| [1] Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, et al. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: a review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2012;45:487-498.[2] Periyasamy-Thandavan S, Jiang M, Schoenlein P, et al. Autophagy: molecular machinery, regulation, and implications for renal pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009; 297:F244-F256.[3] Reggiori F. Membrane origin for autophagy. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2006;74:1-30.[4] Klionsky DJ, Emr SD. Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 2000;290:1717-1721.[5] Fang Y, Tan J, Zhang Q. Signaling pathways and mechanisms of hypoxia-induced autophagy in the animal cells.Cell Biol Int.2015;39:891-898.[6] Meng XX, Yao M, Zhang XD, et al. ER stress-induced autophagy in melanoma. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015; 42: 811-816.[7] Lin WJ, Kuang HY. Oxidative stress induces autophagy in response to multiple noxious stimuli in retinal ganglion cells. Autophagy. 2014; 10: 1692-1701.[8] Liu J, Bi X, Chen T, et al. Shear stress regulates endothelial cell autophagy via redox regulation and Sirt1 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2015; 6: e1827.[9] Zhu HX, Tannous P, Johnstone JL, et al. Cardiac autophagy is a maladaptive response to hemodynamic stress. JCli Invest. 2007; 117: 1782-1793.[10] Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, et al. The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med. 2007; 13: 619-624.[11] Ma KG, Shao ZW, Yang SH, et al. Autophagy is activated in compression-induced cell degeneration and is mediated by reactive oxygen species in nucleus pulposus cells exposed to compression. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2013; 21: 2030-2038.[12] Rothermel BA, Hill JA. Autophagy in load-induced heart disease. Circ Res. 2008;103:1363-1369.[13] Depre C, Wang Q, Yan L, et al. Activation of the cardiac proteasome during pressure overload promotes ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation. 2006;114:1821-1828.[14] Tannous P, Zhu HX, Nemchenko A, et al. Intracellular Protein Aggregation Is a Proximal Trigger of Cardiomyocyte Autophagy. Circ Res. 2008;117(24):3070-3078.[15] Lin L, Tang CY, Xu JF, et al. Mechanical Stress Triggers Cardiomyocyte Autophagy through Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor-Mediated p38MAP Kinase Independently of Angiotensin II. Plos One. 2014;9(2):e89629.[16] Weng LQ, Zhang WB, Ye Y, et al. Aliskiren ameliorates pressure overload-induced heart hypertrophy and fibrosis in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014;35:1005-1014.[17] Lin L, Liu XB, Xu JF, et al. High-density lipoprotein inhibits mechanical stress-induced cardiomyocyte autophagy and cardiac hypertrophy through angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2015; 19:1929-1938.[18] Fu L, Wei CC, Powell PC, et al. Volume overload induces autophagic degradation of procollagen in cardiac fibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;89:241-250.[19] Hariharan N, Ikeda Y, Hong C, et al. Autophagy Plays an Essential Role in Mediating Regression of Hypertrophy during Unloading of the Heart. Plos One. 2013;8(1):e51632.[20] Cao DJ, Jiang N, Blagg A, et al. Mechanical Unloading Activates FoxO3 to Trigger Bnip3-Dependent Cardiomyocyte Atrophy. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2(2):e000016.[21] Baskin KK, Rodriguez MR, Kansara S, et al. MAFbx/Atrogin-1 is required for atrophic remodeling of the unloaded heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;72:168-176.[22] Kassiotis C, Ballal K, Wellnitz K, et al. Markers of Autophagy Are Downregulated in Failing Human Heart After Mechanical Unloading. Circulation. 2009; 120: S191-S197.[23] Hill JA. Autophagy in cardiac plasticity and disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 2011; 32: 282-289.[24] Hariharan N, Maejima Y, Nakae J, et al. Deacetylation of FoxO by Sirt1 Plays an Essential Role in Mediating Starvation-Induced Autophagy in Cardiac Myocytes. Circ Res. 2010; 107: 1470-1482.[25] Skurk C, Izumiya Y, Maatz H, et al. The FOXO3a transcription factor regulates cardiac myocyte size downstream of AKT signaling. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:20814-20823.[26] Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, et al. Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell.2004;117: 399-412.[27] Mammucari C, Milan G, Romanello V, et al. FoxO3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell Metab. 2007;6: 458-471.[28] Zhang HF, Bosch-Marce M, Shimoda LA, et al. Mitochondrial autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:10892-10903.[29] Porrello ER, D'amore A, Curl CL, et al. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor antagonizes angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated cardiomyocyte autophagy. Hypertension. 2009;53:1032-1040.[30] Yadav A, Vallabu S, Arora S, et al. ANG II promotes autophagy in podocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010; 299: C488-C496.[31] Huang J, Sun W, Huang H, et al. miR-34a modulates angiotensin II-induced myocardial hypertrophy by direct inhibition of ATG9A expression and autophagic activity. PLoS One. 2014; 9(4): e94382.[32] Yue H, Li W, Desnoyer R, et al. Role of nuclear unphosphorylated STAT3 in angiotensin II type 1 receptor- induced cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 2010; 85: 90-99.[33] Ramakrishnan P, Hecht BA, Pedersen DR, et al. Oxidant conditioning protects cartilage from mechanically induced damage. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:914-920.[34] Thomas CM, Fuller CJ, Whittles CE, et al. Chondrocyte death by apoptosis is associated with cartilage matrix degradation. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2007;15:27-34.[35] Carames B, Taniguchi N, Seino D, et al. Mechanical Injury Suppresses Autophagy Regulators and Pharmacologic Activation of Autophagy Results in Chondroprotection. Arthritis Rheumus. 2012;64:1182-192.[36] Xu HG, Yu YF, Zheng Q, et al. Autophagy protects end plate chondrocytes from intermittent cyclic mechanical tension induced calcification. Bone. 2014;66:232-239.[37] Pan S. Molecular mechanisms responsible for the atheroprotective effects of laminar shear stress. Antioxid Redox Sign. 2009;11:1669-1682.[38] Guo FX, Li XH, Peng J, et al. Autophagy Regulates Vascular Endothelial Cell eNOS and ET-1 Expression Induced by Laminar Shear Stress in an Ex Vivo Perfused System. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42:1978-1988.[39] Ding Z, Liu S, Deng X, et al. Hemodynamic shear stress modulates endothelial cell autophagy: Role of LOX-1. Int J Cardiol. 2015;184:86-95.[40] Bharath LP, Mueller R, Li Y, et al. Impairment of autophagy in endothelial cells prevents shear-stress-induced increases in nitric oxide bioavailability. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014; 92: 605-612.[41] Gumucio JP, Davis ME, Bradley JR, et al. Rotator cuff tear reduces muscle fiber specific force production and induces macrophage accumulation and autophagy. J Orthop Res. 2012;30:1963-1970.[42] Ning L, Xu Z, Furuya N, et al. Perlecan inhibits autophagy to maintain muscle homeostasis in mouse soleus muscle. Matrix Biology. 2015;48:26-35.[43] Ulbricht A, Eppler FJ, Tapia VE, et al. Cellular mechanotransduction relies on tension-induced and chaperone-assisted autophagy. Curr Biol. 2013;23:430-435.[44] Ulbricht A, Gehlert S, Leciejewski B, et al. Induction and adaptation of chaperone-assisted selective autophagy CASA in response to resistance exercise in human skeletal muscle. Autophagy. 2015; 11: 538-546.[45] Chen HC, Fong TH, Hsu PW, et al. Multifaceted effects of rapamycin on functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats through autophagy promotion, anti-inflammation, and neuroprotection. J Surg Res. 2013;179: e203-e210.[46] Chen Z, Fu Q, Shen B, et al. Enhanced p62 expression triggers concomitant autophagy and apoptosis in a rat chronic spinal cord compression model. Mol Med Rep. 2014; 9: 2091-2096.[47] Wang ZY, Lin JH, Muharram A, et al. Beclin-1-mediated autophagy protects spinal cord neurons against mechanical injury-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2014; 19: 933-945.[48] Park Y, Liu C, Luo T, et al. Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy after Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2015; 2: 1449-1457.[49] Lien SC, Chang SF, Lee PL, et al. Mechanical regulation of cancer cell apoptosis and autophagy: roles of bone morphogenetic protein receptor, Smad1/5, and p38 MAPK. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1833:3124-3133.[50] Chen H, Chen LY, Cheng BA, et al. Cyclic Mechanical Stretching Induces Autophagic Cell Death in Tenofibroblasts Through Activation of Prostaglandin E2 Production. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 36:24-33.[51] Li D, Yan T, Xu Z, et al. Spironolactone Promotes Autophagy via Inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and Reduce Adhesive Damage in Podocytes under Mechanical Stress. Biosci Rep. 2016.[52] Porter KM, Jeyabalan N, Liton PB. MTOR-independent induction of autophagy in trabecular meshwork cells subjected to biaxial stretch. Bba-Mol Cell Res. 2014; 1843: 1054-1062. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞自噬:自噬是真核细胞中在进化上高度保守的分解代谢现象,用于降解回收细胞内生物大分子和细胞器,如错误折叠的蛋白质、衰老或受损的线粒体等,维持细胞的稳态和存活,被认为是Ⅱ型程序性细胞死亡。自噬可分为3种:大自噬、小自噬以及分子伴侣介导的自噬。
力学因素:力学因素是一种重要的应激刺激,细胞为了维持正常的增殖、分化以及其他生理功能,必须适应不断变化的力学环境,一旦出现适应不良的情况,就会表现出一些病理现象,许多疾病的发生就与其组织细胞对力学因素变化适应不良密切相关。异常的力学因素会导致组织细胞出现适应不良的病理现象,自噬也跟这些病理现象密切相关,在许多病变的组织细胞中都发现了自噬的异常表达,如肥大或者衰竭的心脏、出现退行性病变的关节软骨和椎间盘等。
文题释义:
细胞自噬:自噬是真核细胞中在进化上高度保守的分解代谢现象,用于降解回收细胞内生物大分子和细胞器,如错误折叠的蛋白质、衰老或受损的线粒体等,维持细胞的稳态和存活,被认为是Ⅱ型程序性细胞死亡。自噬可分为3种:大自噬、小自噬以及分子伴侣介导的自噬。
力学因素:力学因素是一种重要的应激刺激,细胞为了维持正常的增殖、分化以及其他生理功能,必须适应不断变化的力学环境,一旦出现适应不良的情况,就会表现出一些病理现象,许多疾病的发生就与其组织细胞对力学因素变化适应不良密切相关。异常的力学因素会导致组织细胞出现适应不良的病理现象,自噬也跟这些病理现象密切相关,在许多病变的组织细胞中都发现了自噬的异常表达,如肥大或者衰竭的心脏、出现退行性病变的关节软骨和椎间盘等。.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞自噬:自噬是真核细胞中在进化上高度保守的分解代谢现象,用于降解回收细胞内生物大分子和细胞器,如错误折叠的蛋白质、衰老或受损的线粒体等,维持细胞的稳态和存活,被认为是Ⅱ型程序性细胞死亡。自噬可分为3种:大自噬、小自噬以及分子伴侣介导的自噬。
力学因素:力学因素是一种重要的应激刺激,细胞为了维持正常的增殖、分化以及其他生理功能,必须适应不断变化的力学环境,一旦出现适应不良的情况,就会表现出一些病理现象,许多疾病的发生就与其组织细胞对力学因素变化适应不良密切相关。异常的力学因素会导致组织细胞出现适应不良的病理现象,自噬也跟这些病理现象密切相关,在许多病变的组织细胞中都发现了自噬的异常表达,如肥大或者衰竭的心脏、出现退行性病变的关节软骨和椎间盘等。
文题释义:
细胞自噬:自噬是真核细胞中在进化上高度保守的分解代谢现象,用于降解回收细胞内生物大分子和细胞器,如错误折叠的蛋白质、衰老或受损的线粒体等,维持细胞的稳态和存活,被认为是Ⅱ型程序性细胞死亡。自噬可分为3种:大自噬、小自噬以及分子伴侣介导的自噬。
力学因素:力学因素是一种重要的应激刺激,细胞为了维持正常的增殖、分化以及其他生理功能,必须适应不断变化的力学环境,一旦出现适应不良的情况,就会表现出一些病理现象,许多疾病的发生就与其组织细胞对力学因素变化适应不良密切相关。异常的力学因素会导致组织细胞出现适应不良的病理现象,自噬也跟这些病理现象密切相关,在许多病变的组织细胞中都发现了自噬的异常表达,如肥大或者衰竭的心脏、出现退行性病变的关节软骨和椎间盘等。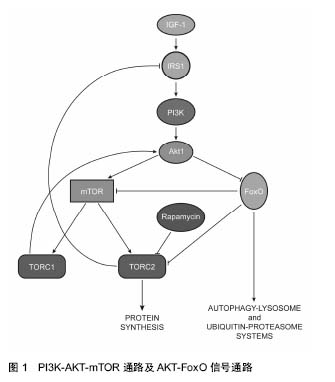
.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞自噬:自噬是真核细胞中在进化上高度保守的分解代谢现象,用于降解回收细胞内生物大分子和细胞器,如错误折叠的蛋白质、衰老或受损的线粒体等,维持细胞的稳态和存活,被认为是Ⅱ型程序性细胞死亡。自噬可分为3种:大自噬、小自噬以及分子伴侣介导的自噬。
力学因素:力学因素是一种重要的应激刺激,细胞为了维持正常的增殖、分化以及其他生理功能,必须适应不断变化的力学环境,一旦出现适应不良的情况,就会表现出一些病理现象,许多疾病的发生就与其组织细胞对力学因素变化适应不良密切相关。异常的力学因素会导致组织细胞出现适应不良的病理现象,自噬也跟这些病理现象密切相关,在许多病变的组织细胞中都发现了自噬的异常表达,如肥大或者衰竭的心脏、出现退行性病变的关节软骨和椎间盘等。
文题释义:
细胞自噬:自噬是真核细胞中在进化上高度保守的分解代谢现象,用于降解回收细胞内生物大分子和细胞器,如错误折叠的蛋白质、衰老或受损的线粒体等,维持细胞的稳态和存活,被认为是Ⅱ型程序性细胞死亡。自噬可分为3种:大自噬、小自噬以及分子伴侣介导的自噬。
力学因素:力学因素是一种重要的应激刺激,细胞为了维持正常的增殖、分化以及其他生理功能,必须适应不断变化的力学环境,一旦出现适应不良的情况,就会表现出一些病理现象,许多疾病的发生就与其组织细胞对力学因素变化适应不良密切相关。异常的力学因素会导致组织细胞出现适应不良的病理现象,自噬也跟这些病理现象密切相关,在许多病变的组织细胞中都发现了自噬的异常表达,如肥大或者衰竭的心脏、出现退行性病变的关节软骨和椎间盘等。