord tissue of a rabbit model of spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2012; 7(20): 1534-1539.[23] Wang J, Pearse DD, et al. Therapeutic hypothermia in spinal cord injury: the status of its use and open questions. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(8):16848-16879.[24] Zhilai Z, Biling M, Sujun Q, et al. Preconditioning in lowered oxygen enhances the therapeutic potential of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2016; 1642: 426-435.[25] Zivin JA, DeGirolami U. Spinal cord infarction: a highly reproducible stroke model. Stroke.1980;11(2): 200-202.[26] Li GL, Farooque M,Olsson Y,et al. Changes of Fas and Fas ligand immunoreactivity after compression trauma to rat spinal cord. Acta Neuropathol Berl. 2000; 100(1): 75-81.[27] Ekshyyan O, Aw TY. Apoptosis in acute and chronic neurological disorders. Front Biosci. 2004; 1(9): 1567-1576.[28] Pahl HL. Signal transduction from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell nucleus. Physiol Rev. 1999; 79(3): 683-701.[29] Szegezdi E,Logue SE,Gorman AM,et al. Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2006;7(9): 880-885.[30] Lee AS. The glucose-regulated proteins: stress induction and clinical applications. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001; 26(8): 504-510.[31] Yamauchi T, Sakurai M, Abe K, et al. Impact of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in spinal cord after transient ischemia. Brain Res. 2007; 1169: 24-33. [32] Rao RV, Bredesen DE. Misfolded proteins, endoplasmic reticulum stress and neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004; 16(6): 653-662. [33] Yu ZF, Mattson MP. Dietary restriction and 2-deoxyglucose administration reduce focal ischemic brain damage and improve behavioral outcome: evidence for a preconditioning mechanism. J Neurosci Res.1999; 57(6): 830-839. [34] Hoozemans JJ, Veerhuis R, Van Haastert ES, et al. The unfolded protein response is activated in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2005;110(2):165-172. [35] Yamauchi T, Sakurai M, Abe K, et al. Ubiquitin-mediated stress response in the spinal cord after transient ischemia. Stroke. 2008; 39(6): 1883-1889. [36] Hetz CA, Soto C. Stressing out the ER: a role of the unfolded protein response in prion-related disorders. Curr Mol Med. 2006; 6(1): 37-43. [37] Pendyala G, Ninemire C, Fox HS. Protective Role for the Disulfide Isomerase PDIA3 in methamphetamine neurotoxicity. PLoS One. 2012; 7(6): e38909. [38] Takata H, Kudo M, Yamamoto T, et al. Increased expression of PDIA3 and its association with cancer cell proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2016; 12(6): 4896-4904.[39] He Y, Shao F, Pi W, et al. Largescale Transcriptomics Analysis Suggests Over-Expression of BGH3, MMP9 and PDIA3 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS One. 2016; 11(1): e0146530.[40] Zhu Y, Cai L, Guo J, et al. Depletion of Dicer promotes epithelial ovarian cancer progression by elevating PDIA3 expression. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37(10): 14009-14023.[41] Su BB, Zhou SW, Gan CB, et al. MiR-330-5p regulates tyrosinase and PDIA3 expression and suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in cutaneous malignant melanoma. J Surg Res. 2016; 203(2): 434-40.[42] Zhuang Z, Zhang L, Wang X, et al. PDIA3 gene induces visceral hypersensitivity in rats with irritable bowel syndrome through the dendritic cell-mediated activation of T cells. PeerJ. 2016; 17(4): e2644.[43] Yuan G, Hua B, Yang Y, et al. The Circadian Gene Clock Regulates Bone Formation Via PDIA3. J Bone Miner Res. 2017; 32(4): 861-871.[44] Xu S, Sankar S, Neamati N. Protein disulfide isomerase: a promising target for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today. 2014; 19(3): 222-240.[45] Trnková L, Ricci D, Grillo C, et al. Green tea catechins can bind and modify ERp57/PDIA3 activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1830(3): 2671-2682. [46] Hoffstrom BG, Kaplan A, Letso R, et al. Inhibitors of protein disulfide isomerase suppress apoptosis induced by misfolded proteins. Nat Chem Biol. 2010; 6(12): 900-906.[47] Frasconi M, Chichiarelli S, Gaucci E, et al. Interaction of ERp57 with calreticulin: analysis of complex formation and effects of vancomycin. Biophys Chem. 2012; 160(1): 46-53.[48] Khan MM, Simizu S, Lai NS, et al. Discovery of a small molecule PDI inhibitor that inhibits reduction of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. ACS Chem Biol. 2011; 6(3): 245-251.[49] Jasuja R, Passam FH, Kennedy DR, et al. Protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors constitute a new class of antithrombotic agents.J Clin Invest.2012; 122 (6):2104-2113.[50] ?iplys E,?itkus E, Slibinskas R. Native signal peptide of human ERp57 disulfide isomerase mediates secretion of active native recombinant ERp57 protein in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Protein Expr Purif.2013; 89(2): 131-135. |
.jpg)
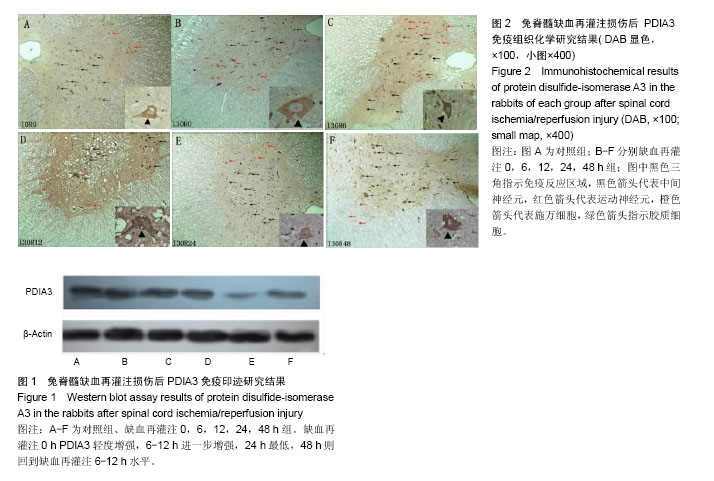
.jpg)