中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (1): 154-158.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.01.027
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
脂肪干细胞成脂分化的分子机制和信号通路
陈犹白1,2,郝永红3,王 岚3,张启旭2,韩 岩1
- 解放军总医院,1整形修复科,3皮肤科,北京市 100853;2美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森肿瘤中心整形外科,美国休斯敦 770303
Molecular mechanism and signaling pathway during adipogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells
Chen You-bai1, 2, Hao Yong-hong3, Wang Lan3, Zhang Qi-xu2, Han Yan1
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 3Department of Dermatology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; 2Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston 770303, Texas, USA
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
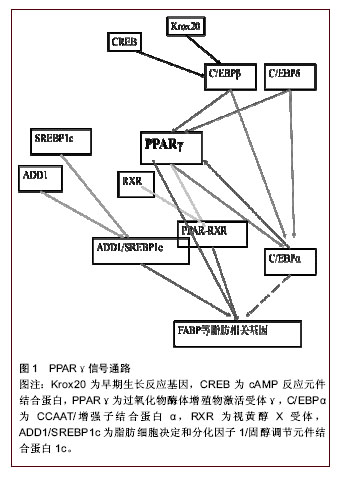
文题释义: 过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, PPARγ):PPAR对脂肪细胞分化和脂质代谢有重要的调节作用,PPAR包括PPARα、PPARβ和PPARγ三种亚型,其中PPARγ在脂肪组织中特异性高表达,是脂肪干细胞成脂分化的关键转录因子。PPARγ有PPARγ1和PPARγ2两个亚型,同一基因由不同启动子起始表达而产生的4种不同的mRNA中,pparγ1、pparγ3、pparγ4编码PPARγ1,pparγ2编码PPARγ2。 Wnt/β-catenin:Wnt是一种脂质修饰的糖蛋白,β-catenin是细胞粘附和迁移必需的钙粘着糖蛋白与肌动蛋白的细胞骨架。Wnt通过激活细胞表面受体,调节β-catenin的表达及细胞定位,影响细胞活动和功能,在细胞的生长发育、增殖、分化、迁移、凋亡和稳态方面起着重要的作用。根据是否有β-catenin的参与,Wnt信号通路可分为经典Wnt和非经典Wnt。
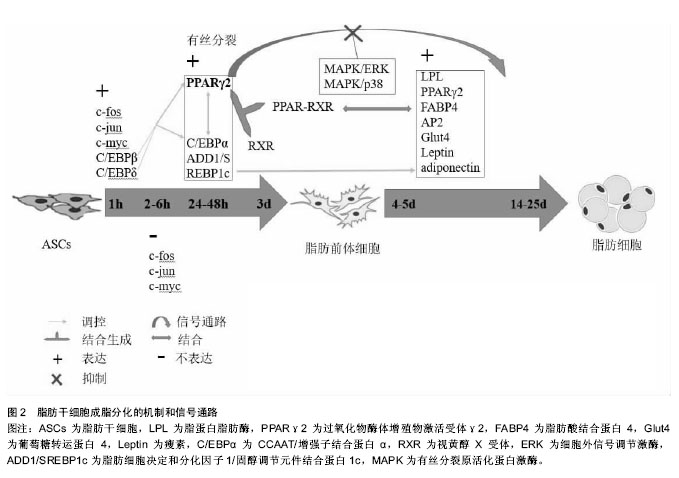
摘要 背景:对脂肪干细胞成脂分化的研究不仅可探索肥胖的过程和机制,还可构建组织工程脂肪,为软组织缺损的重建提供新的思路。 目的:总结脂肪干细胞成脂分化的过程、分子机制和信号通路,讨论miRNA对脂肪干细胞成脂分化的影响及脂肪干细胞成脂和成骨分化的关系。 方法:应用计算机检索PubMed数据库、SinoMed数据库中有关脂肪干细胞分化的文献,检索词为“adipose stem cell,adipose-derived stem cell,adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell,differentiation;脂肪干细胞,分化”,最终选取代表性文献共27篇。 结果与结论:在脂肪干细胞成脂分化过程中,PPARγ/MAPK、PI3K/Akt、Wnt/β-Catenin、cAMP、Notch等信号通路发挥了关键作用,但其相关基因和蛋白、信号通路和分子机制仍不完全清楚。miRNA对脂肪干细胞的成脂分化有重要影响,miR-24、miR-148a、miR-302等可促进脂肪干细胞的成脂分化,miR-22、miR-27等可抑制脂肪干细胞的成脂分化。脂肪干细胞的成骨和成脂分化关系密切,部分生长因子和激素在促进脂肪干细胞成脂分化的同时抑制其成骨分化,部分作用则相反。综合利用各种细胞因子和支架模拟体内微环境,促进脂肪干细胞的增殖和成脂分化,构建组织工程脂肪,是未来的研究方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0001-9081-2296(张启旭)
中图分类号:
.jpg)