| [1] Hughes SP, Freemont AJ, Hukins DW, et al. The pathogenesis of degeneration of the intervertebral disc and emerging therapies in the management of back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(10):1298-1304.
[2] 刘勇君.腺相关病毒介导BMP-7和SOX9双基因共同转染兔退变椎间盘体内试验研究[D].青岛:青岛大学,2013.
[3] Vadalà G, Sowa G, Hubert M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells injection in degenerated intervertebral disc: cell leakage may induce osteophyte formation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(5):348-355.
[4] 周逸驰,李景峰,董视师,等.干细胞治疗椎间盘退变性疾病:现状与展望[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(10): 1635-1639.
[5] Mizuno H, Roy AK, Vacanti CA, et al. Tissue-engineered composites of anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus for intervertebral disc replacement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(12):1290-1297; discussion 1297-1298.
[6] Mercuri JJ, Gill SS, Simionescu DT. Novel tissue-derived biomimetic scaffold for regenerating the human nucleus pulposus. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011; 96(2):422-435.
[7] Frith JE, Cameron AR, Menzies DJ, et al. An injectable hydrogel incorporating mesenchymal precursor cells and pentosan polysulphate for intervertebral disc regeneration. Biomaterials. 2013;34(37):9430-9440.
[8] 孙中仪.NF-kB信号通路与椎间盘退变的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(23):2162-2164.
[9] McBeth J, Jones K. Epidemiology of chronic musculoskeletal pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2007;21(3):403-425.
[10] Dagenais S, Caro J, Haldeman S. A systematic review of low back pain cost of illness studies in the United States and internationally. Spine J. 2008;8(1):8-20.
[11] Roughley P, Hoemann C, DesRosiers E, et al. The potential of chitosan-based gels containing intervertebral disc cells for nucleus pulposus supplementation. Biomaterials. 2006;27(3):388-396.
[12] Sakai D. Future perspectives of cell-based therapy for intervertebral disc disease. Eur Spine J. 2008;17 Suppl 4:452-458.
[13] 赵献峰,刘浩,丰干均,等.脊索细胞促进髓核软骨样细胞增殖及表型维持[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(8): 939-943.
[14] 王磊,吴小涛,史志英,等.转化生长因子β1和胰岛素样生长因子1对体外培养人退变髓核细胞生物学活性的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(3):218-221.
[15] 王锋,郑陈静美,吴小涛.人退变椎间盘髓核细胞体外平面培养的形态学及活性观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013, 21(13):1346-1351.
[16] 王会仁,袁凤来,段平国,等.酶预消化组织块贴壁法培养人退变椎间盘髓核细胞[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(11): 1032-1036.
[17] 王祺,何君仁,牛建鹏,等.正常与退变髓核细胞Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和番红染色的研究[J].中国医疗前沿,2012,7(1):4-5.
[18] Nerlich AG, Bachmeier BE, Schleicher E, et al. Immunomorphological analysis of RAGE receptor expression and NF-kappaB activation in tissue samples from normal and degenerated intervertebral discs of various ages. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1096: 239-248.
[19] 吴庆能,雷刚刚,钟青山,等.退变椎间盘中NF-κB?MMP-13的表达及意义[J].实用临床医学, 2009,10(2): 5-7,10.
[20] Wang P, Qiu W, Dudgeon C, et al. PUMA is directly activated by NF-kappaB and contributes to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2009; 16(9):1192-1202.
[21] 乔晓峰,李长德,解云川,等.腰椎间盘突出症患者髓核组织TNF-α?IL-8以及IL-10的表达及其意义[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(17):4276-4277.
[22] Burke JG, Watson RW, McCormack D, et al. Intervertebral discs which cause low back pain secrete high levels of proinflammatory mediators. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(2):196-201.
[23] Hoyland JA, Le Maitre C, Freemont AJ. Investigation of the role of IL-1 and TNF in matrix degradation in the intervertebral disc. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(6): 809-814.
[24] Zhao CQ, Zhang YH, Jiang SD, et al. ADAMTS-5 and intervertebral disc degeneration: the results of tissue immunohistochemistry and in vitro cell culture. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(5):718-725.
[25] Yurube T, Takada T, Suzuki T, et al. Rat tail static compression model mimics extracellular matrix metabolic imbalances of matrix metalloproteinases, aggrecanases, and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(2):R51.
[26] Nerlich AG, Bachmeier BE, Schleicher E, et al. Immunomorphological analysis of RAGE receptor expression and NF-kappaB activation in tissue samples from normal and degenerated intervertebral discs of various ages. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1096: 239-248.
[27] Podichetty VK. The aging spine: the role of inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2007; 53(5):4-18.
[28] Vo NV, Hartman RA, Yurube T, et al. Expression and regulation of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Spine J. 2013;13(3):331-341.
[29] Ji Q, Zhang Q, Wang Y. Research progress of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif 4 and 5 in osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(9):1080-1084.
[30] Fink K, Boratyński J. The role of metalloproteinases in modification of extracellular matrix in invasive tumor growth, metastasis and angiogenesis. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012;66:609-628.
[31] Sivan SS, Wachtel E, Roughley P. Structure, function, aging and turnover of aggrecan in the intervertebral disc. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(10): 3181-3189. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
腰突颗粒:系临床经验方,具有较好的临床效果,由独活、桑寄生、牛膝、杜仲、熟地黄、川芎、当归、芍药、茯苓、甘草、地龙、土鳖、蜈蚣、三棱、莪术组成,诸药合用,是为标本兼顾,扶正祛邪之剂。
人髓核细胞:髓核是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨终板与纤维环之间。发育成熟的髓核是一个由软骨样细胞分散在细胞间质内,周围围绕着一个比较致密的胶原纤维网的含水球。髓核细胞即其中类软骨样细胞。
文题释义:
腰突颗粒:系临床经验方,具有较好的临床效果,由独活、桑寄生、牛膝、杜仲、熟地黄、川芎、当归、芍药、茯苓、甘草、地龙、土鳖、蜈蚣、三棱、莪术组成,诸药合用,是为标本兼顾,扶正祛邪之剂。
人髓核细胞:髓核是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨终板与纤维环之间。发育成熟的髓核是一个由软骨样细胞分散在细胞间质内,周围围绕着一个比较致密的胶原纤维网的含水球。髓核细胞即其中类软骨样细胞。.jpg) 文题释义:
腰突颗粒:系临床经验方,具有较好的临床效果,由独活、桑寄生、牛膝、杜仲、熟地黄、川芎、当归、芍药、茯苓、甘草、地龙、土鳖、蜈蚣、三棱、莪术组成,诸药合用,是为标本兼顾,扶正祛邪之剂。
人髓核细胞:髓核是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨终板与纤维环之间。发育成熟的髓核是一个由软骨样细胞分散在细胞间质内,周围围绕着一个比较致密的胶原纤维网的含水球。髓核细胞即其中类软骨样细胞。
文题释义:
腰突颗粒:系临床经验方,具有较好的临床效果,由独活、桑寄生、牛膝、杜仲、熟地黄、川芎、当归、芍药、茯苓、甘草、地龙、土鳖、蜈蚣、三棱、莪术组成,诸药合用,是为标本兼顾,扶正祛邪之剂。
人髓核细胞:髓核是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨终板与纤维环之间。发育成熟的髓核是一个由软骨样细胞分散在细胞间质内,周围围绕着一个比较致密的胶原纤维网的含水球。髓核细胞即其中类软骨样细胞。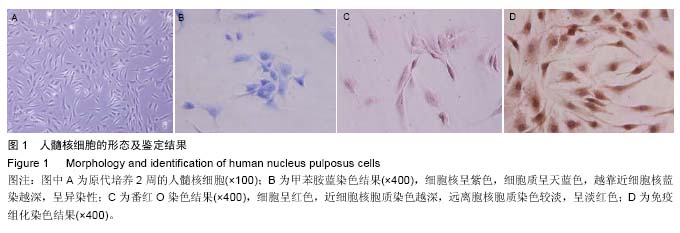

.jpg) 文题释义:
腰突颗粒:系临床经验方,具有较好的临床效果,由独活、桑寄生、牛膝、杜仲、熟地黄、川芎、当归、芍药、茯苓、甘草、地龙、土鳖、蜈蚣、三棱、莪术组成,诸药合用,是为标本兼顾,扶正祛邪之剂。
人髓核细胞:髓核是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨终板与纤维环之间。发育成熟的髓核是一个由软骨样细胞分散在细胞间质内,周围围绕着一个比较致密的胶原纤维网的含水球。髓核细胞即其中类软骨样细胞。
文题释义:
腰突颗粒:系临床经验方,具有较好的临床效果,由独活、桑寄生、牛膝、杜仲、熟地黄、川芎、当归、芍药、茯苓、甘草、地龙、土鳖、蜈蚣、三棱、莪术组成,诸药合用,是为标本兼顾,扶正祛邪之剂。
人髓核细胞:髓核是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨终板与纤维环之间。发育成熟的髓核是一个由软骨样细胞分散在细胞间质内,周围围绕着一个比较致密的胶原纤维网的含水球。髓核细胞即其中类软骨样细胞。