| [1] Golob AL, Laya MB. Osteoporosis: screening, prevention, and management. Med Clin North Am. 2015;99(3): 587-606.[2] Reginster JY, Ferrari S, Hadji P. Current challenges in the treatment of osteoporosis: an opportunity for bazedoxifene. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014; 30(6): 1165-1176.[3] Raisz LG. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12): 3318-3325.[4] Sigurdsson G, Halldorsson BV, Styrkarsdottir U, et al. Impact of genetics on low bone mass in adults. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(10): 1584-1590.[5] Ralston SH, Uitterlinden AG. Genetics of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2010;31(5): 629-662.[6] Bjørnerem Å, Bui M, Wang X, et al. Genetic and environmental variances of bone microarchitecture and bone remodeling markers: a twin study. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(3): 519-527.[7] Hunter DJ, de Lange M, Andrew T, et al. Genetic variation in bone mineral density and calcaneal ultrasound: a study of the influence of menopause using female twins. Osteoporos Int. 2001;12(5): 406-411.[8] Zheng HF, Tobias JH, Duncan E, et al. WNT16 influences bone mineral density, cortical bone thickness, bone strength, and osteoporotic fracture risk. PLoS Genet. 2012; 8(7): e1002745.[9] He W, Liu M, Huang X, et al. The influence of vitamin D receptor genetic variants on bone mineral density and osteoporosis in Chinese postmenopausal women. Dis Markers. 2015; 2015: 760313.[10] Lin CC, Li TC, Liu CS, et al. Associations of TNF-alpha and IL-6 polymorphisms with osteoporosis through joint effects and interactions with LEPR gene in Taiwan: Taichung Community Health Study for Elders (TCHS-E). Mol Biol Rep. 2016; 43(10): 1179-1191.[11] Li Y, Zhou J, Wu Y, et al. Association of osteoporosis with genetic variants of circadian genes in Chinese geriatrics. Osteoporos Int. 2016; 27(4):1485-1492.[12] Thomas T, Gori F, Spelsberg TC, et al. Response of bipotential human marrow stromal cells to insulin-like growth factors: effect on binding protein production, proliferation, and commitment to osteoblasts and adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1999;140(11):5036-5044.[13] Zhang W, Shen X, Wan C, et al. Effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation: differential signalling via Akt and ERK. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012;30(4):297-302.[14] 徐萍,张克勤,刘超, 等. 重组人胰岛素样生长因子I对大鼠成骨细胞增殖、凋亡及I型胶原蛋白合成的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2006,12(1): 17-21.[15] 刘冰,卢蕾阳,高飞,等. 胰岛素样生长因子-1对甲状旁腺激素介导成骨细胞增殖及成骨活性的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014, 20(11): 1298-1301.[16] Klammt J, Kiess W, Pfaffle R. IGF1R mutations as cause of SGA. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab.2011;25(1):191-206.[17] 杜桂迎,余卫,林强,等. WHO双能X线吸收仪骨质疏松症诊断标准及其相关问题[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2016, 9(3): 330-338.[18] MacDonald K, Porter GA, Guernsey DL, et al. A polymorphic variant of the insulin-like growth factor type I receptor gene modifies risk of obesity for esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009;33(1): 37-40.[19] Wang O, Hu Y, Gong S, et al. A survey of outcomes and management of patients post fragility fractures in China. Osteoporos Int. 2015; 26(11): 2631-2640.[20] 王金华,石红卫. 绝经后女性骨标志物与骨质疏松症的相关性研究[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2015,30(17): 2732-2733.[21] Lee DO, Jee BC, Ku SY, et al. Relationships between the insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptor gene G3174A polymorphism, serum IGF-I levels, and bone mineral density in postmenopausal Korean women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26(1): 42-46.[22] Bonafè M, Barbieri M, Marchegiani F, et al. Polymorphic variants of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptor and phosphoinositide 3-kinase genes affect IGF-I plasma levels and human longevity: cues for an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of life span control. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(7): 3299-3304.[23] Albani D, Batelli S, Polito L, et al. A polymorphic variant of the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor correlates with male longevity in the Italian population: a genetic study and evaluation of circulating IGF-1 from the "Treviso Longeva (TRELONG)" study. BMC Geriatr. 2009; 9: 19.[24] Cheng J, Liu J, Li X, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor polymorphism and ischemic stroke: a case-control study in Chinese population. Acta Neurol Scand. 2008;118(5): 333-338.[25] Gately K, Forde L, Gray S, et al. Mutational analysis of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase domain in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Mol Clin Oncol. 2015;3(5): 1073-1079.[26] Kalow W, Tang BK, Endrenyi L. Hypothesis: comparisons of inter- and intra-individual variations can substitute for twin studies in drug research. Pharmacogenetics. 1998;8(4): 283-289.[27] Zhou PR, Xu XJ, Zhang ZL, et al. SOST polymorphisms and response to alendronate treatment in postmenopausal Chinese women with osteoporosis. Pharmacogenomics. 2015; 16(10): 1077-1088.[28] 高雷, 高华增, 任艳. 绝经后骨质疏松症相关骨代谢指标、细胞因子IGF-1的临床观察[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2014,18(6): 919-921.[29] Chen L, Zou X, Zhang RX, et al. IGF1 potentiates BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells through the enhancement of BMP/Smad signaling. BMB Rep. 2016;49(2): 122-127.[30] Feng X, Huang D, Lu X, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 can promote proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via mTOR pathway. Dev Growth Differ. 2014;56(9): 615-624.[31] Lau KH, Baylink DJ, Zhou XD, et al. Osteocyte-derived insulin-like growth factor I is essential for determining bone mechanosensitivity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 305(2): E271-281.[32] Sheng MH, Lau KH, Baylink DJ. Role of Osteocyte-derived Insulin-Like Growth Factor I in Developmental Growth, Modeling, Remodeling, and Regeneration of the Bone. J Bone Metab. 2014;21(1): 41-54.[33] Di Bona D, Accardi G, Virruso C, et al. Association between genetic variations in the insulin/insulin-like growth factor (Igf-1) signaling pathway and longevity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014;12(5): 674-681.[34] Stanilova SA1, Ivanova MG, Karakolev IA, et al. Association of +3179G/A insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor polymorphism and insulin-like growth factor-1 serum level with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2013;22(13): 1388-1393.[35] Liu TC, Hsieh MJ, Liu MC, et al. The Clinical Significance of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Polymorphism in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(5). pii: E763. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050763.[36] Stanilov NS, Karakolev IA, Deliysky TS, et al. Association of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor polymorphism with colorectal cancer development. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(12): 8099-8106.[37] Cartegni L, Chew SL, Krainer AR. Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: exonic mutations that affect splicing. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3(4):285-298.[38] Pagani F, Baralle FE. Genomic variants in exons and introns: identifying the splicing spoilers. Nat Rev Genet. 2004; 5(5): 389-396.[39] Duan J, Wainwright MS, Comeron JM, et al. Synonymous mutations in the human dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) affect mRNA stability and synthesis of the receptor. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12(3): 205-216. |
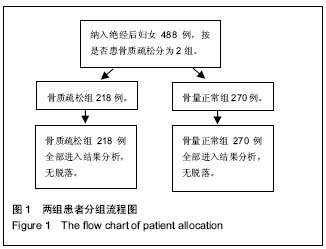
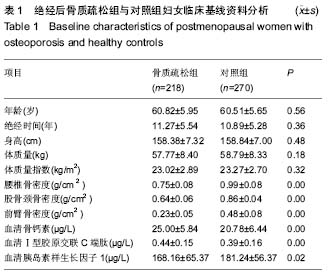
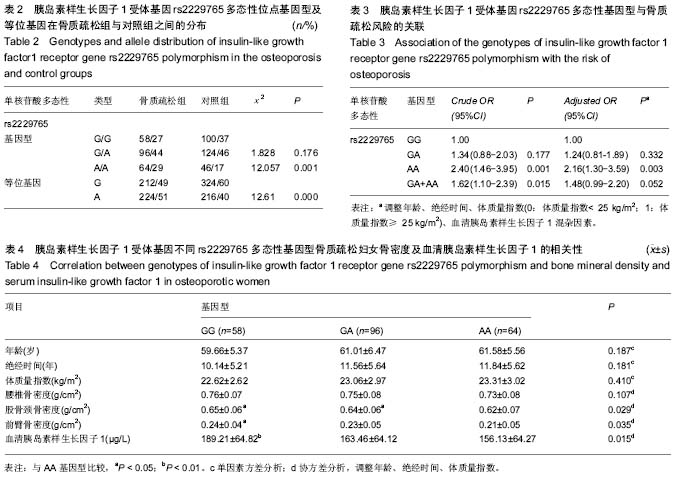
.jpg)
.jpg)