| [1] Santiago H, Comerota AJ. Embolization during treatment of deep venous thrombosis: incidence, importance, and prevention.Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;14(2):58-64.
[2] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(2):65-71.
[3] Wade R, Sideris E, Paton F, et al. Graduated compression stockings for the prevention of deep-vein thrombosis in postoperative surgical patients: a systematic review and economic model with a value of information analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2015; 19(98):1-220.
[4] Yngve FY, Francis CW, Johanson NA, et al. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2):e278S-e325S.
[5] Mont MA, Jacobs JJ, Boggio LN, et al. Preventing venous thromboembolic disease in patients undergoing elective hip and knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(12):768-776.
[6] Pavon JM, Adam SS, Razouki ZA, et al. Effectiveness of intermittent pneumatic compression devices for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in high-risk surgical patients: a systematic review. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(2):524-532.
[7] Pitto RP, Hamer H, Heiss-Dunlop W, et al. Mechanical prophylaxis of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip replacement a randomised clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(5):639-642.
[8] Craigie S, Tsui JF, Agarwal A, et al. Adherence to mechanical thromboprophylaxis after surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res. 2015;136(4):723-726.
[9] 杜世正.自我管理项目对慢性肌肉骨骼痛类疾病干预效果的系统评价研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2011.
[10] 胡雁.循证护理学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.
[11] 刘鸣.系统评价、Meta-分析设计与实施方法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011.
[12] 曾宪涛,刘慧,陈曦,等.Meta分析系列之四:观察性研究的质量评价工具[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012, 4(4): 297-299.
[13] 张娟娟,汪东海,代继宏.大气可吸入性颗粒物暴露与儿童哮喘显著关联:基于22篇观察性研究的Meta分析[J].中国循证儿科杂志,2015,10(5):337-344.
[14] Rostom A, Dube C, Cranney A, et al. Celiac Disease. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). 2004.
[15] 王在标,尹慢慢,蔡慧,等.ABO血型与胃癌发生风险的病例-对照研究及meta分析[J].第二军医大学学报,2014,35(5):560-565.
[16] 雷婷,马亚娜,聂宏伟,等.中国现阶段老年期痴呆患病率的Meta分析[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(4):809-814.
[17] 虞涛,王旭,吴鉴今,等.利奈唑胺治疗耐多药结核病的疗效与安全性的Meta分析[J].中国药房,2014,25(8):731-735.
[18] 翁鸿,鄢金柱,田国祥,等.牙周病与高血压发病相关性:一项基于观察性研究的Meta分析[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2015,7(1):16-19.
[19] 罗杰,冷卫东.系统评价/Meta分析理论与实践[M].北京:军事医学科学出版社,2013:348-375.
[20] B L, T W, Hn Z, et al. The prevalence of hyperuricemia in China: a meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2011; 11(24):2965-2966.
[21] Proctor MC, Greenfield LJ, Wakefield TW, et al. A clinical comparison of pneumatic compression devices: the basis for selection. J Vasc Surg. 2001;34(3): 459-463.
[22] Cornwell EE 3rd, Chang D, Velmahos G, et al. Compliance with sequential compression device prophylaxis in at-risk trauma patients: a prospective analysis. Am Surg. 2002;68(5):470-473.
[23] Westrich GH, Jhon PH, Sánchez PM. Compliance in using a pneumatic compression device after total knee arthroplasty. Am J Orthop. 2003;32(3):135-140.
[24] Parnaby C. A new anti-embolism stocking. Use of below-knee products and compliance. Br J Perioper Nurs. 2004;14(7):302-307.
[25] Chan JC, Roche SJ, Lenehan B, et al. Compliance and satisfaction with foot compression devices: an orthopaedic perspective. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127(7):567-571.
[26] Raju S, Hollis K, Neglen P. Use of Compression stockings in chronic venous disease: patient compliance and Efficacy. Ann Vasc Surg. 2007;21(6): 790-795.
[27] Brady D, Raingruber B, Peterson J, et al. The Use of knee-length versus thigh-length compression stockings and sequential compression devices. Critl Care Nurs Q. 2007;30(3):255-262.
[28] Bockheim HM, Mcallen KJ, Baker R, et al. Mechanical prophylaxis to prevent venous thromboembolism in surgical patients: a prospective trial evaluating compliance. J Crit Care. 2009;24(2):192-196.
[29] Cindolo L, Salzano L, Mirone V, et al. Thromboprophylaxis in radical retropubic prostatectomy: efficacy and patient compliance of a dual modality. Urol Int. 2009;83(1):12-18.
[30] Froimson MI, Murray TG, Fazekas AF. Venous thromboembolic disease reduction with a portable pneumatic compression device. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(2):310-316.
[31] Ritsema DF, Watson JM, Stiteler AP, et al. Sequential compression devices in postoperative urologic patients: an observational trial and survey study on the influence of patient and hospital factors on compliance. BMC Urol. 2013;13(3):259-261.
[32] Brady MA, Carroll AW, Cheang KI, et al. Sequential compression device compliance in postoperative obstetrics and gynecology patients. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125(1):19-25.
[33] 李昂.2010-2050年中国老年痴呆的预测研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2015.
[34] Comerota AJ, Katz ML, White JV. Why does prophylaxis with external pneumatic compression for deep vein thrombosis fail? Am J Surg. 1992;164(3): 265-268.
[35] Obi AT, Alvarez R, Reames BN, et al. A prospective evaluation of standard versus battery-powered sequential compression devices in post-surgical patients. Am J Surg. 2015;209(4):675-681.
[36] Vandenbroucke JP, von Elm E, Altman DG, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration. Int J Surg. 2014;12(12):1500-1524. |
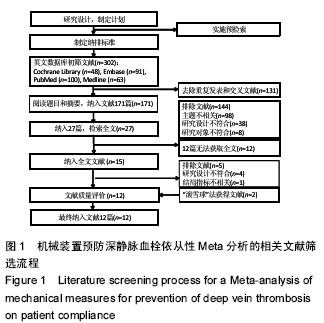
.jpg)
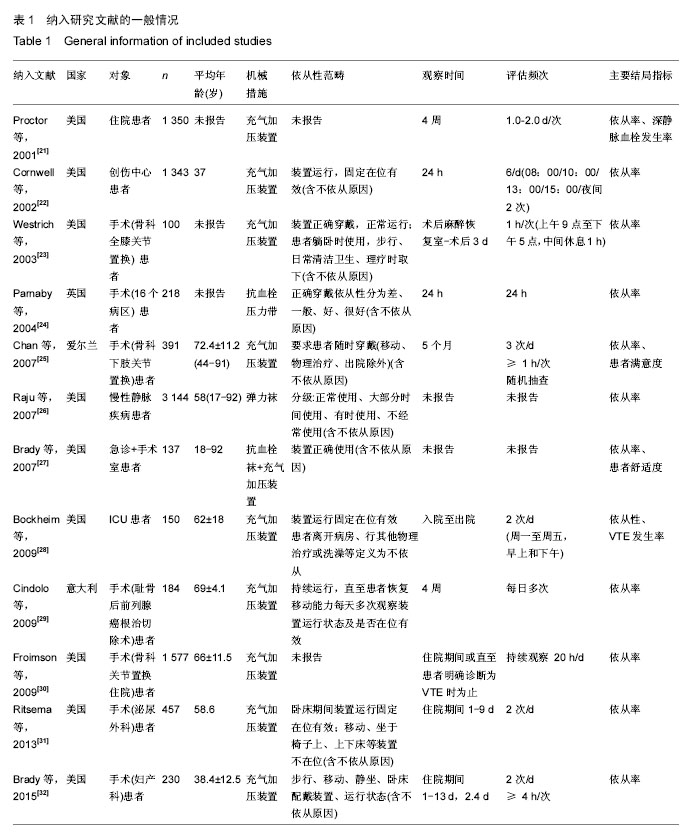
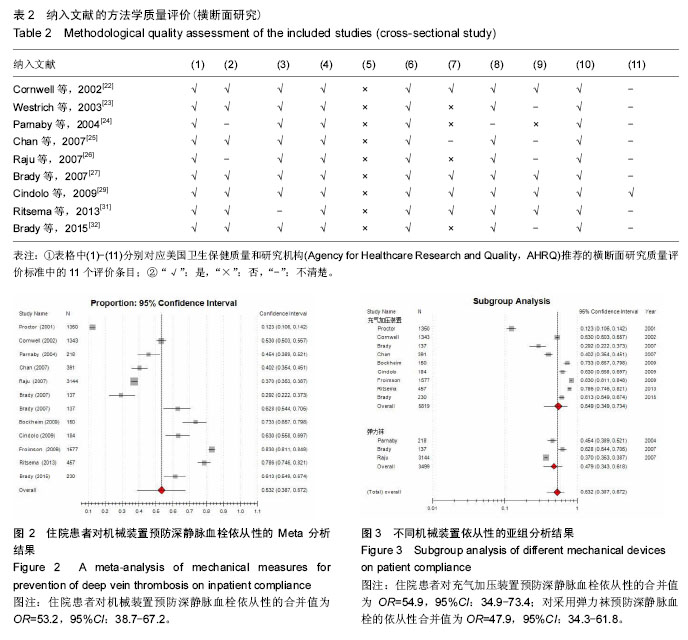
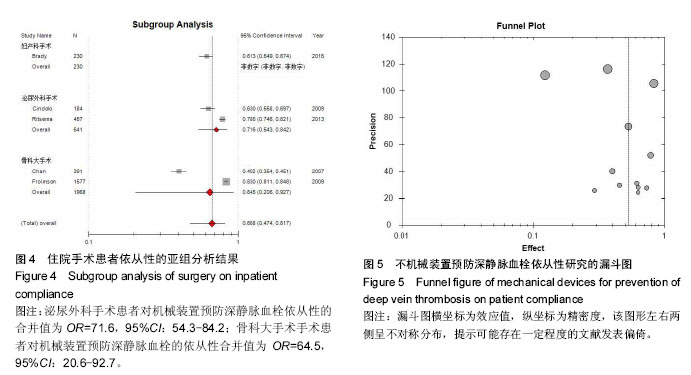

.jpg)